基于python的excel检查和读写软件
2023-12-23 19:14:05
软件版本:python3.6
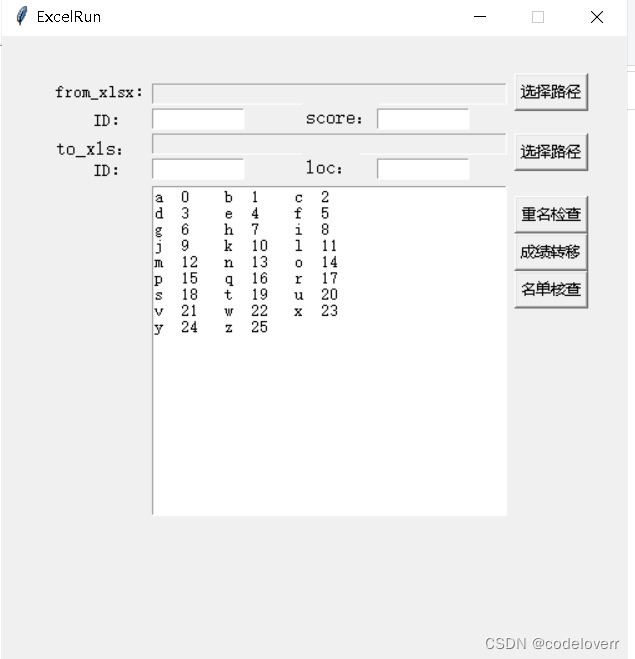
窗口和界面gui代码:
class mygui:
def _init_(self):
pass
def run(self):
root = Tkinter.Tk()
root.title('ExcelRun')
max_w, max_h = root.maxsize()
root.geometry(f'500x500+{int((max_w - 500) / 2)}+{int((max_h - 300) / 2)}') # 居中显示
root.resizable(width=False, height=False)
# 标签组件
label = Tkinter.Label(root, text='from_xlsx:', font=('宋体', 10))
label.place(x=40, y=35)
# 输入框控件
entry_text = Tkinter.StringVar()
entry = Tkinter.Entry(root, textvariable=entry_text, font=('FangSong', 10), width=40, state='readonly')
entry.place(x=120, y=38)
idlabel1 = Tkinter.Label(root, text='ID:', font=('宋体', 10))
idlabel1.place(x=70, y=58)
fpath1_num1 = Tkinter.StringVar()
entry2 = Tkinter.Entry(root, textvariable=fpath1_num1, font=('FangSong', 10), width=10)
entry2.place(x=120, y=58)
idlabel2 = Tkinter.Label(root, text='score:', font=('宋体', 12))
idlabel2.place(x=240, y=53)
fpath1_num2 = Tkinter.StringVar()
entry3 = Tkinter.Entry(root, textvariable=fpath1_num2, font=('FangSong', 10), width=10)
entry3.place(x=300, y=58)
label2 = Tkinter.Label(root, text='to_xls:', font=('宋体', 12))
label2.place(x=40, y=78)
filepath2 = Tkinter.StringVar()
filepath2entry = Tkinter.Entry(root, textvariable=filepath2, font=('FangSong', 10), width=40, state='readonly')
filepath2entry.place(x=120, y=78)
id2label1 = Tkinter.Label(root, text='ID:', font=('宋体', 10))
id2label1.place(x=70, y=98)
filepath2_num1 = Tkinter.StringVar()
filepath2_num1entry = Tkinter.Entry(root, textvariable=filepath2_num1, font=('FangSong', 10), width=10)
filepath2_num1entry.place(x=120, y=98)
id2label2 = Tkinter.Label(root, text='loc:', font=('宋体', 12))
id2label2.place(x=240, y=93)
filepath2_num2 = Tkinter.StringVar()
filepath2_num2entry = Tkinter.Entry(root, textvariable=filepath2_num2, font=('FangSong', 10), width=10)
filepath2_num2entry.place(x=300, y=98)
button = Tkinter.Button(root, text='选择路径', command=lambda: self.get_path(entry_text,outputtext))
button.place(x=410, y=30)
button_path2 = Tkinter.Button(root, text='选择路径', command=lambda: self.get_path(filepath2,outputtext))
button_path2.place(x=410, y=78)
button2 = Tkinter.Button(root, text='重名检查', command=lambda: self.get_path2(entry_text,outputtext,fpath1_num1))
button2.place(x=410, y=128)
button3 = Tkinter.Button(root, text='成绩转移', command=lambda: self.get_path3(\
entry_text.get(),int(fpath1_num1.get()),int(fpath1_num2.get()),\
filepath2.get(),int(filepath2_num1.get()),int(filepath2_num2.get()),outputtext))
button3.place(x=410, y=158)
button4 = Tkinter.Button(root, text='名单核查', command=lambda: self.get_path4(\
entry_text.get(),int(fpath1_num1.get()),\
filepath2.get(),int(filepath2_num1.get()),outputtext))
button4.place(x=410, y=188)
outputtext = Text(root, height=20, width=40)
# 将多行输入文本放入(pack)窗口中
outputtext.place(x=120, y=120)
var='a'
lst=[chr(ord(var)+i) for i in range(26)]
for i in range(0,26):
outputtext.insert("end",lst[i]+' '+str(i)+'\t')
if (i+2)%3==1:
outputtext.insert("end",'\n')
root.mainloop()
f=mygui()excel检查和读写代码:
from xlrd import open_workbook
from xlutils.copy import copy
import xlrd
import os
import random
class zuoye__2_excel:
def run(self,path1,p1num1,p1num2,path2xls,p2num1,p2num2):
dic={}
dic2={}
rb2 = open_workbook(path1)
rs2 = rb2.sheet_by_index(0)
nrows = rs2.nrows
ncols = rs2.ncols
wb = copy(rb2)
#通过get_sheet()获取的sheet有write()方法
ws = wb.get_sheet(0)
#ws.write(0, 0, 'changed!')
#
for i in range(0, nrows):
#########################################################################################################
id=rs2.cell_value(i,p1num1)
id=int(id)
sc=rs2.cell_value(i,p1num2)
dic[id]=sc
#INDEX=rs.cell_value(i,2)
#########################################################################################################
#name=rs.cell_value(i,1)
#########################################################################################################
rb2 = open_workbook(path2xls)
rs2 = rb2.sheet_by_index(0)
nrows2 = rs2.nrows
ncols2 = rs2.ncols
wb2 = copy(rb2)
#通过get_sheet()获取的sheet有write()方法
ws2 = wb2.get_sheet(0)
#ws.write(0, 0, 'changed!')
for i in range(0, nrows2):
id1=rs2.cell_value(i,p2num1)
#id3= id1.replace(" ", "")
if type(id1)==str or not id1>0 :
continue
id2=int(id1)
#id2=''.join([i for i in id3 if i.isdigit()])
#name2=rs2.cell_value(i,6)
#dic2[id2]=i
#dic[id2]=rs2.cell_value(i,5)
if id2 in dic:
#########################################################################################################
ws2.write(i,p2num2, dic[id2])
else:
print(id2)
filepath='w'+str(random.randint(10000, 30000))+'.xls'
if os.path.exists(filepath):
print('文件存在!')
return '文件存在,重新保存!'
else:
wb2.save(filepath)
return '文件保存到:'+filepath+'!';
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/codeloverr/article/details/135166966
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!