敏感信息泄漏怎么破?来试试极狐GitLab 的密钥检测吧
前言
在应用程序开发过程中,一个很常见的问题就是:开发人员为了本地 debug 方便,会 hardcode 一些信息,比如连接数据库的用户名、密码、连接第三方 app 的 token、certificate 等,如果在提交代码的时候没有及时删除 hardcode 的信息,则非常容易造成敏感信息泄漏,带来被拖库、撞库等风险。
因此,敏感信息管理是 DevSecOps 中一个非常重要的话题。诚然,敏感信息的管理需要软件开发中的每一个人来负责,有安全意识,但是是人就总有疏忽犯错的时候,所以最好的方式之一就是将敏感信息的检测集成到 CI/CD 中,做到持续监测,而且能在开发人员提交代码的时候就进行,真正做到安全左移。
极狐GitLab 提供开箱即用的 DevSecOps 功能,包括七大功能:容器镜像扫描、静态应用安全测试 (SAST)、动态应用安全扫描(DAST)、密钥检测、License合规、依赖项扫描以及模糊测试。关于镜像安全扫描,可以查看文章极狐GitLab DevSecOps 七剑下天山之容器镜像安全扫描。这篇文章将介绍极狐GitLab DevSecOps 中关于敏感信息检测的功能。
极狐GitLab 敏感信息检测
极狐GitLab 敏感信息检测(Secret Detection)功能是开箱即用的,在 11.9 版本中引入。既可以对提交代码中的敏感信息进行检测,也可以对远程仓库进行重复性的扫描来进行敏感信息检测;既可以使用默认的规则进行敏感信息检测,也可以通过自定义规则来完成敏感信息检测。极狐GitLab 敏感信息检测是与语言无关的,也就以为是“全谱”可用的。
检测原理
敏感信息检测的思路一般是:读取文件内容 --> 根据定义规则进行内容匹配 -> 出具检测报告。极狐GitLab 敏感信息检测依旧是通过特定的分析器(analyzer)来完成的,而分析器的核心组件是开源的 Gitleaks。
Gitleaks
Gitleaks 是一款开源的 SAST 工具,可以用来对 hadrcode 的密码、API key、token 等敏感信息做检测。Gitleaks 具有安装容易,使用方便的特点。
Gitleaks 的安装
Gitleaks 的安装有多种方式,本文以 macOS 为例来演示,使用下面的命令即可在 macOS 上安装 Gitleaks:
$?brew?install?gitleaks
可以使用 gitleaks -h 或者 gitleaks --version 来检查是否安装成功:
$?gitleaks?--version
7.6.1
Gitleaks 的使用
Gitleaks 可以直接扫描本地文件,也可以直接扫描远端仓库。
-
使用 Gitleaks 来扫描本地文件
先来看看对于本地文件的扫描。新建一个包含敏感信息的文件,诸如:
$?cat?>?secret.txt?<<??EOF
password="12232"
token="ADB#@DC"
EOF
添加一个 gitleaks.toml 文件,写入匹配规则:
$?cat?>?config.toml?<<?EOF
title?=?"gitleaks?config"
[[rules]]
description?=?"Password?Type"
regex?=?'''[0-9]'''
tags?=?["gitlab",?"security"]
EOF
gitleaks 的匹配规则是用 TOML 来定义的。
利用上述匹配规则,能够对全部是数字的信息进行匹配,并且将其标记为敏感信息,可以用如下命令进行扫描检测:
$?gitleaks?--config-path=config.toml?\
???????????--path=secret.txt?--no-git?\
???????????-v?--report=report.json
参数说明:
-
--config-path:指定写入了匹配规则的配置文件,一般是 xx.toml
-
--path:指定要扫描检测的文件或者目录
-
--report:指定输出报告的路径
-
--no-git:将扫描目录视为普通目录去扫描检测,否则会去查找 .git 目录,找不到就提示失败
可以看到如下的扫描结果:
{
??"line":?"password=\"12232\"",
??"lineNumber":?1,
??"offender":?"1",
??"offenderEntropy":?-1,
??"commit":?"",
??"repo":?"",
??"repoURL":?"",
??"leakURL":?"",
??"rule":?"Password?Type",
??"commitMessage":?"",
??"author":?"",
??"email":?"",
??"file":?".",
??"date":?"0001-01-01T00:00:00Z",
??"tags":?"gitlab,?security"
}
INFO[0000]?scan?time:?224?microseconds
WARN[0000]?leaks?found:?1
结果显示,扫描出一处匹配(leaks found: 1),扫描时长(scan time: 224 microseconds,可以看出非常快)。而这一处泄漏就是第一行 password="12232"。这和最开始设置匹配规则时候的设想是一样的。
同时会在当前目录下看到一个 report.json 的文件:
$ls?-ltr?report.json
-rw-r--r--??1?xiaomage??wheel??328?Oct?26?14:24?report.json
里面记录的内容和上述标准输出的内容是一致的。
需要注意的是,如果检测出敏感信息,则扫描命令的退出结果为非 0 值:
$?gitleaks?--config-path=config.toml?--path=secret.txt?--no-git?-v?--report=report.json
$?echo?$?
1
如果想要指定执行命令的退出结果,则可以使用参数?--leaks-exit-code:
$?gitleaks?--config-path=config.toml?--path=secret.txt?--no-git?-v?--report=report.json?--leaks-exit-code=0
$?echo?$?
0
-
使用 Gitleaks 扫描远端仓库
将上述的 secret.txt 文件和 gitleaks.toml 文件存放到极狐GitLab 的仓库中,如下:
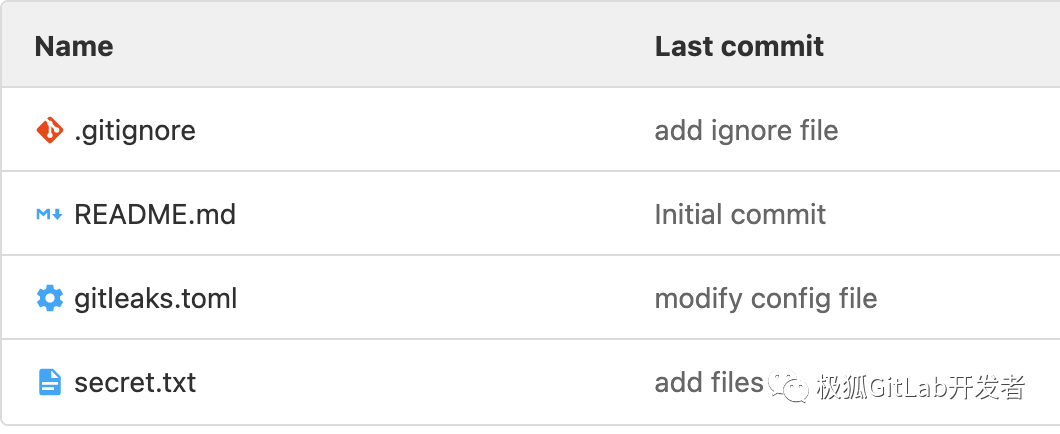
执行如下命令进行远端仓库扫描:
$?gitleaks?--repo-url=git@gitlab.cn:majinghe/secret-detection.git?\
--username=jhma@gitla.cn?--access-token=personal-token?\
--ssh-key=path-to-ssh-key?--repo-config-path=gitleaks.toml?\
--report=report.json
参数说明:
-
--repo-url:指定远端仓库的地址
-
--username:扫描私有仓库时指定仓库的用户名
-
--access-token:扫描私有仓库时指定的 personal access token,用来做权限验证;如果 --repo-url 是用 https 的方式,则此参数可换成 --password
-
--ssh-key:指定访问私有仓库所需的 ssh-key
-
--repo-config-path:指定远端仓库中的规则匹配文件
-
--report:指定扫描报告的名称
扫描结果如下:
INFO[0000]?cloning...?git@gitlab.cn:majinghe/secret-detection.git
INFO[0000]?scan?time:?999?microseconds
INFO[0000]?commits?scanned:?9
WARN[0000]?leaks?found:?9
很奇怪的是看到了?9?处检测点,但是文件里面只有一处啊,到底怎么回事呢?
对于 Gitleaks 来讲,如果不做额外的参数指定,则上述扫描命令会对远端仓库的所有 commit?进行扫描,上述仓库有 9 个 commit,所以扫描了 9 次。可以通过参数来制定针对某一个 commit 或者某一个范围的 commit 信息进行扫描。若指定某个 commit 进行扫描,可看到:
$?gitleaks?--repo-url=https://gitlab.cn/majinghe/secret-detection.git?--username=极狐GitLab-username?--password=极狐GitLab-password?--repo-config-path=gitleaks.toml?--report=report.json?--commit=83c4c5e364bc249e410a5aa92716a35da8080111
INFO[0000]?cloning...?https://gitlab.cn/majinghe/secret-detection.git
INFO[0001]?scan?time:?204?microseconds
INFO[0001]?commits?scanned:?1
WARN[0001]?leaks?found:?2
出现了 2 处匹配检测点,是因为将 gitleaks.toml 也进行了扫描:
{
??"line":?"regex?=?'''[0-9]'''",
??"lineNumber":?4,
??"offender":?"0",
??"offenderEntropy":?-1,
??"commit":?"83c4c5e364bc249e410a5aa92716a35da8080111",
??"repo":?"secret-detection.git",
??"repoURL":?"https://gitlab.cn/majinghe/secret-detection.git",
??"leakURL":?"https://gitlab.cn/majinghe/secret-detection.git/blob/83c4c5e364bc249e410a5aa92716a35da8080111/config.toml#L4",
??"rule":?"Password?Type",
??"commitMessage":?"add?files\n",
??"author":?"xiaomage",
??"email":?"jhma@gitlab.cn",
??"file":?"config.toml",
??"date":?"2021-10-26T14:38:20+08:00",
??"tags":?"gitlab,?security"
?}
可以通过在 gitleaks.toml 中定制化一下匹配规则来只扫描 secret.txt 文件:
title?=?"gitleaks?config"
[[rules]]
description?=?"Password?Type"
file?=?'''secret.txt'''
regex?=?'''[0-9]'''
tags?=?["gitlab",?"security"]
重新扫描检测:
$?gitleaks?--repo-url=https://gitlab.cn/majinghe/secret-detection.git?--username=jhma@gitlab.cn?--password=GitOpsIsMyMainJobIn2021?--repo-config-path=gitleaks.toml?--report=report.json?--commit=83c4c5e364bc249e410a5aa92716a35da8080111
INFO[0000]?cloning...?https://gitlab.cn/majinghe/secret-detection.git
INFO[0000]?scan?time:?130?microseconds
INFO[0000]?commits?scanned:?1
WARN[0000]?leaks?found:?1
此次扫描只匹配到一处检测点,内容如下:
[
?{
??"line":?"password=\"12232\"",
??"lineNumber":?1,
??"offender":?"1",
??"offenderEntropy":?-1,
??"commit":?"83c4c5e364bc249e410a5aa92716a35da8080111",
??"repo":?"secret-detection.git",
??"repoURL":?"https://gitlab.cn/majinghe/secret-detection.git",
??"leakURL":?"https://gitlab.cn/majinghe/secret-detection.git/blob/83c4c5e364bc249e410a5aa92716a35da8080111/secret.txt#L1",
??"rule":?"Password?Type",
??"commitMessage":?"add?files\n",
??"author":?"xiaomage",
??"email":?"jhma@gitlab.cn",
??"file":?"secret.txt",
??"date":?"2021-10-26T14:38:20+08:00",
??"tags":?"gitlab,?security"
?}
]
可以看到成功匹配到 secret.txt 里面的敏感信息。
当然,Gitleaks 还有很多其他的参数来进行多种细粒度的扫描。
极狐GitLab 敏感信息检测实践
单独使用镜像做扫描
极狐GitLab 敏感信息检测是通过分析器(analyzer)来实现的,而 analyzer 的核心就是 Gitleaks。analyzer 的镜像为:
registry.gitlab.com/security-products/secret-detection:3
可以直接使用此镜像来完成敏感信息扫描。将上面测试用的包含 secret.txt 和 gitleaks.toml 文件的仓库 clone 到本地,然后执行下面的命令启动一个容器:
$?docker?run?--rm?-d?-it?-v?$(pwd):/tmp/?registry.gitlab.com/security-products/secret-detection:3?sh
可以用 docker exec -it ?进入容器,在里面可以看到容器里面已经安装了 Gitleaks 和 anaylyzer:
$?gitleaks?--version
v7.5.0
$?./analyzer?--version
[INFO]?[secrets]?[2021-10-27T01:27:43Z]???GitLab?secrets?analyzer?v3.22.0
analyzer?version?3.22.0
analyzer 就是极狐GitLab 执行敏感信息检测的法宝,其本身是对 gitleaks 做了封装。大体思路就是读取 analyzer 命令后面的参数,然后拼装成 gitleaks 命令,再执行命令。
将 /tmp/gitleaks.tmol 文件拷贝至根目录,执行如下命令即可完成敏感信息扫描:
$?./analyzer?run?--target-dir?/tmp/secret.txt
[INFO]?[secrets]?[2021-10-27T01:25:46Z]???GitLab?secrets?analyzer?v3.22.0
[INFO]?[secrets]?[2021-10-27T01:25:46Z]???Detecting?project
[INFO]?[secrets]?[2021-10-27T01:25:46Z]???Found?project?in?/tmp
[INFO]?[secrets]?[2021-10-27T01:25:46Z]???Running?analyzer
[INFO]?[secrets]?[2021-10-27T01:25:47Z]???Creating?report
拷贝的原因是 analyzer 默认读取根目录下自带的 gitleaks.toml 文件。为了匹配到测试使用的敏感信息,对匹配规则做了一些定制化改动。
查看扫描报告:
$?cat?tmp/gitleaks-100398148.json
[
?{
??"line":?"password=\"12232\"",
??"lineNumber":?1,
??"offender":?"1",
??"offenderEntropy":?-1,
??"commit":?"",
??"repo":?"",
??"repoURL":?"",
??"leakURL":?"",
??"rule":?"Password?Type",
??"commitMessage":?"",
??"author":?"",
??"email":?"",
??"file":?".",
??"date":?"0001-01-01T00:00:00Z",
??"tags":?"gitlab,?security"
?}
]
可以看到结果和用 gitleaks 命令扫描是一样的。关于 analyzer 更多的用法可以使用?analyzer h?查看:
$?./analyzer?h
[INFO]?[secrets]?[2021-10-27T01:32:42Z]???GitLab?secrets?analyzer?v3.22.0
NAME:
???analyzer?-?GitLab?secrets?analyzer?v3.22.0
USAGE:
???analyzer?[global?options]?command?[command?options]?[arguments...]
VERSION:
???3.22.0
AUTHOR:
???GitLab
COMMANDS:
???run,?r??????Run?the?analyzer?on?detected?project?and?generate?a?compatible?artifact
???search,?s???Search?for?compatible?projects?and?return?project?directory
???analyze,?a??Analyze?detected?project?and?generate?report
???convert,?c??Convert?analyzer?output?to?a?compatible?artifact
???help,?h?????Shows?a?list?of?commands?or?help?for?one?command
GLOBAL?OPTIONS:
???--help,?-h?????show?help?(default:?false)
???--version,?-v??print?the?version?(default:?false)
当然,analyzer 很灵活的一点就是可以自己来根据极狐GitLab 提供的 Dockerfile 来构建自己所需的景象,内容如下:
FROM?golang:1.15-alpine?AS?build
ENV?CGO_ENABLED=0?GOOS=linux
WORKDIR?/go/src/app
COPY?.?.
#?build?the?analyzer?binary?and?automatically?set?the?AnalyzerVersion
#?variable?to?the?most?recent?version?from?the?CHANGELOG.md?file
RUN?CHANGELOG_VERSION=$(grep?-m?1?'^##?v.*$'?"CHANGELOG.md"?|?sed?'s/##?v//')?&&?\
????????PATH_TO_MODULE=`go?list?-m`?&&?\
????????go?build?-ldflags="-X?'$PATH_TO_MODULE/metadata.AnalyzerVersion=$CHANGELOG_VERSION'"?-o?analyzer
FROM?alpine:latest
ARG?SCANNER_VERSION
ENV?SCANNER_VERSION?${SCANNER_VERSION:-v7.5.0}
RUN?wget?-O?/usr/local/bin/gitleaks?https://github.com/zricethezav/gitleaks/releases/download/${SCANNER_VERSION}/gitleaks-linux-amd64?&&?\
????chmod?a+x?/usr/local/bin/gitleaks?&&?\
????apk?add?--no-cache?git
COPY?--from=build?--chown=root:root?/go/src/app/analyzer?/
COPY?/gitleaks.toml?/gitleaks.toml
ENTRYPOINT?[]
CMD?["/analyzer",?"run"]
和极狐GitLab CI 集成使用
只需要简单配置极狐GitLab CI,即可将敏感信息检测集成到极狐GitLab CI/CD 中:
variables:
??SECURE_ANALYZERS_PREFIX:?"registry.gitlab.com/security-products"
??SECRETS_ANALYZER_VERSION:?"3"
services:
??-?docker:20.10.7-dind
stages:??????????
??-?test
secret_detection:
??stage:?test
??image:?"$SECURE_ANALYZERS_PREFIX/secret-detection:$SECRETS_ANALYZER_VERSION"
??services:?[]
??allow_failure:?true
??artifacts:
????reports:
??????secret_detection:?gl-secret-detection-report.json
????paths:?[gl-secret-detection-report.json]
??script:
????-?cp?config/gitleaks.toml?/
????-?../../../analyzer?run?--target-dir?.?
????-?cat?gl-secret-detection-report.json
可以查看构建日志:
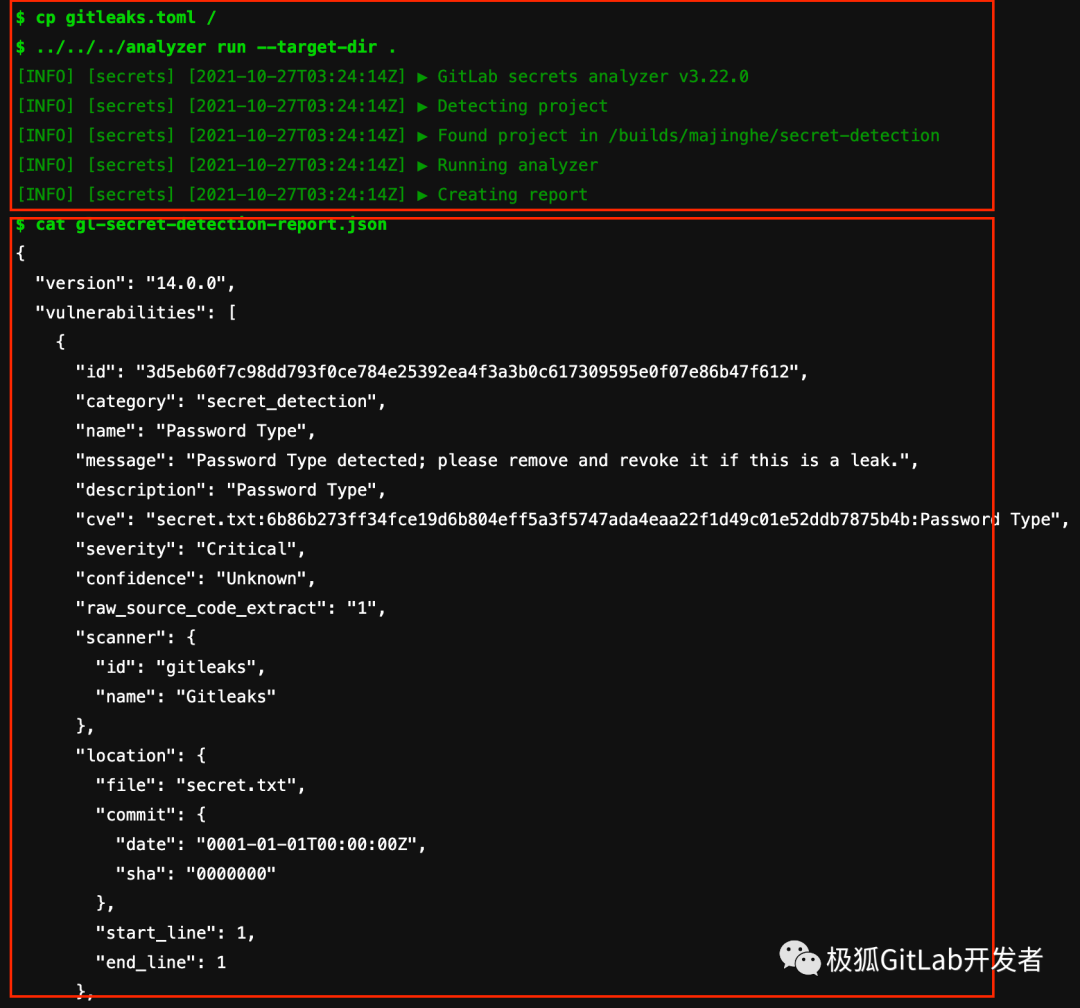
内容过长,只截取了部分,可以从红色方框看到扫描的过程以及扫描报告。因为在极狐GitLab CI 中加了 artifacts 关键字,所以也可以直接下载报告到本地进行查阅,下载方式可以参考公众号文章极狐GitLab DevSecOps 七剑下天山之容器镜像安全扫描。
极狐GitLab DevSecOps CI/CD
可以将容器镜像扫描、敏感信息检测加入极狐GitLab CI 中,打造 DevSecOps CI/CD:
variables:
??CS_ANALYZER_IMAGE:?registry.gitlab.com/security-products/container-scanning/trivy:4
??KUBECONFIG:?/tmp/.kube/config
??SECURE_ANALYZERS_PREFIX:?"registry.gitlab.com/security-products"
??SECRETS_ANALYZER_VERSION:?"3"
services:
??-?docker:20.10.7-dind
stages:??????????
??-?build
??-?test
??-?deploy
build:
??image:?docker:latest
??stage:?build
??services:
????-?docker:20.10.7-dind
??script:
????-?docker?login?-u?"$CI_REGISTRY_USER"?-p?"$CI_REGISTRY_PASSWORD"?$CI_REGISTRY
????-?docker?build?-t?$CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE:3.0.0?.
????-?docker?push?$CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE:3.0.0
container_scanning:
??image:?"$CS_ANALYZER_IMAGE"
??stage:?test
??variables:
????GIT_STRATEGY:?fetch
????DOCKER_USER:?"$CI_REGISTRY_USER"
????DOCKER_PASSWORD:?"$CI_REGISTRY_PASSWORD"
????DOCKER_IMAGE:?$CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE:3.0.0
??allow_failure:?false
??artifacts:
????reports:
??????container_scanning:?gl-container-scanning-report.json
????paths:?[gl-container-scanning-report.json]
??dependencies:?[]
??script:
????-?gtcs?scan
secret_detection:
??stage:?test
??image:?"$SECURE_ANALYZERS_PREFIX/secret-detection:$SECRETS_ANALYZER_VERSION"
??services:?[]
??allow_failure:?true
??artifacts:
????reports:
??????secret_detection:?gl-secret-detection-report.json
????paths:?[gl-secret-detection-report.json]
??script:
????-?cp?gitleaks.toml?/
????-?../../../analyzer?run?--target-dir?.?
????-?cat?gl-secret-detection-report.json
deploy:
??stage:?deploy
??image:
????name:?bitnami/kubectl:latest
????entrypoint:?[""]
??script:
?????-?mkdir?-p?/tmp/.kube
?????-?echo?$kube_config?|?base64?-d?>?$KUBECONFIG
?????-?kubectl?-n?gitlab-k8s-demo?apply?-f?deployment.yaml
可以查看 Pipeline 的构建流程:
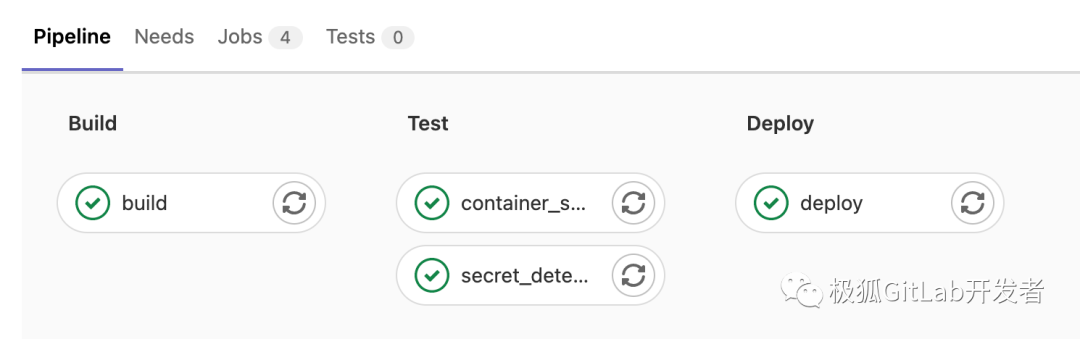
上述流程是极狐GitLab DevSecOps 中关于敏感信息检测的原理及演示,但是实际使用中,需要用户根据自身的需求,完成更复杂的配置、集成,而对于这些极狐GitLab 都有很好的支持。
写在最后
敏感信息检测其实是一个相对而言比较繁琐的安全工作,需要根据特定的敏感信息(不同厂商、不同产品的 API token,keys 等都有所不同)编写特定的匹配工作。可以将敏感信息检测集成到极狐GitLab CI/CD 中,实现安全左移、安全持续自动化,利用极狐GitLab 构建真正的 DevSecOps 体系。从而来保证软件供应链的安全。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!