Java:仿写一个简易的tomcat(步骤 + 详细代码)
文章目录
流程图

实现代码解析
一、构建测试样例
这里我构建了三个样例:
在运行时,我调用的是TestDemo1(向页面返回一个时间并显示),来测试是否正确。
TestDemo2:打印“TestDemo2”
TestDemo3:打印“TestDemo3”
package test;
import Server.Myrequest;
import Server.Myresponse;
import Server.Servlet1;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Date;
@Servlet1(urlName = "abc")
public class TestDemo1{
public void doGet(Myrequest request, Myresponse response) throws IOException {
// 假设,输出key1和key2的val
String val1 = request.getVal("key1");
String val2 = request.getVal("key2");
System.out.println("testDemo1的 doget 方法 " + "key1= " + val1 + "key2= " + val2);
// 返回值
String http = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n" +
"Server: Simple HttpServer/1.0\r\n" +
"Date: Fri, 07 Jul 2023 23:15:09 GMT\r\n" +
"Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n" +
"Content-Length: 162\r\n" +
"Connection: keep-alive\r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"<h1>" + new Date() + "</h1><input type=\"text\" / ><input type=\"button\" value=\"按钮\" />";
response.getWriter().write(http.getBytes("UTF-8"));
// 清理缓冲
response.getWriter().flush();
response.getWriter().close();
}
public void doPost(Myrequest request, Myresponse response) {
// 假设,输出key1和key2的val
String val1 = request.getVal("key1");
String val2 = request.getVal("key2");
System.out.println("testDemo1的 dopost 方法 " + "key1= " + val1 + "key2= " + val2);
}
}
TestDemo2:bbb
package test;
import Server.Myrequest;
import Server.Myresponse;
import Server.Servlet1;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Date;
@Servlet1(urlName = "bbb")
public class TestDemo2{
public void doGet(Myrequest request, Myresponse response) throws IOException {
// 假设,输出key1和key2的val
String val1 = request.getVal("key1");
String val2 = request.getVal("key2");
System.out.println("testDemo1的 doget 方法 " + "key1= " + val1 + "key2= " + val2);
// 返回值
String http = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n" +
"Server: Simple HttpServer/1.0\r\n" +
"Date: Fri, 07 Jul 2023 23:15:09 GMT\r\n" +
"Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n" +
"Content-Length: 162\r\n" +
"Connection: keep-alive\r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"<h1>" + "这是TestDemo2" + "</h1><input type=\"text\" / ><input type=\"button\" value=\"按钮\" />";
response.getWriter().write(http.getBytes("UTF-8"));
// 清理缓冲
response.getWriter().flush();
response.getWriter().close();
}
public void doPost(Myrequest request, Myresponse response) {
// 假设,输出key1和key2的val
String val1 = request.getVal("key1");
String val2 = request.getVal("key2");
System.out.println("testDemo1的 dopost 方法 " + "key1= " + val1 + "key2= " + val2);
}
}
TestDemo3:ccc
package test;
import Server.Myrequest;
import Server.Myresponse;
import Server.Servlet1;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
@Servlet1(urlName = "ccc")
public class TestDemo3{
public void doGet(Myrequest request, Myresponse response) throws IOException {
// 假设,输出key1和key2的val
String val1 = request.getVal("key1");
String val2 = request.getVal("key2");
System.out.println("testDemo1的 doget 方法 " + "key1= " + val1 + "key2= " + val2);
// 返回值
String http = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n" +
"Server: Simple HttpServer/1.0\r\n" +
"Date: Fri, 07 Jul 2023 23:15:09 GMT\r\n" +
"Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n" +
"Content-Length: 162\r\n" +
"Connection: keep-alive\r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"<h1>" + "这是TestDemo3" + "</h1><input type=\"text\" / ><input type=\"button\" value=\"按钮\" />";
response.getWriter().write(http.getBytes("UTF-8"));
// 清理缓冲
response.getWriter().flush();
response.getWriter().close();
}
public void doPost(Myrequest request, Myresponse response) {
// 假设,输出key1和key2的val
String val1 = request.getVal("key1");
String val2 = request.getVal("key2");
System.out.println("testDemo1的 dopost 方法 " + "key1= " + val1 + "key2= " + val2);
}
}
二、自定义注解
我们在使用servlet时,是通过注解来确定的,选取哪个,所以我们先创建一个自己的Servlet注解,用来标记对应的类。
package Server;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.TYPE})
public @interface Servlet1 {
public String urlName() default "123";
}
三、 自定义 request 类、response 类
Myrequest
使用servlet时,我们用resquest来获取前端传来的参数,所以request中用hashmap来供我们读取数据。
package Server;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Myrequest {
private HashMap<String, String> hash = new HashMap<>();
// 根据传入查找
public String getVal(String key) {
return hash.get(key);
}
// 传入key:val
public void put(String key, String val) {
hash.put(key, val);
}
}
Myresponse
同样,我们在处理完请求后,要进行返回,response显然是调用的输出流,我们写一个与servlet类似的用法。
package Server;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class Myresponse {
private OutputStream os; // 输出流
// 构造方法,把tcp输出流构造进来,为了后面我们输出
public Myresponse(OutputStream os) {
this.os = os;
}
// 获取输出流
public OutputStream getWriter() {
return this.os;
}
}
四、反射,创建servlet对象
在使用tomcat时,如果每次调用servlet都重新反射查找文件来创建对象,效率会很低。
我们可以在tomcat启动时,就把所以的servlet类都找到,并且创建对象,这样在调用时,就可以直接从hashmap中寻找,极大的提高了效率。
当然类中的doget,dopost方法,我们也一并创建好对象,这样才能invoke代理调用。
这也是单例模式:一个类只需要有一个对象存在。
package Server;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class SearchFile {
public static HashMap<String, Object[]> map = new HashMap<>(); // servlet类名:{类对象,doget方法类, dopost方法类};
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException {
}
// 初始化
public static void init() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException {
String path = "D:\\桌面\\自学代码练习\\sevlet\\src\\test"; // 项目路径
traversalFolder(new File(path)); // 递归寻找java文件
}
// 遍历文件夹,找到java文件,创建对象,传入map中
private static void traversalFolder(File folder) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException {
File[] files = folder.listFiles();
for (File f: files) {
if (f.isDirectory()) { // 如果是文件夹,继续遍历,递归
traversalFolder(f);
} else { // 若不是,判断是否是java文件
// 获取路径,反射创建
String filePath = f.getAbsolutePath(); // D:\桌面\自学代码练习\sevlet\src\test\TestDemo1.java
String path = filePath.split("src")[1]; // Path= \test\TestDemo1.java
path = path.substring(1, path.length()); // Path= test\TestDemo1.java
// 去掉.java后缀,这里我一开始不小心替换成空格,找错找了两小时。。。,我还以为前面错了呢
path = path.replace(".java", ""); // Path= test\TestDemo1
path = path.replace("\\", "."); // test.TestDemo1
// 反射,根据路径,获取此类
Class<?> c1 = Class.forName(path);
// 获取注释
Servlet1 annotation = c1.getAnnotation(Servlet1.class);
if (annotation != null) {
String urlName = annotation.urlName(); // 获取名字
// 放入map中
map.put(urlName, new Object[]{c1.newInstance(), c1.getDeclaredMethod("doGet", new Class[] {Myrequest.class, Myresponse.class}), c1.getDeclaredMethod("doPost", new Class[] {Myrequest.class, Myresponse.class})});
}
}
}
}
}
五、接收请求,调用方法
用来处理传进来的请求,并调用方法。
创建 Myrequest 和 Myresponse 对象。
request调用put,把发送来的key:val放入。
response传入输出流,为了我们回应。
获取urlName对应的hashMap,invoke调用doget方法。
这里我默认调用的doget方法,大家可以自己改写,加一个传入参数和if判断。
package Server;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Tomcat {
public static void chose(String urlName, String[] params, OutputStream os) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Myrequest ret = new Myrequest();
Myresponse res = new Myresponse(os);
// 让ret记录参数hash{key:val}
for (String str: params) {
String key = str.split("=")[0];
String val = str.split("=")[1];
ret.put(key, val);
}
Object[] arr = SearchFile.map.get(urlName); // 获取对应的{类,该类的doGet方法类,该类的doPost的方法类}
// 获取doGet方法
Method m = (Method) arr[1];
// 代理
m.invoke(arr[0], ret, res);
}
}
六、处理传入的TCP协议
也是我们写的tomcat的启动位置。
TCP协议其实就是字符串,我们通过处理字符串来获取我们需要的部分。
TCP协议的样子:
GET /ccc?key1=val1&key2=val2 HTTP/1.1Host: 127.0.0.1Connection: keep-alivesec-ch-ua: "Not_A Brand";v="8", "Chromium";v="120", "Microsoft Edge";v="120"sec-ch-ua-mobile: ?0sec-ch-ua-platform: "Windows"Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/120.0.0.0Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.7Sec-Fetch-Site: noneSec-Fetch-Mode: navigateSec-Fetch-User: ?1Sec-Fetch-Dest: documentAccept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, brAccept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en;q=0.8,en-GB;q=0.7,en-US;q=0.6
例如:调用的servlet方法,传入的data等。
这里可以自己改写成多线程的方式。
还有处理字符串并不太统一,有些特殊情况没有考虑。
package Server;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException {
SearchFile.init(); // 初始化,把所有类先实例一个对象,重复利用,算是优化
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(80);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
// 缓冲输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
// 接收传来的协议(字符串)
String httpstr = ""; // 拼接传过来的协议
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null && !line.isEmpty()) {
httpstr += line;
}
System.out.println(httpstr);
// 处理字符串
// 截取我们需要
String str = httpstr.split("/")[1].split(" ")[0]; // abc?&key1=val1&key2=val2
// 获取传入的路径(想要请求哪个servlet)
String urlName = str.split("\\?")[0];
System.out.println("urlName= " + urlName); // abc
// 获取参数{key=value}数组
String paramStr = str.split("\\?")[1];
System.out.println("paramStr= " + paramStr); // key1=val1&key2=val2
String[] params = paramStr.split("&"); // {"key1=val1","key2=val2"}
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
// 把参数给tomcat类处理, 这里就简单写,默认get,想调用post,可以自己改写一下,output传入
Tomcat.chose(urlName, params, os);
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
}
七、测试运行
运行main方法,然后浏览器地址栏中输入以下内容:
127.0.0.1:80/abc?key1=val1&key2=val2
调用成功:
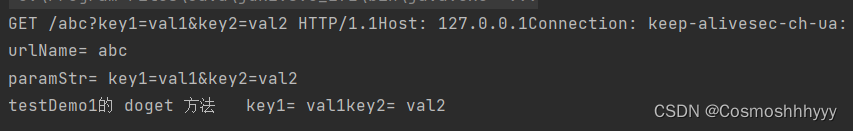
返回成功:
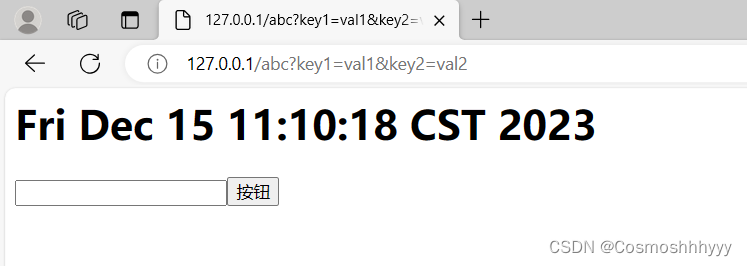
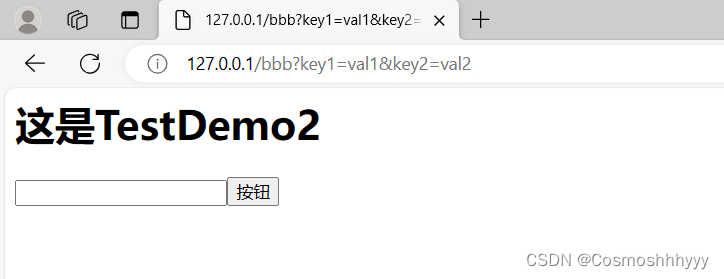
另两个test也测试成功:
127.0.0.1:80/bbb?key1=val1&key2=val2
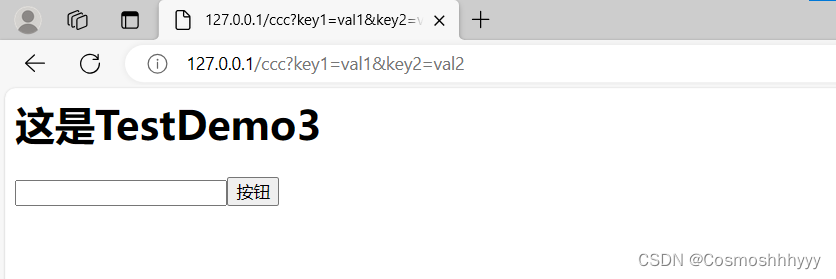
127.0.0.1:80/ccc?key1=val1&key2=val2
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!