LeetCode 232.用栈实现队列(详解) (???.??)
2024-01-10 16:14:01
题目描述:

解题思路:?
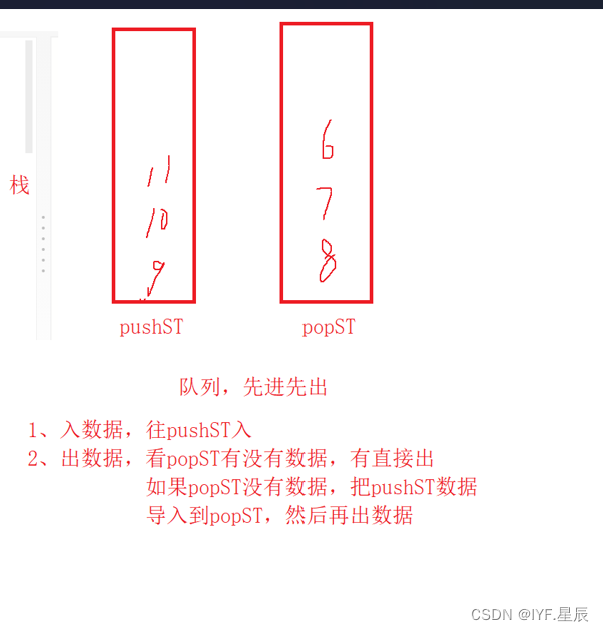
创建两个栈,一个用于入数据,一个用于出数据。分别是pushST和popST;
1.如果是入数据就直接入进pushST
2.如果是出数据,先检查popST中有无数据,如果有数据,就直接出。如果没数据,就将pushST中的数据放进popST中,再从popST中出数据。
当pushST中的数据入到popST时,数据是顺序的,刚好满足队列的条件,直接出
用c语言实现栈,没法直接引用,这里需要自己创建一个栈,在完成上述操作。如果还不会栈的小伙伴可以看看我的这篇博客?【数据结构】栈【详解】?? ? ? ? ??-CSDN博客?

栈的实现:
//栈的声明与定义 typedef int STDataType;//定义栈中的数据类型 struct Stack { STDataType* a;//用于指向后续开辟的空间 int top; // 栈顶 int capacity; // 容量,方便增容 }; //typedef struct Stack ST; typedef struct Stack Stack; //初始化栈 void StackInit(Stack* pst); //摧毁栈 void StackDestroy(Stack* pst); //入栈 void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x); //出栈 void StackPop(Stack* pst); //返回栈顶元素 STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst); // 空返回1 非空返回0 //int StackEmpty(Stack* pst); //栈的判空操作 bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst); //返回栈的大小 int StackSize(Stack* pst); void StackInit(Stack* pst) { assert(pst); //pst->a = NULL; //pst->top = 0; //pst->capacity = 0; pst->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4); pst->top = 0; pst->capacity = 4; } void StackDestroy(Stack* pst) { assert(pst); free(pst->a); pst->a = NULL; pst->capacity = pst->top = 0; } // 性质就决定在栈顶出入数据 void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x) { assert(pst); if (pst->top == pst->capacity) { STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType)*pst->capacity * 2); if (tmp == NULL) { printf("realloc fail\n"); exit(-1); // 结束整个程序 } pst->a = tmp; pst->capacity *= 2; } pst->a[pst->top] = x; pst->top++; } void StackPop(Stack* pst) { assert(pst); assert(!StackEmpty(pst)); pst->top--; } STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst) { assert(pst); assert(!StackEmpty(pst)); return pst->a[pst->top - 1]; } // 空返回1 非空返回0 //int StackEmpty(Stack* pst); bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst) { assert(pst); return pst->top == 0; } int StackSize(Stack* pst) { assert(pst); return pst->top; }
队列的实现(需要用到前面的栈):?
//用栈定义队列,其中包含两个栈,用于入数据和出数据 typedef struct { Stack pushST; Stack popST; } MyQueue; /** Initialize your data structure here. */ //队列的初始化 MyQueue* myQueueCreate() { MyQueue* q = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue)); StackInit(&q->pushST); StackInit(&q->popST); return q; } /** Push element x to the back of queue. */ //入队列 void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) { StackPush(&obj->pushST, x); } /** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */ //出队列 int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) { /*if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST)) { while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST)) { StackPush(&obj->popST, StackTop(&obj->pushST)); StackPop(&obj->pushST); } } */ int top = myQueuePeek(obj); StackPop(&obj->popST); return top; } /** Get the front element. */ //判断栈内数据的情况,并返回栈顶元素 int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) { if (StackEmpty(&obj->popST)) { while (!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST)) { StackPush(&obj->popST, StackTop(&obj->pushST)); StackPop(&obj->pushST); } } return StackTop(&obj->popST); } /** Returns whether the queue is empty. */ //队列的判空 bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) { return StackEmpty(&obj->pushST) && StackEmpty(&obj->popST); } //摧毁队列 void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) { StackDestroy(&obj->pushST); StackDestroy(&obj->popST); free(obj); }

?完整代码:
//栈的声明与定义 typedef int STDataType;//定义栈中的数据类型 struct Stack { STDataType* a;//用于指向后续开辟的空间 int top; // 栈顶 int capacity; // 容量,方便增容 }; //typedef struct Stack ST; typedef struct Stack Stack; //初始化栈 void StackInit(Stack* pst); //摧毁栈 void StackDestroy(Stack* pst); //入栈 void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x); //出栈 void StackPop(Stack* pst); //返回栈顶元素 STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst); // 空返回1 非空返回0 //int StackEmpty(Stack* pst); //栈的判空操作 bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst); //返回栈的大小 int StackSize(Stack* pst); void StackInit(Stack* pst) { assert(pst); //pst->a = NULL; //pst->top = 0; //pst->capacity = 0; pst->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4); pst->top = 0; pst->capacity = 4; } void StackDestroy(Stack* pst) { assert(pst); free(pst->a); pst->a = NULL; pst->capacity = pst->top = 0; } // 性质就决定在栈顶出入数据 void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x) { assert(pst); if (pst->top == pst->capacity) { STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType)*pst->capacity * 2); if (tmp == NULL) { printf("realloc fail\n"); exit(-1); // 结束整个程序 } pst->a = tmp; pst->capacity *= 2; } pst->a[pst->top] = x; pst->top++; } void StackPop(Stack* pst) { assert(pst); assert(!StackEmpty(pst)); pst->top--; } STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst) { assert(pst); assert(!StackEmpty(pst)); return pst->a[pst->top - 1]; } // 空返回1 非空返回0 //int StackEmpty(Stack* pst); bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst) { assert(pst); return pst->top == 0; } int StackSize(Stack* pst) { assert(pst); return pst->top; } //用栈定义队列,其中包含两个栈,用于入数据和出数据 typedef struct { Stack pushST; Stack popST; } MyQueue; /** Initialize your data structure here. */ //队列的初始化 MyQueue* myQueueCreate() { MyQueue* q = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue)); StackInit(&q->pushST); StackInit(&q->popST); return q; } /** Push element x to the back of queue. */ //入队列 void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) { StackPush(&obj->pushST, x); } /** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */ //出队列 int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) { /*if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST)) { while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST)) { StackPush(&obj->popST, StackTop(&obj->pushST)); StackPop(&obj->pushST); } } */ int top = myQueuePeek(obj); StackPop(&obj->popST); return top; } /** Get the front element. */ //判断栈内数据的情况,并返回栈顶元素 int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) { if (StackEmpty(&obj->popST)) { while (!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST)) { StackPush(&obj->popST, StackTop(&obj->pushST)); StackPop(&obj->pushST); } } return StackTop(&obj->popST); } /** Returns whether the queue is empty. */ //队列的判空 bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) { return StackEmpty(&obj->pushST) && StackEmpty(&obj->popST); } //摧毁队列 void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) { StackDestroy(&obj->pushST); StackDestroy(&obj->popST); free(obj); }
博客到这里也是结束了,喜欢的小伙伴可以点赞加关注支持下博主,这对我真的很重要~~
?
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/2302_79862386/article/details/135504223
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!