高级人工智能之群体智能:蚁群算法
群体智能
鸟群:

鱼群:

1.基本介绍
蚁群算法(Ant Colony Optimization, ACO)是一种模拟自然界蚂蚁觅食行为的优化算法。它通常用于解决路径优化问题,如旅行商问题(TSP)。
蚁群算法的基本步骤
初始化:设置蚂蚁数量、信息素重要程度、启发因子重要程度、信息素的挥发速率和信息素的初始量。
构建解:每只蚂蚁根据概率选择下一个城市,直到完成一次完整的路径。
更新信息素:在每条路径上更新信息素,通常新的信息素量与路径的质量成正比。
迭代:重复构建解和更新信息素的步骤,直到达到预设的迭代次数。
2.公式化蚁群算法
-
转移概率 P i j k P_{ij}^k Pijk? 表示蚂蚁 k k k从城市 i i i转移到城市 j j j的概率。它是基于信息素强度 τ i j \tau_{ij} τij?(信息素重要程度为 α \alpha α和启发式信息 η i j \eta_{ij} ηij?)(启发式信息重要程度为 β \beta β )计算的:
P i j k = [ τ i j ] α ? [ η i j ] β ∑ l ∈ allowed k [ τ i l ] α ? [ η i l ] β P_{ij}^k = \frac{[\tau_{ij}]^\alpha \cdot [\eta_{ij}]^\beta}{\sum_{l \in \text{allowed}_k} [\tau_{il}]^\alpha \cdot [\eta_{il}]^\beta} Pijk?=∑l∈allowedk??[τil?]α?[ηil?]β[τij?]α?[ηij?]β?
其中, allowed k \text{allowed}_k allowedk? 是蚂蚁 k k k 可以选择的下一个城市集合。
-
信息素更新规则。在每次迭代结束后,所有路径上的信息素会更新。更新规则通常包括信息素的挥发和信息素的沉积:
τ i j ← ( 1 ? ρ ) ? τ i j + Δ τ i j \tau_{ij} \leftarrow (1 - \rho) \cdot \tau_{ij} + \Delta \tau_{ij} τij?←(1?ρ)?τij?+Δτij?
其中,( ρ \rho ρ ) 是信息素的挥发率,( Δ τ i j \Delta \tau_{ij} Δτij? ) 是本次迭代中所有蚂蚁在路径 ( i , j ) (i, j) (i,j) 上留下的信息素总量,通常计算方式为_
Δ τ i j = ∑ k = 1 m Δ τ i j k \Delta \tau_{ij} = \sum_{k=1}^{m} \Delta \tau_{ij}^k Δτij?=∑k=1m?Δτijk?
而对于每只蚂蚁 k k k ,在路径 ( i , j ) (i, j) (i,j) 上留下的信息素量 Δ τ i j k \Delta \tau_{ij}^k Δτijk? 通常与其走过的路径长度成反比:
Δ τ i j k = { Q L k , if?ant? k ?travels?on?edge? ( i , j ) 0 , otherwise \Delta \tau_{ij}^k= \begin{cases} \frac{Q}{L_k}, & \text{if ant } k \text{ travels on edge } (i, j) \\ 0, & \text{otherwise} \end{cases} Δτijk?={Lk?Q?,0,?if?ant?k?travels?on?edge?(i,j)otherwise?
这里, Q Q Q是一个常数, L k L_k Lk?是蚂蚁 k k k的路径长度。
-
启发式信息 ( η i j \eta_{ij} ηij? ) 通常是目标函数的倒数,例如在TSP问题中,它可以是两城市间距离的倒数:
η i j = 1 d i j \eta_{ij} = \frac{1}{d_{ij}} ηij?=dij?1?
其中, d i j d_{ij} dij? 是城市 i i i和 j j j 之间的距离。
这些公式构成了蚁群算法的数学基础。通过调整参数 α \alpha α , β \beta β, 和 ρ \rho ρ,可以控制算法的搜索行为,从而适应不同的优化问题。
3.代码实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class AntColonyOptimizer:
def __init__(self, distances, n_ants, n_best, n_iterations, decay, alpha=1, beta=1):
# 初始化参数
self.distances = distances # 城市间的距离矩阵
self.pheromone = np.ones(self.distances.shape) / len(distances) # 初始化信息素矩阵
self.all_inds = range(len(distances)) # 所有城市的索引
self.n_ants = n_ants # 蚂蚁数量
self.n_best = n_best # 每轮保留的最佳路径数
self.n_iterations = n_iterations # 迭代次数
self.decay = decay # 信息素的挥发率
self.alpha = alpha # 信息素重要程度
self.beta = beta # 启发因子的重要程度
def run(self):
# 运行算法
shortest_path = None
shortest_path_length = float('inf')
for iteration in range(self.n_iterations): # 对每次迭代
all_paths = self.gen_all_paths() # 生成所有蚂蚁的路径
self.spread_pheromone(all_paths, self.n_best, shortest_path_length) # 更新信息素
shortest_path, shortest_path_length = self.find_shortest_path(all_paths) # 找到最短路径
self.plot_paths(shortest_path, iteration, shortest_path_length) # 绘制路径
return shortest_path, shortest_path_length
def gen_path_dist(self, path):
# 计算路径长度
total_dist = 0
for i in range(len(path) - 1):
total_dist += self.distances[path[i], path[i+1]]
return total_dist
def gen_all_paths(self):
# 生成所有蚂蚁的路径
all_paths = []
for _ in range(self.n_ants):
path = [np.random.randint(len(self.distances))] # 选择一个随机起点
while len(path) < len(self.distances):
move_probs = self.gen_move_probs(path) # 生成移动概率
next_city = np_choice(self.all_inds, 1, p=move_probs)[0] # 选择下一个城市
path.append(next_city)
all_paths.append((path, self.gen_path_dist(path))) # 添加路径和长度
return all_paths
def spread_pheromone(self, all_paths, n_best, shortest_path_length):
# 更新信息素
sorted_paths = sorted(all_paths, key=lambda x: x[1]) # 按路径长度排序
for path, dist in sorted_paths[:n_best]: # 只取最好的n_best条路径
for i in range(len(path) - 1):
self.pheromone[path[i], path[i+1]] += 1.0 / self.distances[path[i], path[i+1]]
def find_shortest_path(self, all_paths):
# 寻找最短路径
shortest_path = min(all_paths, key=lambda x: x[1]) # 根据路径长度找到最短的那条
return shortest_path[0], shortest_path[1]
def gen_move_probs(self, path):
# 生成移动概率
last_city = path[-1]
probs = np.zeros(len(self.distances))
for i in self.all_inds:
if i not in path:
pheromone = self.pheromone[last_city, i] ** self.alpha
heuristic = (1.0 / self.distances[last_city, i]) ** self.beta
probs[i] = pheromone * heuristic
return probs / probs.sum()
def plot_paths(self, best_path, iteration, path_length):
# 绘制路径
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
for i in range(len(coords)): # 绘制所有可能的路径
for j in range(i+1, len(coords)):
plt.plot([coords[i][0], coords[j][0]], [coords[i][1], coords[j][1]], 'k:', alpha=0.5)
for i in range(len(best_path) - 1): # 绘制最短路径
start_city = best_path[i]
end_city = best_path[i+1]
plt.plot([coords[start_city][0], coords[end_city][0]], [coords[start_city][1], coords[end_city][1]], 'b-', linewidth=2)
plt.scatter(*zip(*coords), color='red') # 标记城市位置
for i, coord in enumerate(coords): # 添加城市标签
plt.text(coord[0], coord[1], str(i), color='green')
plt.title(f'Iteration: {iteration}, Shortest Path Length: {round(path_length, 2)}')
plt.xlabel('X Coordinate')
plt.ylabel('Y Coordinate')
plt.show()
def np_choice(a, size, replace=True, p=None):
# numpy的随机选择函数
return np.array(np.random.choice(a, size=size, replace=replace, p=p))
# 城市坐标
coords = np.random.rand(10, 2) # 假设有10个城市
# 计算距离矩阵
distances = np.zeros((10, 10))
for i in range(10):
for j in range(10):
distances[i, j] = np.linalg.norm(coords[i] - coords[j]) # 使用欧几里得距离
# 运行蚁群算法
aco = AntColonyOptimizer(distances, n_ants=10, n_best=5, n_iterations=100, decay=0.5, alpha=1, beta=2)
path, dist = aco.run()
执行结果:


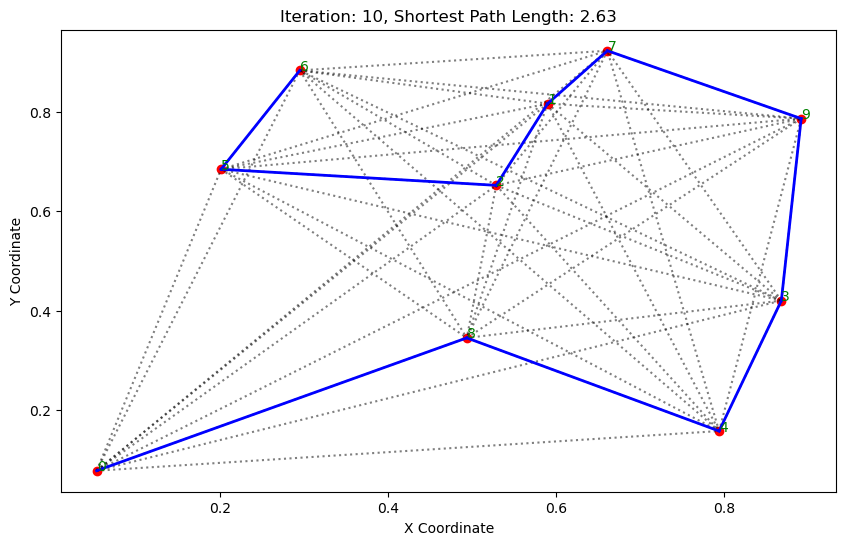
.
.
.
.
.
.
......
......
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!