【C++ Primer Plus学习记录】if语句
目录
一、if语句
if语句让程序能够决定是否应执行特定的语句。
if有两种格式:if和if else。
if语句的语法与while相似:
if(test-condition)
statement;如果test-condition(测试条件)为true,则程序将执行statement(语句),后者既可以是一条语句,也可以是语句块。如果测试条件为false,则程序将跳过语句。和循环测试条件一样,if测试条件也将被强制转换为bool值,因此0将被转换为false,非零为true。整个if语句被视为一条语句。
例如,假设读者希望程序计算输入中的空格数和字符总数,则可以在while循环中使用cin.get(char)来读取字符,然后使用if语句识别空格字符并计算其总数。程序清单6.1完成了这项工作,它使用句点(.)来确定句子的结尾。
//if
#if 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char ch;
int spaces = 0;
int total = 0;
cin.get(ch);//成员函数cin.get(char)读取输入中的下一个字符(即使它是空格),并将其赋给变量ch
while (ch != '.')
{
if (ch == ' ')
spaces++;
total++;
cin.get(ch);
}
cout << spaces << " spaces, " << total << " characters total in sentence\n";//字符总数中包括按回车键生成的换行符
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#endif二、if else语句
if语句让程序决定是否执行特定的语句或语句块,而if else语句则让程序决定执行两条语句或语句块中的哪一条,这种语句对于选择其中一种操作很有用。
if else语句的通用格式如下:
if(test-condition)
statement1
else
statement2如果测试条件为true或非零,则程序将执行statement1,跳过statement2;如果测试条件为false或0,则程序将跳过statement1,执行statement2。
从语法上看,整个if else结构被视为一条语句。
例如,假设要通过对字母进行加密编码来修改输入的文本(换行符不变)。这样,每个输入行都被转换为一行输出,且长度不变。这意味着程序对换行符采用一种操作,而对其他字符采用另一种操作。正如程序清单6.2所表明的,该程序还演示了限定符std::,这是编译指令using的替代品之一。
//if else
#if 1
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
char ch;
std::cout << "Type, and I shall repeat.\n";
std::cin.get(ch);//成员函数cin.get(char)读取输入中的下一个字符(即使它是空格),并将其赋给变量ch
while (ch != '.')
{
if (ch == '\n')
std::cout << ch;
else
std::cout << ++ch;//ASCII码
std::cin.get(ch);
}
std::cout << "\nPlease excuse the slight confusion.\n";
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#endif运行情况:
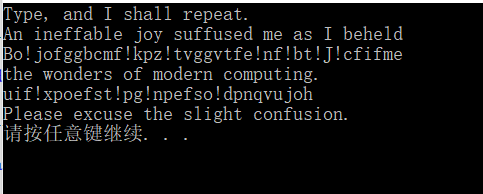 ?
?
三、格式化if else语句
if else中的两种操作都必须是一条语句。如果需要多条语句,则需要用大括号将它们括起来,组成一个块语句。
四、if else if else结构
程序清单6.3使用这种格式创建了一个小型测验程序。
#if 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int Fave = 27;
int main()
{
int n;
cout << "Enter a number in the range 1-100 to find";
cout << "my favorite number: ";
do
{
cin >> n;
if (n < Fave)
cout << "Too low -- guess again: ";
else if (n > Fave)
cout << "Too high -- guess again: ";
else
cout << Fave << " is right!\n";
} while (n != Fave);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#endif本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!