IOday6作业
2023-12-15 20:39:12
1>使用有名管道,完成两个进程的相互通信
//create.c
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
if((mkfifo("myfifo1",0664))== -1)
{
perror("mkfifo");
return -1;
}
if((mkfifo("myfifo2",0664))== -1)
{
perror("mkfifo");
return -1;
}
getchar();
system("rm myfifo1");
system("rm myfifo2");
return 0;
}
//01file.c
#include<myhead.h>
void* write_file(void* arg)
{
int wfd;
//打开管道
if((wfd = open("./myfifo1",O_WRONLY)) == -1)
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
char buf[128]="";
while(1)
{
printf("请写入:");
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);
buf[strlen(buf)-1]=0;
write(wfd,buf,sizeof(buf));
if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0)
{
break;
//exit(0);
}
}
close(wfd);
//pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void* read_file(void* arg)
{
int rfd;
if((rfd = open("./myfifo2",O_RDONLY)) == -1)
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
char buf[128]="";
while(1)
{
bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));
read(rfd,buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("输出的是%s\n",buf);
if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0)
{
break;
}
}
close(rfd);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//创建线程
pthread_t wtid = -1;//
pthread_t rtid = -1;
if(pthread_create(&wtid,NULL,write_file,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_t");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&rtid,NULL,read_file,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_t");
return -1;
}
//回收线程
pthread_join(rtid,NULL);
pthread_join(wtid,NULL);
return 0;
}
//02file.c
#include<myhead.h>
void* write_file(void* arg)
{
int wfd;
if((wfd = open("./myfifo2",O_WRONLY)) == -1)
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
char buf[128]="";
while(1)
{
printf("请写入:");
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);
buf[strlen(buf)-1]=0;
write(wfd,buf,sizeof(buf));
if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0)
{
break;
//exit(0);
}
}
close(wfd);
//pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void* read_file(void* arg)
{
int rfd;
if((rfd = open("./myfifo1",O_RDONLY)) == -1)
{
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
char buf[128]="";
while(1)
{
bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));
read(rfd,buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("输出的是%s\n",buf);
if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0)
{
break;
}
}
close(rfd);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//打开管道
//创建线程
pthread_t wtid = -1;//
pthread_t rtid = -1;
if(pthread_create(&wtid,NULL,write_file,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_t");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&rtid,NULL,read_file,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_t");
return -1;
}
//回收线程
pthread_join(rtid,NULL);
pthread_join(wtid,NULL);
return 0;
}
效果图:
?1> 使用无名管道完成父子进程间的通信
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//创建存放两个文件描述符的数组
int fd[2];
int pid = -1;
//打开无名管道
if(pipe(fd) == -1)
{
perror("pipe");
return -1;
}
//创建子进程
pid = fork();
if(pid > 0)
{
//父进程
//关闭读端
close(fd[0]);
char buf[128]="";
while(1)
{
printf("请输入:");
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = 0;
write(fd[1],buf,strlen(buf));
if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0)
{
break;
}
}
close(fd[1]);
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
//子进程
close(fd[1]);
char buf[128]="";
while(1)
{
bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));
read(fd[0],buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("输出是:%s\n",buf);
if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0)
{
break;
}
}
close(fd[0]);
}
else
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
wait(NULL);
return 0;
}
?效果图:

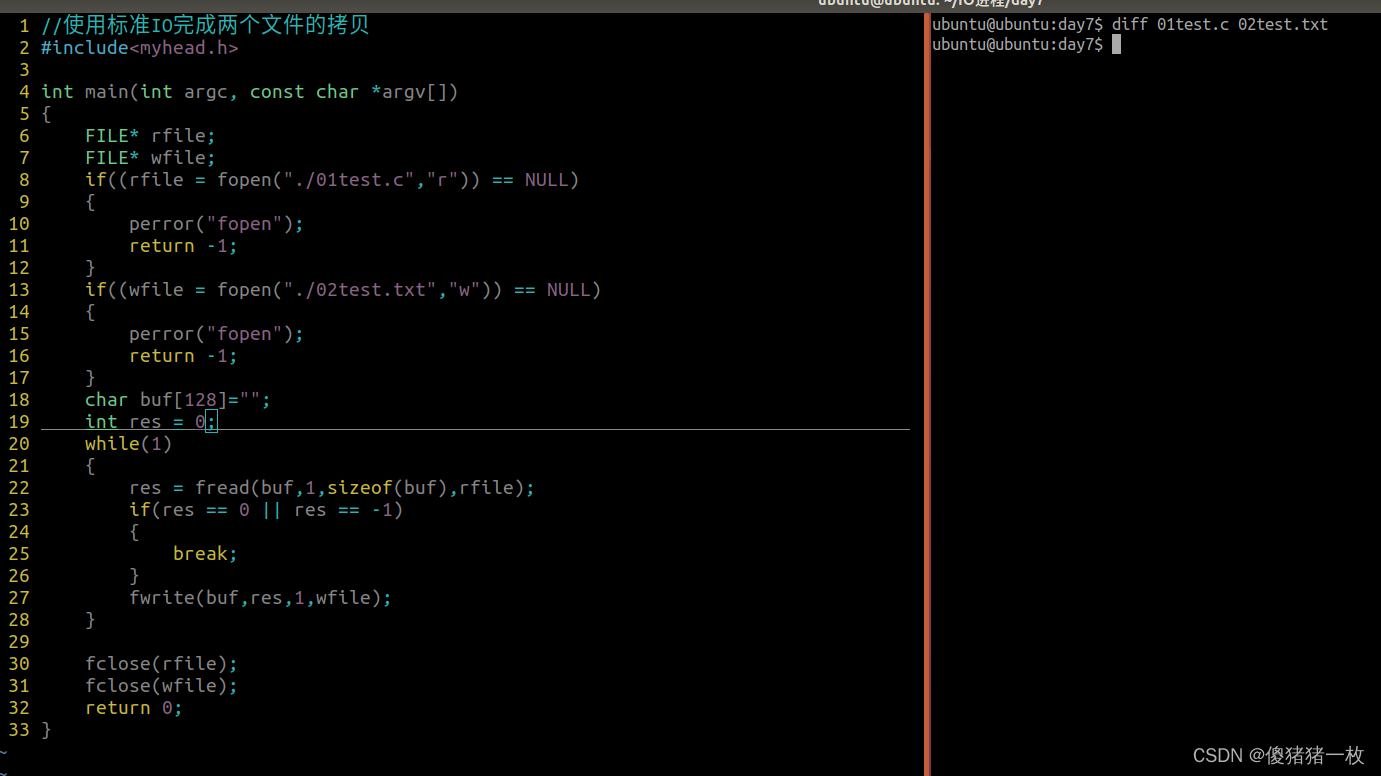
2> 使用标准IO完成两个文件的拷贝
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE* rfile;
FILE* wfile;
if((rfile = fopen("./01test.c","r")) == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
return -1;
}
if((wfile = fopen("./02test.txt","w")) == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
return -1;
}
char buf[128]="";
int res = 0;
while(1)
{
res = fread(buf,1,sizeof(buf),rfile);
if(res == 0 || res == -1)
{
break;
}
fwrite(buf,res,1,wfile);
}
fclose(rfile);
fclose(wfile);
return 0;
}
?效果图:
3> 使用文件IO实现两个文件的拷贝
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pid_t rpid = -1;
pid_t wpid = -1;
if((rpid = open("./01test.c",O_RDONLY))==-1)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
if((wpid = open("./03test.txt",O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC,0664))==-1)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
char buf[128]="";
int res = 0;
while(1)
{
bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));
res = read(rpid,buf,sizeof(buf));
if(res == 0||res == -1)
{
break;
}
write(wpid,buf,res);
}
close(rpid);
close(wpid);
return 0;
}
?效果图:

4> 使用多进程完成两个文件的拷贝
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pid_t pid = -1;
int rfd = -1;
int wfd = -1;
if((rfd = open("./01test.c",O_RDONLY))==-1)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
if((wfd = open("./04test.txt",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0664))==-1)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
int len = lseek(rfd,0,SEEK_END);
pid = fork();
if(pid > 0)
{
lseek(rfd,0,SEEK_SET);
lseek(wfd,0,SEEK_SET);
char buf[128]="";
int res = -1;
int num = 0;
while(1)
{
res = read(rfd,buf,sizeof(buf));
num += res;
if(num > len/2||res == 0)
{
write(wfd,buf,res-(num-len/2));
break;
}
write(wfd,buf,res);
}
close(rfd);
close(wfd);
wait(NULL);
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
lseek(rfd,len/2,SEEK_SET);
lseek(wfd,len/2,SEEK_SET);
char buf[128]="";
int res = -1;
int num = 0;
while(1)
{
res = read(rfd,buf,sizeof(buf));
num += res;
if(num > (len-len/2) || res == 0)
{
write(wfd,buf,res-(num-len/2));
break;
}
write(wfd,buf,res);
}
close(rfd);
close(wfd);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
else
{
perror("fork");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
?效果图:

5> 使用多线程完成两个文件的拷贝
#include<myhead.h>
typedef struct
{
const char* srcfile;
const char* destfile;
int place;
int offset;
}arg;
void* read_file(void* aarg)
{
arg ofile=*((arg*)aarg);
printf(" %s %s %d %d\n",ofile.srcfile,ofile.destfile,ofile.place,ofile.offset);
int rfd = -1;
int wfd = -1;
if((rfd = open(ofile.srcfile,O_RDONLY))==-1)
{
perror("open");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
if((wfd = open(ofile.destfile,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT,0664))==-1)
{
perror("open");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
lseek(rfd,ofile.place,SEEK_SET);
lseek(wfd,ofile.place,SEEK_SET);
char buf[128]="";
int res = 0;
int num = 0;
while(1)
{
bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));
res = read(rfd,buf,sizeof(buf));
num += res;
if(num >= ofile.offset||res == 0)
{
write(wfd,buf,res-(num-ofile.offset));
break;
}
write(wfd,buf,res);
}
close(rfd);
close(wfd);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pthread_t rtid = -1;
pthread_t wtid = -1;
pid_t fd = -1;
if((fd = open(argv[1],O_RDONLY))==-1)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
int len = lseek(fd,0,SEEK_END);
close(fd);
arg ofile_information={argv[1],argv[2],0,len/2};
if((pthread_create(&rtid,NULL,read_file,&ofile_information)) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_creat");
return -1;
}
arg tfile_information={argv[1],argv[2],len/2,len-(len/2)};
if((pthread_create(&wtid,NULL,read_file,&tfile_information)) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_creat");
return -1;
}
pthread_join(rtid,NULL);
pthread_join(wtid,NULL);
return 0;
}
效果图:

6> 将互斥锁的案例重新写一遍
#include<myhead.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
int money = 5000;
void* cost(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
money -= 50;
printf("小王花了50,还剩%d\n",money);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
//初始化
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
if(pthread_create(&tid,NULL,cost,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
//上锁
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
money -= 100;
printf("小张花了100,还剩:%d\n",money);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
pthread_join(tid,NULL);
return 0;
}
?效果图:

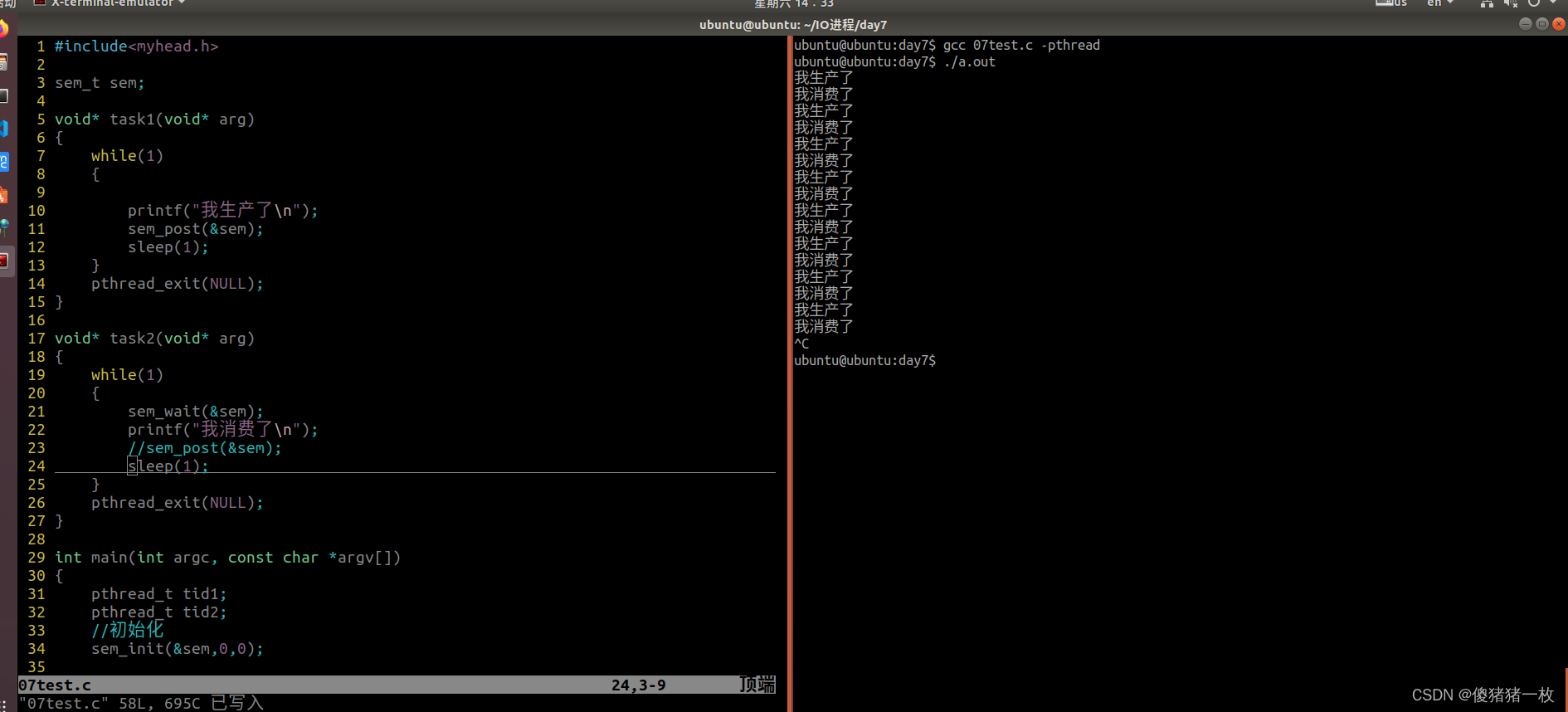
7> 将无名信号量实现生产者消费者程序重新实现一遍
#include<myhead.h>
sem_t sem;
void* task1(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
printf("我生产了\n");
sem_post(&sem);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void* task2(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
sem_wait(&sem);
printf("我消费了\n");
//sem_post(&sem);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid1;
pthread_t tid2;
//初始化
sem_init(&sem,0,0);
if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,task1,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,task2,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
sem_destroy(&sem);
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
return 0;
}
效果图:
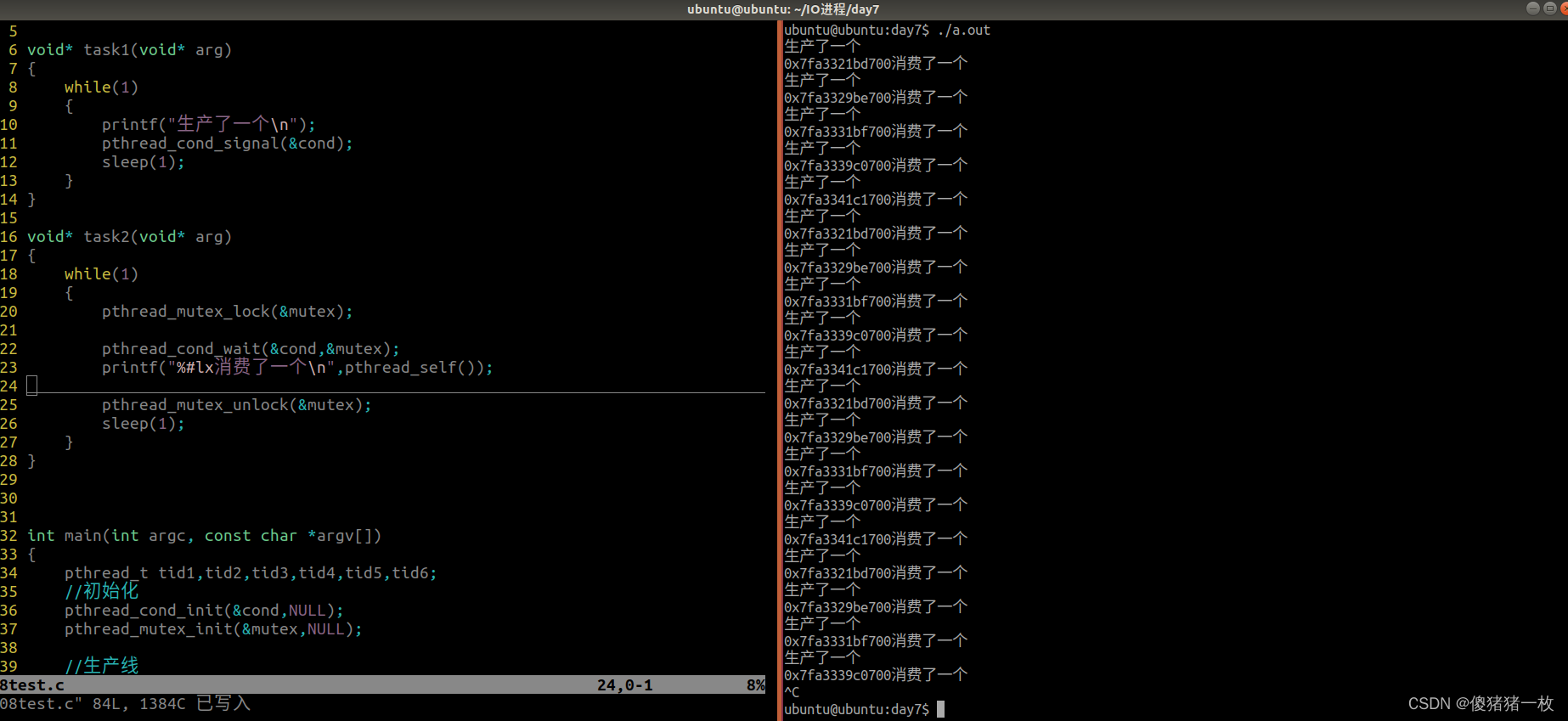
8> 将条件变量实现生产者消费者程序重新实现一遍
#include<myhead.h>
pthread_cond_t cond;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void* task1(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
printf("生产了一个\n");
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
sleep(1);
}
}
void* task2(void* arg)
{
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);
printf("%#lx消费了一个\n",pthread_self());
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(1);
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid1,tid2,tid3,tid4,tid5,tid6;
//初始化
pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
//生产线
if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,task1,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
//消费线
if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,task2,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid3,NULL,task2,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid4,NULL,task2,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid5,NULL,task2,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid6,NULL,task2,NULL) != 0)
{
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
pthread_join(tid1,NULL);
pthread_join(tid2,NULL);
pthread_join(tid3,NULL);
pthread_join(tid4,NULL);
pthread_join(tid5,NULL);
pthread_join(tid6,NULL);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
效果图:
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/Djdbds/article/details/134886216
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!

