代码随想录算法训练营DAY15|二叉树2
算法训练DAY15|二叉树2
层序遍历
学会二叉树的层序遍历,可以一口气打完以下十题:
#102.二叉树的层序遍历
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。

#思路
我们之前讲过了三篇关于二叉树的深度优先遍历的文章:
接下来我们再来介绍二叉树的另一种遍历方式:层序遍历。
层序遍历一个二叉树。就是从左到右一层一层的去遍历二叉树。这种遍历的方式和我们之前讲过的都不太一样。
需要借用一个辅助数据结构即队列来实现,队列先进先出,符合一层一层遍历的逻辑,而用栈先进后出适合模拟深度优先遍历也就是递归的逻辑。
而这种层序遍历方式就是图论中的广度优先遍历,只不过我们应用在二叉树上。
使用队列实现二叉树广度优先遍历,动画如下:
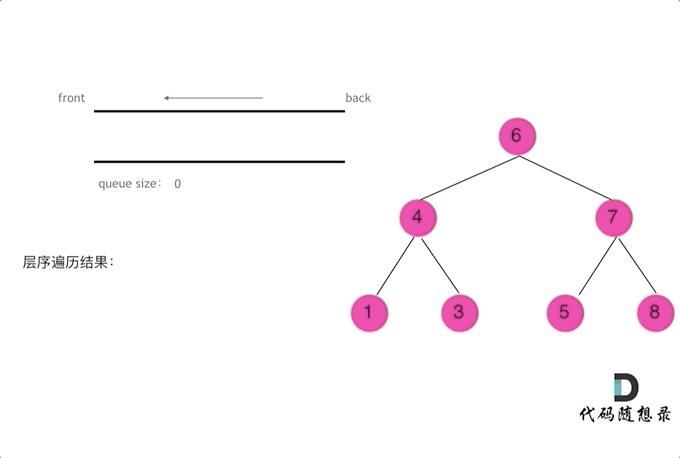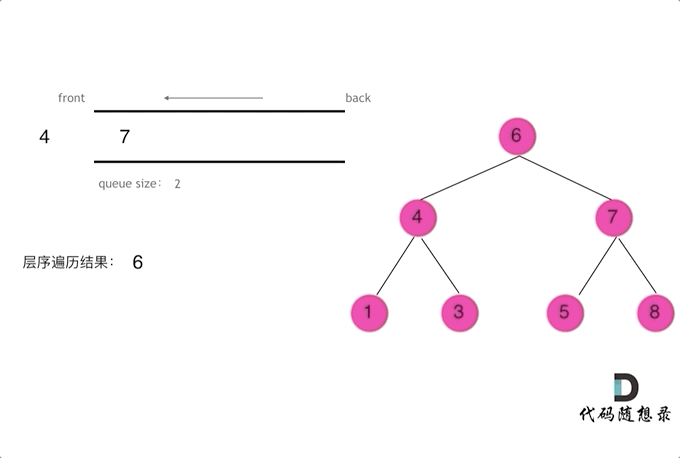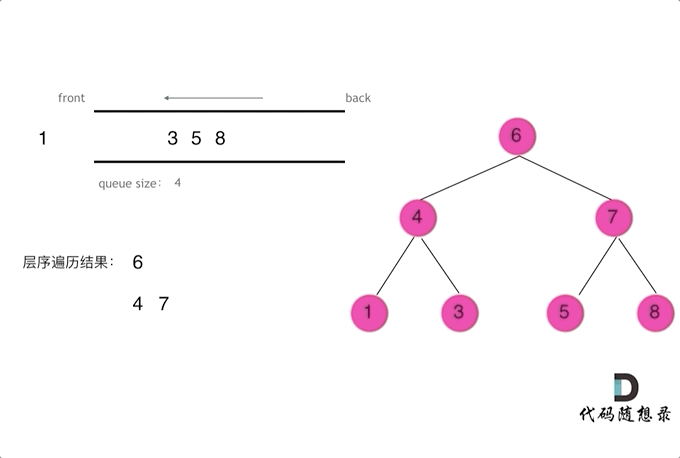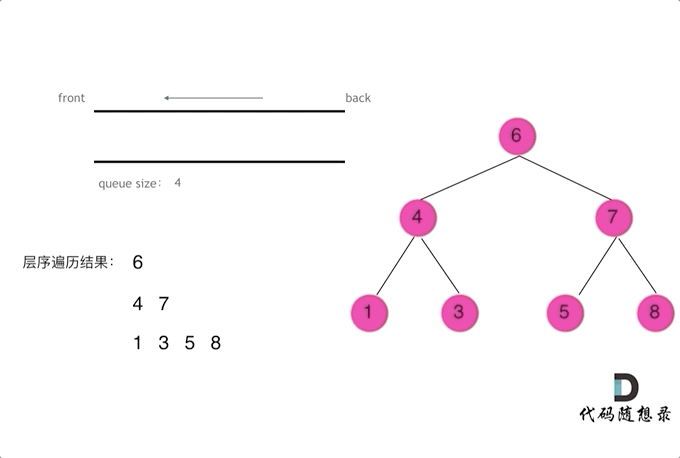
这样就实现了层序从左到右遍历二叉树。
代码如下:这份代码也可以作为二叉树层序遍历的模板,打十个就靠它了。
c++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
? ?vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
? ? ? ?queue<TreeNode*> que;
? ? ? ?if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
? ? ? ?vector<vector<int>> result;
? ? ? ?while (!que.empty()) {
? ? ? ? ? ?int size = que.size();
? ? ? ? ? ?vector<int> vec;
? ? ? ? ? ?// 这里一定要使用固定大小size,不要使用que.size(),因为que.size是不断变化的
? ? ? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?TreeNode* node = que.front();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?que.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?vec.push_back(node->val);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?result.push_back(vec);
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return result;
? }
};
# 递归法
class Solution {
public:
? ?void order(TreeNode* cur, vector<vector<int>>& result, int depth)
? {
? ? ? ?if (cur == nullptr) return;
? ? ? ?if (result.size() == depth) result.push_back(vector<int>());
? ? ? ?result[depth].push_back(cur->val);
? ? ? ?order(cur->left, result, depth + 1);
? ? ? ?order(cur->right, result, depth + 1);
? }
? ?vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
? ? ? ?vector<vector<int>> result;
? ? ? ?int depth = 0;
? ? ? ?order(root, result, depth);
? ? ? ?return result;
? }
};
199.二叉树的右视图
class Solution {
public:
? ?void order(TreeNode* root,vector<vector<int>> &vec,int depth){
? ? ? ?if(root==nullptr) return;
? ? ? ?if(depth == vec.size()) vec.push_back(vector<int>());
? ? ? ?vec[depth].push_back(root->val);
? ? ? ?order(root->left,vec,depth+1);
? ? ? ?order(root->right,vec,depth+1);
? }
? ?vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
? ? ? ?vector<vector<int>> result;
? ? ? ?int depth = 0;
? ? ? ?order(root,result,depth);
? ? ? ?vector<int> result1;
? ? ? ?for(int i=0;i<result.size();i++){
? ? ? ? ? ?result1.push_back(result[i][result[i].size()-1]);
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return result1;
? }
};
?
?
class Solution {
public:
? ?vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
? ? ? ?queue<TreeNode*> que; ? ? ?
? ? ? ?if(root!=nullptr) que.push(root);
? ? ? ?vector<int> vec;
? ? ? ?while(!que.empty()){
? ? ? ? ? ?int size = que.size(); ? ? ?
? ? ? ? ? ?for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?TreeNode* node = que.front();
? ? ? ? ? que.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if(i==size-1){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?vec.push_back(node->val);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } ? ?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
? ? ? ? ? } ? ?
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return vec;
? }
};
637.二叉树的层平均值
class Solution {
public:
? ?vector<double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode* root) {
? ? ? ?queue<TreeNode*> que;
? ? ? ?vector<double> result;
? ? ? ?if(root!=nullptr) que.push(root);
? ? ? ?while(!que.empty()){
? ? ? ? ? ?int size = que.size();
? ? ? ? ? ?long aver = 0;
? ? ? ? ? ?for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?TreeNode* node = que.front();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?que.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?aver+=node->val;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if(node->left) que.push(node->left);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if(node->right) que.push(node->right);
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?result.push_back(aver*1.0/size);
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return result;
? }
};
429.N叉树的层序遍历
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。 (即从左到右,逐层遍历)。
例如,给定一个 3叉树 :

返回其层序遍历:
[ [1], [3,2,4], [5,6] ]
#思路
这道题依旧是模板题,只不过一个节点有多个孩子了
C++代码:
class Solution {
public:
? ?vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
? ? ? ?queue<Node*> que;
? ? ? ?if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
? ? ? ?vector<vector<int>> result;
? ? ? ?while (!que.empty()) {
? ? ? ? ? ?int size = que.size();
? ? ? ? ? ?vector<int> vec;
? ? ? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?Node* node = que.front();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?que.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?vec.push_back(node->val);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < node->children.size(); i++) { // 将节点孩子加入队列
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->children[i]) que.push(node->children[i]);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?result.push_back(vec);
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return result;
?
? }
};
515.在每个树行中找最大值
您需要在二叉树的每一行中找到最大的值。
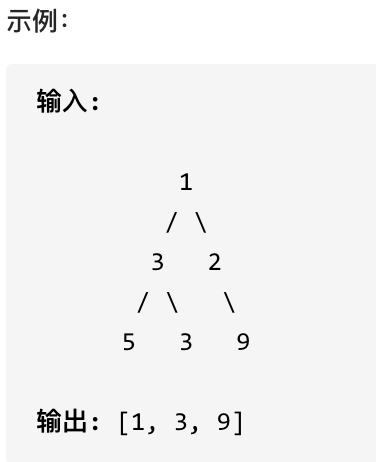
#思路
层序遍历,取每一层的最大值
C++代码:
class Solution {
public:
? ?vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
? ? ? ?queue<TreeNode*> que;
? ? ? ?if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
? ? ? ?vector<int> result;
? ? ? ?while (!que.empty()) {
? ? ? ? ? ?int size = que.size();
? ? ? ? ? ?int maxValue = INT_MIN; // 取每一层的最大值
? ? ? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?TreeNode* node = que.front();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?que.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?maxValue = node->val > maxValue ? node->val : maxValue;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?result.push_back(maxValue); // 把最大值放进数组
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return result;
? }
};
116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
给定一个完美二叉树,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {
?int val;
?Node *left;
?Node *right;
?Node *next;
}
1 2 3 4 5 6
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
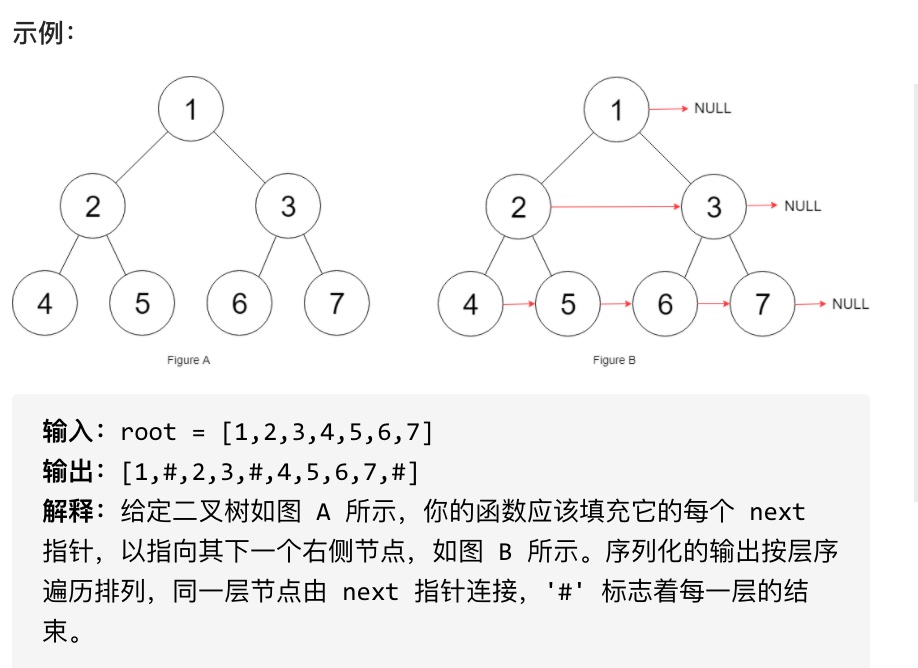
#思路
本题依然是层序遍历,只不过在单层遍历的时候记录一下本层的头部节点,然后在遍历的时候让前一个节点指向本节点就可以了
C++代码:
class Solution {
public:
? ?Node* connect(Node* root) {
? ? ? ?queue<Node*> que;
? ? ? ?if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
? ? ? ?while (!que.empty()) {
? ? ? ? ? ?int size = que.size();
? ? ? ? ? ?// vector<int> vec;
? ? ? ? ? ?Node* nodePre;
? ? ? ? ? ?Node* node;
? ? ? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (i == 0) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?nodePre = que.front(); // 取出一层的头结点
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?que.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?node = nodePre;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } else {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?node = que.front();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?que.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?nodePre->next = node; // 本层前一个节点next指向本节点
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?nodePre = nodePre->next;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?nodePre->next = NULL; // 本层最后一个节点指向NULL
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return root;
?
? }
};
117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
#思路
这道题目说是二叉树,但116题目说是完整二叉树,其实没有任何差别,一样的代码一样的逻辑一样的味道
C++代码:
class Solution {
public:
? ?Node* connect(Node* root) {
? ? ? ?queue<Node*> que;
? ? ? ?if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
? ? ? ?while (!que.empty()) {
? ? ? ? ? ?int size = que.size();
? ? ? ? ? ?vector<int> vec;
? ? ? ? ? ?Node* nodePre;
? ? ? ? ? ?Node* node;
? ? ? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (i == 0) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?nodePre = que.front(); // 取出一层的头结点
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?que.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?node = nodePre;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? } else {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?node = que.front();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?que.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?nodePre->next = node; // 本层前一个节点next指向本节点
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?nodePre = nodePre->next;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ?nodePre->next = NULL; // 本层最后一个节点指向NULL
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return root;
? }
};
104.二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

返回它的最大深度 3 。
#思路
使用迭代法的话,使用层序遍历是最为合适的,因为最大的深度就是二叉树的层数,和层序遍历的方式极其吻合。
在二叉树中,一层一层的来遍历二叉树,记录一下遍历的层数就是二叉树的深度,如图所示:
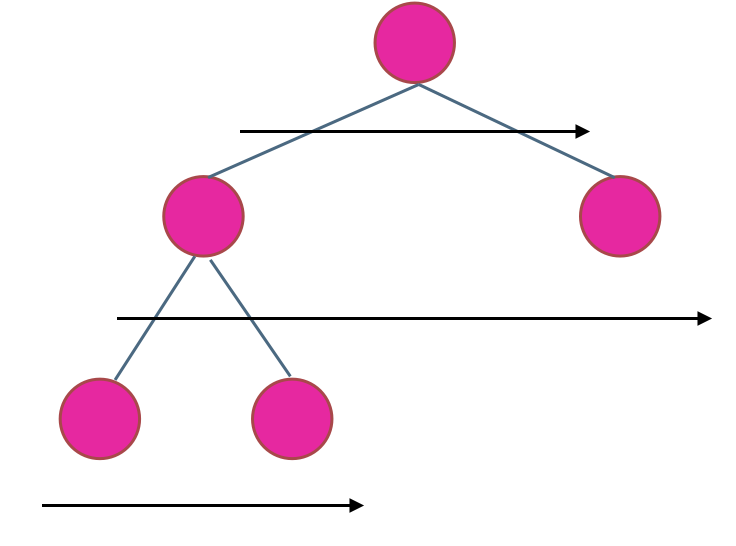
所以这道题的迭代法就是一道模板题,可以使用二叉树层序遍历的模板来解决的。
C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
? ?int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
? ? ? ?if (root == NULL) return 0;
? ? ? ?int depth = 0;
? ? ? ?queue<TreeNode*> que;
? ? ? ?que.push(root);
? ? ? ?while(!que.empty()) {
? ? ? ? ? ?int size = que.size();
? ? ? ? ? ?depth++; // 记录深度
? ? ? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?TreeNode* node = que.front();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?que.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return depth;
? }
};
111.二叉树的最小深度
#思路
相对于 104.二叉树的最大深度 ,本题还也可以使用层序遍历的方式来解决,思路是一样的。
需要注意的是,只有当左右孩子都为空的时候,才说明遍历的最低点了。如果其中一个孩子为空则不是最低点
代码如下:(详细注释)
class Solution {
public:
? ?int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
? ? ? ?if (root == NULL) return 0;
? ? ? ?int depth = 0;
? ? ? ?queue<TreeNode*> que;
? ? ? ?que.push(root);
? ? ? ?while(!que.empty()) {
? ? ? ? ? ?int size = que.size();
? ? ? ? ? ?depth++; // 记录最小深度
? ? ? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?TreeNode* node = que.front();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?que.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (!node->left && !node->right) { // 当左右孩子都为空的时候,说明是最低点的一层了,退出
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?return depth;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return depth;
? }
};
226.翻转二叉树
翻转一棵二叉树。
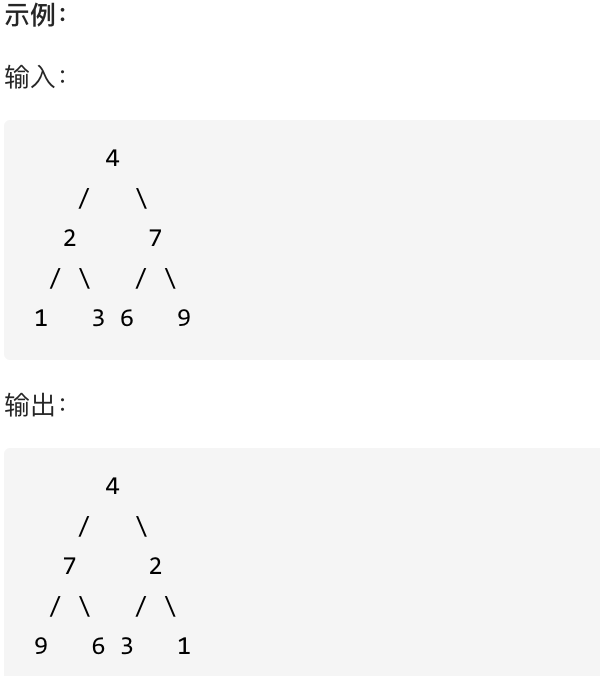
广度优先遍历
也就是层序遍历,层数遍历也是可以翻转这棵树的,因为层序遍历也可以把每个节点的左右孩子都翻转一遍,代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
? ?TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
? ? ? ?queue<TreeNode*> que;
? ? ? ?if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
? ? ? ?while (!que.empty()) {
? ? ? ? ? ?int size = que.size();
? ? ? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?TreeNode* node = que.front();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?que.pop();
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?swap(node->left, node->right); // 节点处理
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }
? ? ? ?return root;
? }
};
我们来看一下递归三部曲:
-
确定递归函数的参数和返回值
参数就是要传入节点的指针,不需要其他参数了,通常此时定下来主要参数,如果在写递归的逻辑中发现还需要其他参数的时候,随时补充。
返回值的话其实也不需要,但是题目中给出的要返回root节点的指针,可以直接使用题目定义好的函数,所以就函数的返回类型为TreeNode*。
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root)
-
确定终止条件
当前节点为空的时候,就返回
if (root == NULL) return root;
-
确定单层递归的逻辑
因为是先前序遍历,所以先进行交换左右孩子节点,然后反转左子树,反转右子树。
swap(root->left, root->right); invertTree(root->left); invertTree(root->right);
基于这递归三步法,代码基本写完,C++代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
? ?TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
? ? ? ?if (root == NULL) return root;
? ? ? ?swap(root->left, root->right); ?// 中
? ? ? ?invertTree(root->left); ? ? ? ? // 左
? ? ? ?invertTree(root->right); ? ? ? ?// 右
? ? ? ?return root;
? }
};
#迭代法
跳过
101. 对称二叉树
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。

最后递归的C++整体代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
? ?bool compare(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {
? ? ? ?// 首先排除空节点的情况
? ? ? ?if (left == NULL && right != NULL) return false;
? ? ? ?else if (left != NULL && right == NULL) return false;
? ? ? ?else if (left == NULL && right == NULL) return true;
? ? ? ?// 排除了空节点,再排除数值不相同的情况
? ? ? ?else if (left->val != right->val) return false;
?
? ? ? ?// 此时就是:左右节点都不为空,且数值相同的情况
? ? ? ?// 此时才做递归,做下一层的判断
? ? ? ?bool outside = compare(left->left, right->right); ? // 左子树:左、 右子树:右
? ? ? ?bool inside = compare(left->right, right->left); ? ?// 左子树:右、 右子树:左
? ? ? ?bool isSame = outside && inside; ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?// 左子树:中、 右子树:中 (逻辑处理)
? ? ? ?return isSame;
?
? }
? ?bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
? ? ? ?if (root == NULL) return true;
? ? ? ?return compare(root->left, root->right);
? }
};
迭代法
跳过
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!