前端带你学后端系列 ③【高并发JUC之篇二(基础补充篇)】
前端带你学后端系列 ③【高并发JUC之篇二】
Ⅰ 对线程Thread的补充
① Thread线程类怎么用?
Thread 类,用于描述一个线程。JVM 会将这些 Thread 对象组织起来,用于线程调度,线程管理。
- 我们可以用Thread类【创建】线程
- 可以通过Thread暴漏的方法,获取线程的各个【属性】(比如线程的优先级,线程的状态,线程的是否存活等)
- 可以通过start()方法,启动一个线程。可以通过join() 方法,让线程等待。当然,还有wait() notify() notifyAll()方法。
先介绍join()的用法
join() 是Thread的实例方法,
官方解释为:等待该线程终止。
thread.join() 方法阻塞调用此方法的线程(calling thread),直到线程thread完成,此线程再继续;通常用于在main() 主线程内,等待其它线程完成再结束 main() 主线程。
例子demo
public class ThreadExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("线程1"+i);
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("线程2"+i);
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
//等两个线程结束后查看结果
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println("join通常用在主线程,等待两个thread执行完了以后再执行");
}
}
② 线程安全问题【修改共享资源】
因为线程是抢占式的,当很多线程抢占式的修改共享资源的话,就会出现线程安全问题。
举个例子:
class Counter {
private int count = 0;
public void add() {
count++;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
public class ThreadExample_unsafe {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Counter counter = new Counter();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
counter.add();
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
counter.add();
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
//等两个线程结束后查看结果
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println(counter.getCount());
}
}

通常解决线程安全问题的方法:synchronized
synchronized ,保证了操作的原子性
class Counter {
private int count = 0;
public synchronized void add() {
count++;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
public class ThreadExample_unsafe {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Counter counter = new Counter();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
counter.add();
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
counter.add();
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
//等两个线程结束后查看结果
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println(counter.getCount());
}
}
// 使用锁以后,就能保证了原子性
public synchronized void add() {
count++;
}
③ 继续介绍我们的【锁】,即【线程安全问题】
Java锁是一种多线程同步的机制,用于控制多个线程对共享资源的并发访问。Java锁的作用是保证线程间的互斥性(Mutual Exclusion),即同一时刻只有一个线程可以访问共享资源,从而避免多线程间的竞态条件(Race Condition)和其他并发问题。
接下来,我们对几个锁进行一下介绍
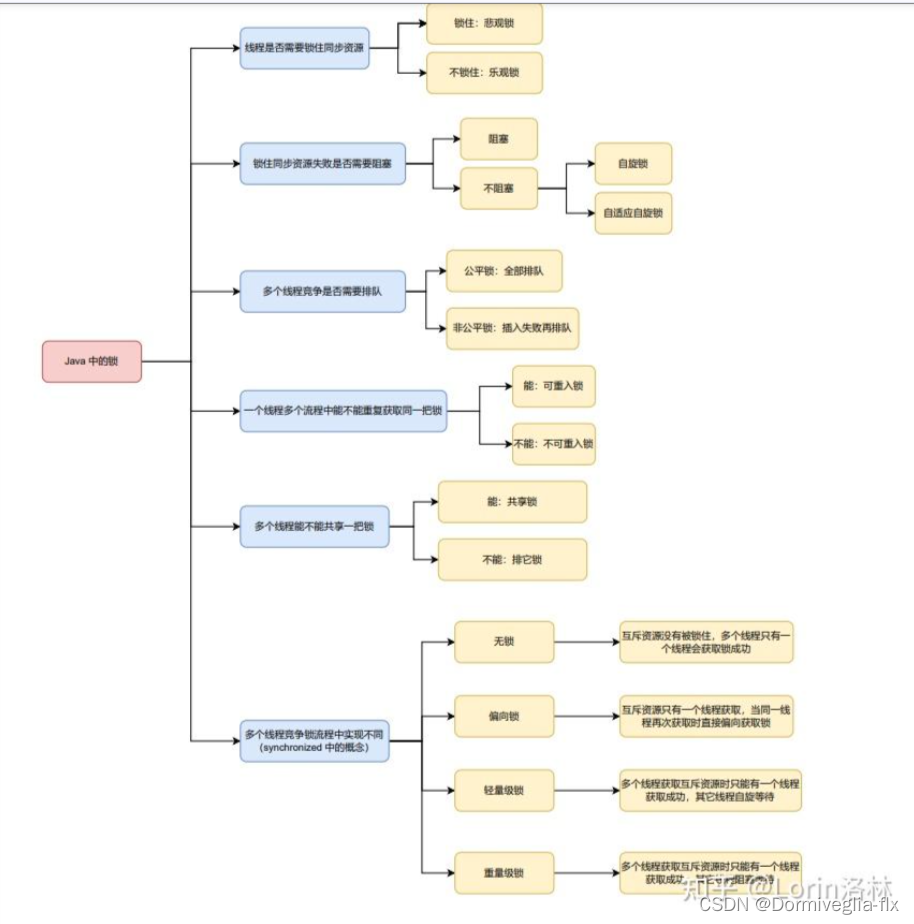
① 乐观锁与悲观锁
乐观锁和悲观锁是一种广义上的概念,体现了
线程对互斥资源进行操作的两种不同的态度。
悲观锁认为自己访问时,一定有其它线程来修改,因此在访问互斥资源时悲观锁会先加锁;
乐观锁认为自己在访问时不会有其它线程来修改,访问时不加锁,而是在更新数据时去判断有无被其他线程修改,若没被修改则写入成功,若被其他线程修改则进行重试或报错。
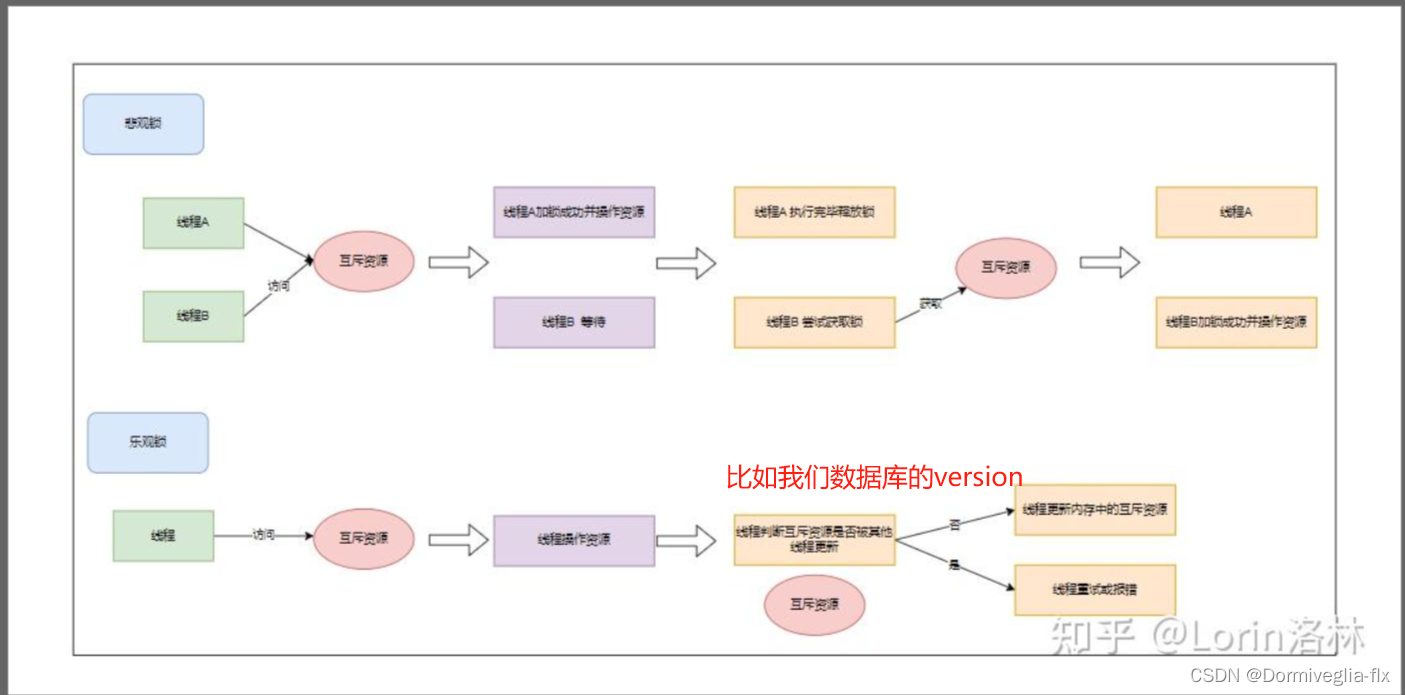
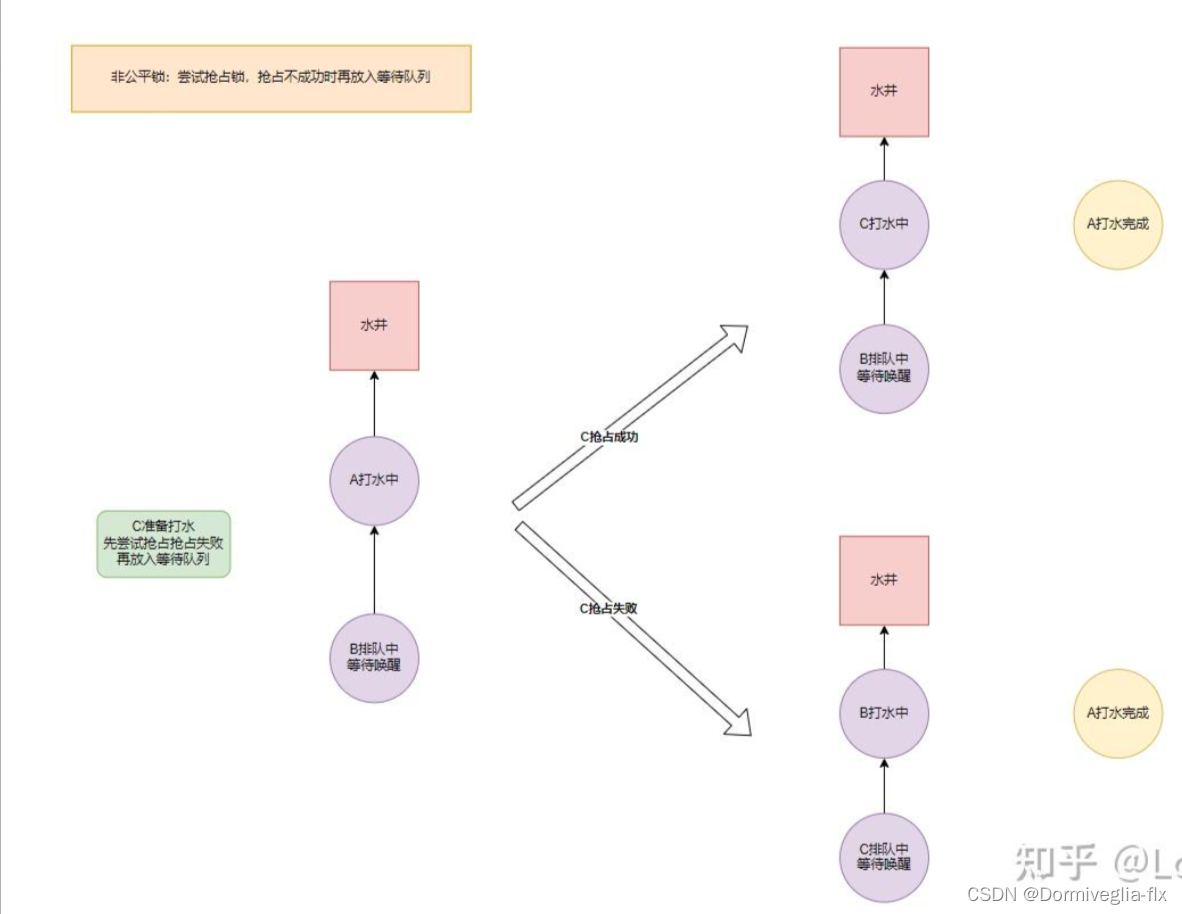
② 公平锁 & 非公平锁
公平锁和非公平锁指的是获取线程获取锁时的
顺序。
公平锁指按照锁申请的顺序来获取锁,线程直接进入队列中,队列中的第一个线程才能获取锁。
非公平锁指多个线程获取锁时,直接尝试获取锁,只有当线程未获取到锁时才放入队列中。
③ 排它锁 & 共享锁
排它锁和共享锁的主要区别在于
互斥资源锁是否能被多个线程同时持有。
同时
只能被一个线程持有称为排它锁;当能够被多个线程同时持有称为共享锁
④ wait方法、notify方法、notifyAll方法等【线程通信】问题

public class WaitDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object lock = new Object();
Object lock2 = new Object();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("线程1开始执行");
try {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("线程1调用wait方法....");
// 无限期的等待状态
lock.wait();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程1执行完成");
}, "线程1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("线程2开始执行");
try {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("线程2调用wait方法....");
// 无限期的等待状态
lock.wait();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程2执行完成");
}, "线程2");
t2.start();
t1.start();
// 唤醒 lock 对象上休眠的线程的(随机唤醒一个)
Thread t4 = new Thread(() -> {
//先让线程1,2先执行
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("线程4:开始执行");
synchronized (lock) {
// 发出唤醒通知
lock.notify();
System.out.println("线程4:执行了唤醒操作");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("线程4:synchronized 执行完了");
}
}, "线程4");
t4.start();
}
}
输出:
线程1开始执行
线程2开始执行
线程1调用wait方法....
线程2调用wait方法....
线程4:开始执行
线程4:执行了唤醒操作
线程4:synchronized 执行完了
线程1执行完成
线程2执行完成
Ⅱ JUC并发编程的各个组件的补充
① ReentrantLock – 高并发(线程同步)【线程安全问题】
synchronized 和 ReentrantLock 都是用于实现
多线程同步的工具,它们的目的都是为了保证多个线程对共享资源的安全访问。
Synchronized 加锁的demo
public class Counter {
private int count;
public void add() {
synchronized(this) {
count ++;
System.out.println("ThreadName:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", count:" + getCount());
}
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Counter counter = new Counter();
// 创建5个线程,同时对count进行加一操作
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
counter.add();
}
}).start();
}
// 假设休眠1秒,5个线程执行完毕
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("count:" + counter.getCount());
}
ReentrantLock加锁的demo
public class Counter {
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private int count;
public void add() {
// 加锁
lock.lock();
try {
count ++;
System.out.println("ThreadName:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", count:" + getCount());
} finally {
// 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Counter counter = new Counter();
// 创建5个线程,同时对count进行加一操作
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
counter.add();
}
}).start();
}
// 假设休眠1秒,5个线程执行完毕
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("count:" + counter.getCount());
}
② Atomic原子类体系及CAS原理–高并发(线程同步)【线程安全问题】
CAS,是原子操作的一种,可用于在多线程编程中实现不被打断的数据交换操作,从而
避免多线程同时改写某一数据时由于执行顺序不确定性以及中断的不可预知性产生的数据不一致问题。
直接
从根源解决问题,让共享的数据原子化,就可以不用锁了。当然原子类效率比锁高。
package atomic;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class AtomicTest {
// 原子性int
private static AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(0);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 多个线程并发地增加计数器的值
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
// 等同于++操作
counter.incrementAndGet();
}
});
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
counter.incrementAndGet();
}
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println("Counter value: " + counter.get());
}
}
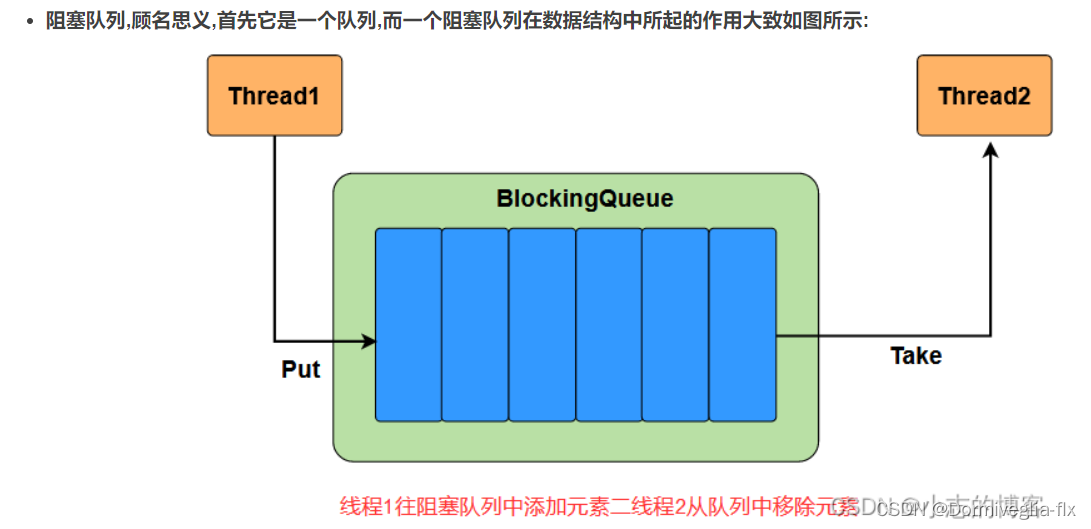
③ Java BlockingQueue(阻塞队列)–高并发(限流)
① 概念与分类

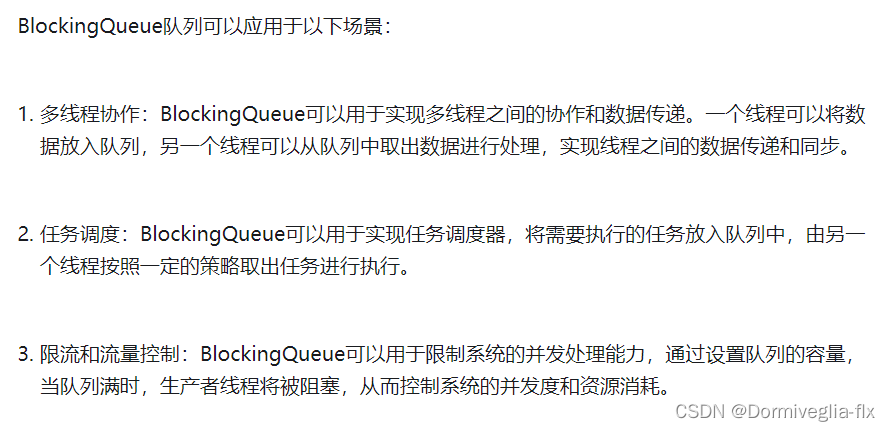
② 应用场景
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!