vue3 + fastapi 实现选择目录所有文件自定义上传到服务器
文章目录

?前言
大家好,我是yma16,本文分享关于vue3 + fastapi 实现选择目录文件上传到服务器指定位置。
vue3系列相关文章:
前端vue2、vue3去掉url路由“ # ”号——nginx配置
csdn新星计划vue3+ts+antd赛道——利用inscode搭建vue3(ts)+antd前端模板
认识vite_vue3 初始化项目到打包
python_selenuim获取csdn新星赛道选手所在城市用echarts地图显示
python系列文章:
python爬虫_基本数据类型
python爬虫_函数的使用
python爬虫_requests的使用
python爬虫_selenuim可视化质量分
python爬虫_django+vue3可视化csdn用户质量分
python爬虫_正则表达式获取天气预报并用echarts折线图显示
python爬虫_requests获取bilibili锻刀村系列的字幕并用分词划分可视化词云图展示
python爬虫_selenuim登录个人markdown博客站点
python爬虫_requests获取小黄人表情保存到文件夹
python_selenuim获取csdn新星赛道选手所在城市用echarts地图显示
💖 技术栈选择
前端:vue3 + ts + antd
后端:python + fastapi
vue3优势
Vue3相比较于Vue2有以下几个优势:
-
更快的渲染速度:Vue3通过重新设计响应式系统和虚拟DOM,可以实现更快的渲染速度。在内存使用和性能方面,Vue3比Vue2更加高效。
-
更好的TypeScript支持:Vue3更好地支持TypeScript,TypeScript在Vue3中的使用更加直接、正式、稳定,并且类型推导更加准确。
-
更好的组件化开发:Vue3可以更方便地编写组件,将模板、脚本和样式分离开来,使得代码更加易读易维护。
-
更好的开发体验:Vue3增加了很多新的特性,如Composition API、Teleport、Suspense等,这些特性使得开发过程更加简单、便捷、灵活。
-
更多的生态支持:随着Vue3的面世,越来越多的插件和库开始支持Vue3,例如Vue Router、Vuex等,这些生态工具的发展将有助于Vue3的快速发展。
fastapi优势
FastAPI的优势主要体现在以下几个方面:
-
高性能:FastAPI使用异步编程模型,使用基于事件循环的异步处理请求,可以轻松处理大量的并发请求,提高服务器性能。
-
简单易用的API开发:FastAPI能够自动生成API文档,因此开发者可以通过它来快速地编写API,而不必花费大量时间去编写文档。
-
高可靠性:FastAPI 自动进行类型检查,能够避免类型错误引起的运行时错误,提高了API的稳定性。
-
支持原生Python语法:FastAPI可以使用Python原生语法来编写代码,不需要学习新的语言,可以更方便地使用Python的生态系统。
-
兼容多种前端框架:FastAPI 可以与多种前端框架配合使用,包括React、Angular、Vue.js等,提供了更大的开发自由度。
-
广泛的社区支持:FastAPI社区非常活跃,拥有大量的开发者和用户,提供了丰富的资源和支持。
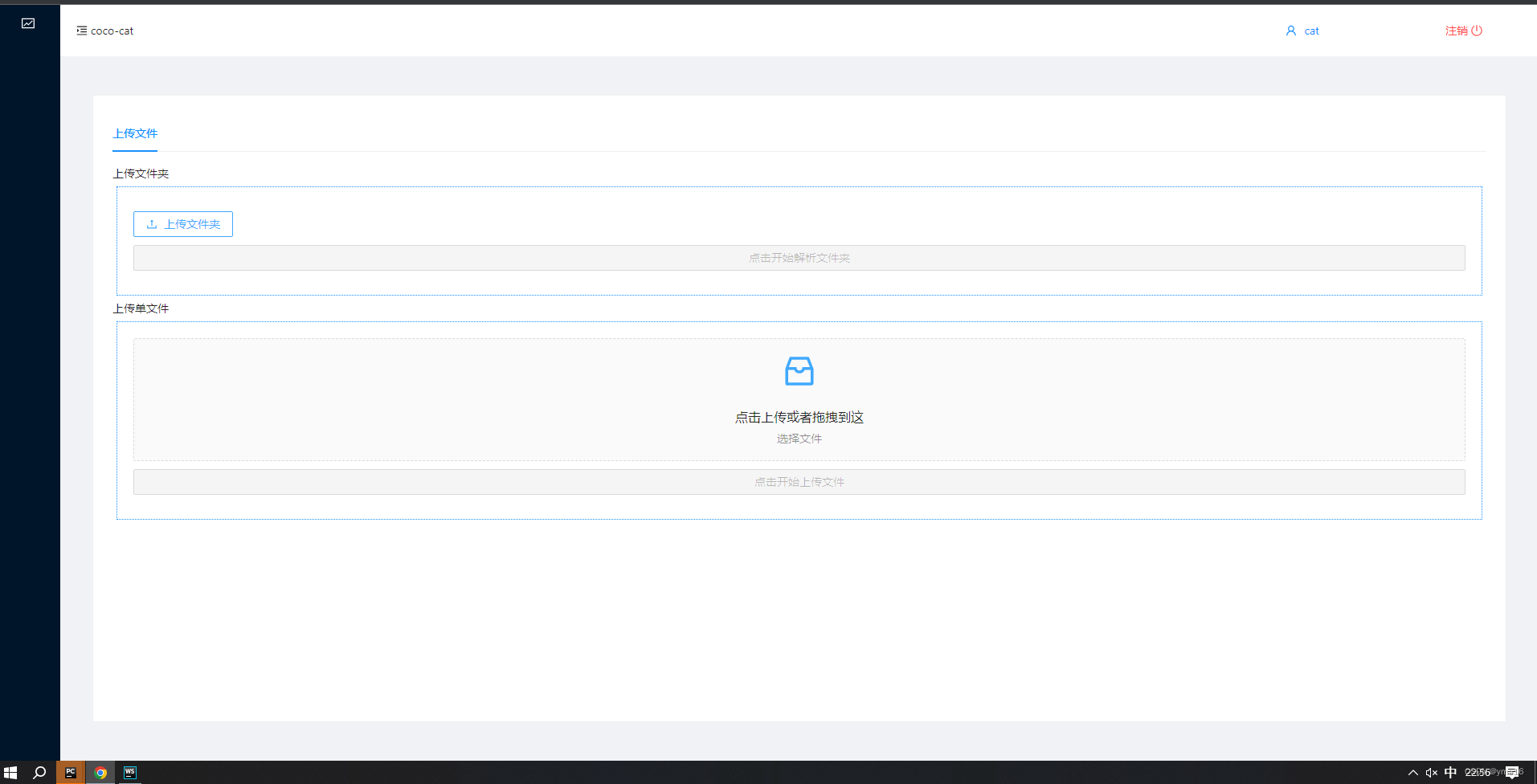
?前端页面搭建
布局:
上下结构
上方为选择目录
下方为选择文件夹
实现效果图如下
vue3 语法糖代码实现
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { ref,reactive,computed } from 'vue';
import { InboxOutlined } from '@ant-design/icons-vue';
import { message } from 'ant-design-vue';
import { uploadFile,uploadUrl } from "../../service/gpt/index";
import { UploadOutlined } from '@ant-design/icons-vue';
const state:any=reactive({
fileList:[],
loading:false,
text:'',
dirList:[],
dirPath:'',
customFile:null,
activeKey:'1',
movieUrl:''
});
const upUrl=async ()=>{
state.loading=true
try{
const res=await uploadUrl({
url:state.movieUrl
})
console.log('res',res)
}
catch (e) {
message.error(JSON.stringify(e))
}
finally {
setTimeout(()=>{
state.loading=false
},200)
}
}
const remove=(e:any)=> {
console.log('drop file',e);
state.fileList=[]
}
const removeDir=(e:any)=>{
state.dirList=state.dirList.filter((file:any)=>file.uid!==e.uid)
}
const customRequesHandle=(e:any)=>{
console.log(e,'custom')
}
const beforeUpload = (file:any) => {
console.log('file before',file)
state.fileList=[file]
return false;
};
const beforeUploadDir = (file:any) => {
state.dirList.push(file)
return false;
};
const uploadSingleFile= async ()=>{
state.loading=true
console.log(typeof state.fileList[0],'file 类型')
try{
const formData=new FormData();
formData.append('file',state.fileList[0])
const res=await uploadFile(formData)
console.log('res',res)
}catch (e) {
message.error(JSON.stringify(e))
}
finally {
setTimeout(()=>{
state.loading=false
},200)
}
}
const upBtnDisabled=computed(()=>{
return state.fileList.length===0
})
const change=(e:any)=>{
console.log('change e',e)
}
const upDir=async ()=>{
if(state.dirList.length===0){
return message.warning('请选择文件夹!')
}
state.loading=true
const paramsData:any={
dirList:state.dirList,
dirPath:state.dirPath,
}
try{
state.dirList.forEach(async (file:any)=>{
try{
const formData=new FormData();
formData.append('file',file)
const res=await uploadFile(formData)
console.log('res',res)
}catch(r){
message.error(JSON.stringify(r))
}
})
}catch (e) {
message.error(JSON.stringify(e))
}
finally {
setTimeout(()=>{
state.loading=false
},200)
}
}
const previewDirFile=async (file:any)=>{
return new Promise(resolve=>resolve(false))
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<a-spin :spinning="state.loading" tip="upload...">
<div class="header-tools">
</div>
<a-tabs v-model:activeKey="state.activeKey">
<a-tab-pane key="1" tab="上传文件">
<div>
上传文件夹
<div style="margin: 5px;border: 1px dotted #1890ff;padding: 20px">
<div style="margin: 10px 0;max-height: 200px;overflow: auto">
<a-upload :before-upload="beforeUploadDir" v-model:file-list="state.dirList"
list-type="picture"
@remove="removeDir" directory>
<a-button>
<upload-outlined></upload-outlined>
上传文件夹
</a-button>
</a-upload>
<div >
</div>
</div>
<div style="margin:10px 0">
<a-button type="primary" block @click="upDir" :disabled="state.dirList.length===0" >点击开始解析文件夹</a-button>
</div>
</div>
上传单文件
<div style="margin: 5px;border: 1px dotted #1890ff;padding: 20px">
<div>
<a-upload-dragger
:file-list="state.fileList"
list-type="picture"
:multiple="false"
:before-upload="beforeUpload"
@remove="remove"
@change="change"
>
<p class="ant-upload-drag-icon">
<inbox-outlined></inbox-outlined>
</p>
<p class="ant-upload-text">点击上传或者拖拽到这</p>
<p class="ant-upload-hint">
选择文件
</p>
</a-upload-dragger>
</div>
<div style="margin:10px 0">
<a-button type="primary" block @click="uploadSingleFile" :disabled="upBtnDisabled">点击开始上传文件</a-button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</a-tab-pane>
</a-tabs>
</a-spin>
</div>
</template>
<style>
.header-tools{
text-align: center;
font-size: 24px;
font-weight: bold;
}
.content-box{
}
.des{
margin:20px 0;
}
</style>
💖 调整请求content-type传递formData
axios封装
import axios from "axios";
// 实例
const createInstance = (baseURL:string)=>{
return axios.create({
baseURL:baseURL,
timeout: 10000,
headers: {'X-Custom-Header': 'yma16'}
})
};
// @ts-ignore
const http:any=createInstance('');
// 添加请求拦截器
http.interceptors.request.use(function (config:any) {
// 在发送请求之前做些什么
return config;
}, function (error:any) {
// 对请求错误做些什么
return Promise.reject(error);
});
// 添加响应拦截器
http.interceptors.response.use(function (response:any) {
// 2xx 范围内的状态码都会触发该函数。
// 对响应数据做点什么
return response;
}, function (error:any) {
// 超出 2xx 范围的状态码都会触发该函数。
// 对响应错误做点什么
return Promise.reject(error);
});
// 文件上传
const createUploadInstance = (baseURL:string)=>{
return axios.create({
baseURL:baseURL,
timeout: 10000,
headers: {"Content-Type": "multipart/form-data"}
})
};
// @ts-ignore
const uploadHttp:any=createUploadInstance('');
// 添加请求拦截器
uploadHttp.interceptors.request.use(function (config:any) {
// 在发送请求之前做些什么
return config;
}, function (error:any) {
// 对请求错误做些什么
return Promise.reject(error);
});
// 添加响应拦截器
uploadHttp.interceptors.response.use(function (response:any) {
// 2xx 范围内的状态码都会触发该函数。
// 对响应数据做点什么
return response;
}, function (error:any) {
// 超出 2xx 范围的状态码都会触发该函数。
// 对响应错误做点什么
return Promise.reject(error);
});
export {http,uploadHttp};
service对接后端
import {uploadHttp} from "../../http/index";
export const uploadFile: any = (formData: any) => {
return uploadHttp.post("/api/uploadFile/action", formData);
};
?后端接口实现
安装环境
pip install uvicorn
pip install fastapi
pip install python-multipart
上传单个文件接口实现:
from fastapi import FastAPI, status, File, Form, UploadFile
from fastapi import FastAPI, status, File, Form, UploadFile
from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
import os
app = FastAPI()
# 跨域配置
origins = [
"http://localhost:3000",
]
app.add_middleware(
CORSMiddleware,
allow_origins=origins,
allow_credentials=True,
allow_methods=["*"],
allow_headers=["*"],
)
@app.get("/api")
async def root():
return {"data": "fast api!"}
# 上传文件
@app.post("/api/uploadFile/action")
async def create_file(
file:UploadFile
):
writeBytes('./media',file)
return {
'code':200,
"msg":'success'
}
# 将file写入dirs目录文件
def writeBytes(dirs,file):
bytesFile=file.file.read()
filename=file.filename
if not os.path.exists(dirs):
os.makedirs(dirs)
with open(dirs+'/'+ filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(bytesFile)
uvicorn运行fastapi
uvicorn server.main:app --reload --port 7777
💖 swagger文档测试接口
swagger文档地址:
http://ip:port/docs
上传成功!
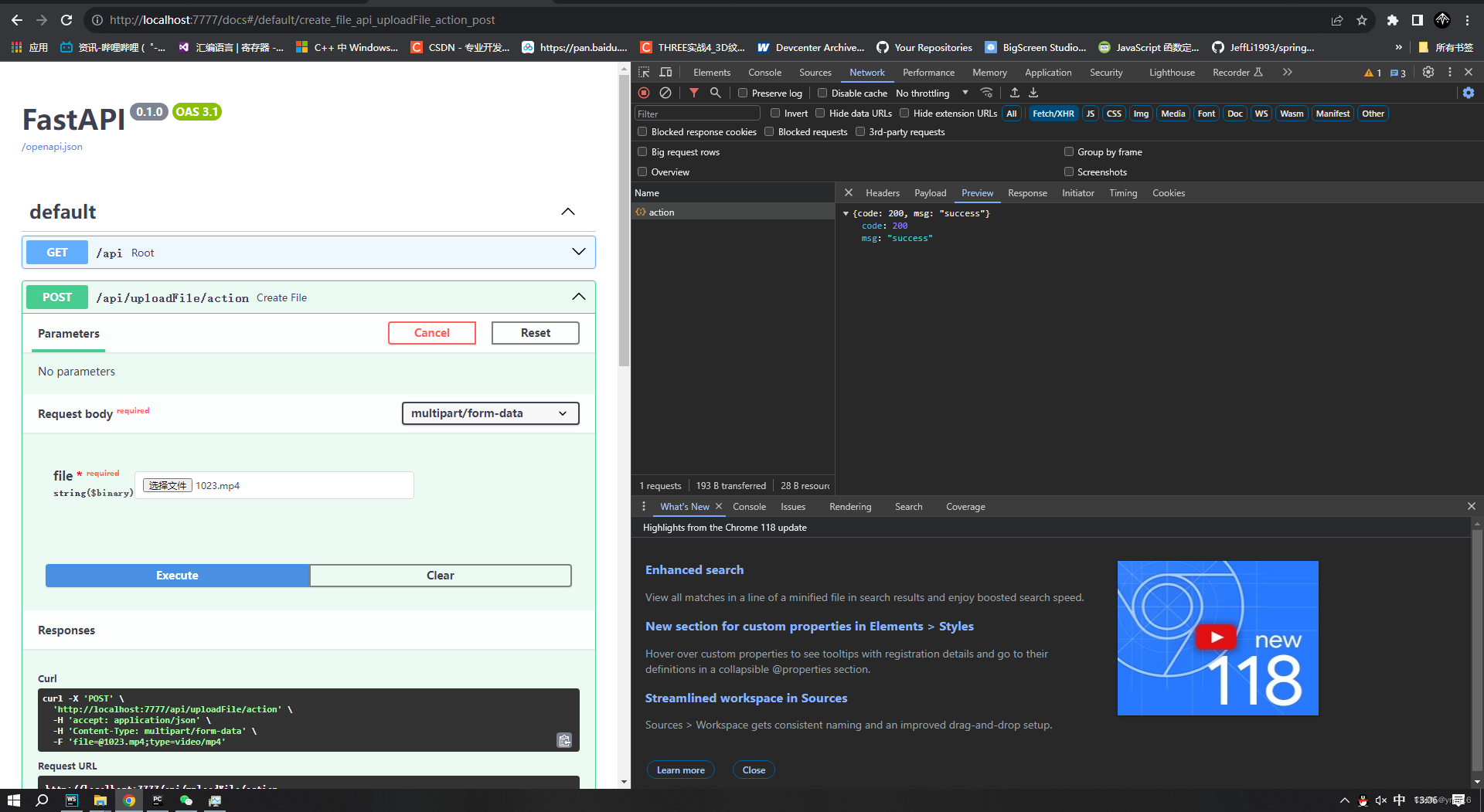
?前后端实现效果
💖 上传单个文件

💖 上传目录文件

上传目录文件的接口实现:
- file为二进制文件
- dir为目录名称
- name为完整的文件名称
# 上传目录文件
@app.post("/api/uploadDirFile/action")
async def uploadDirFile(
file:UploadFile,
dir:str=Form(),
name:str=Form()
):
print(dir,'dir_____________')
writeBytes('./media/'+dir,name,file)
return {
'code':200,
"msg":'success'
}
# 将二进制数据写入目录文件
def writeBytes(dirs,name,file):
bytesFile=file.file.read()
filename=name
if not os.path.exists(dirs):
os.makedirs(dirs)
with open(dirs+'/'+ filename, "wb") as f:
f.write(bytesFile)
?总结
文件上传注意事项
前端:
- 请求头配置
headers: {"Content-Type": "multipart/form-data"} - 参数传递使用
new FormData()
后端:
- 接受参数使用 Uploadfile格式
- 解析文件内容名称包括类型按格式写入文件
multipart/form-data
multipart/form-data 是一种常用的 HTTP 请求方法,通常用于上传文件或大量数据。它将请求的数据分成多个部分(part),每一部分使用一个 boundary 分隔符来分开,每个部分包含一个头部和一个内容体,头部描述了该部分的属性,如数据类型、数据编码等。在 HTTP 消息体中,每个部分之间必须以 “–boundary\r\n” 开始,以 “–boundary–\r\n” 结束,即在结尾处添加额外的 “–” 标记。在客户端使用该方法请求时,需要明确指定请求头中的 Content-Type 为 multipart/form-data。服务端接收到该请求后,需要解析出每个部分中的请求数据。
?结束
本文分享到这结束,如有错误或者不足之处欢迎指出!

👍 点赞,是我创作的动力!
?? 收藏,是我努力的方向!
?? 评论,是我进步的财富!
💖 感谢你的阅读!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!