FFmpeg的AVFilter框架总成AVFilter-AVFilterContext
2023-12-15 04:53:32
毫无疑问,还是和前面的一样一个context和一个包含有回调函数指针的插件结构体,想要实现自己的插件,主要实现里面的回调函数就可以了,当然,AVFilter比其它模块稍微复杂一点还要牵扯到其它一些辅助模块,在其它章节介绍
下面是关键函数调用图:
/**
* Add a frame to the buffer source.
*
* @param ctx an instance of the buffersrc filter
* @param frame frame to be added. If the frame is reference counted, this
* function will make a new reference to it. Otherwise the frame data will be
* copied.
*
* @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on error
*
* This function is equivalent to av_buffersrc_add_frame_flags() with the
* AV_BUFFERSRC_FLAG_KEEP_REF flag.
*/
av_warn_unused_result
int av_buffersrc_write_frame(AVFilterContext *ctx, const AVFrame *frame);
/**
* Add a frame to the buffer source.
*
* @param ctx an instance of the buffersrc filter
* @param frame frame to be added. If the frame is reference counted, this
* function will take ownership of the reference(s) and reset the frame.
* Otherwise the frame data will be copied. If this function returns an error,
* the input frame is not touched.
*
* @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on error.
*
* @note the difference between this function and av_buffersrc_write_frame() is
* that av_buffersrc_write_frame() creates a new reference to the input frame,
* while this function takes ownership of the reference passed to it.
*
* This function is equivalent to av_buffersrc_add_frame_flags() without the
* AV_BUFFERSRC_FLAG_KEEP_REF flag.
*/
av_warn_unused_result
int av_buffersrc_add_frame(AVFilterContext *ctx, AVFrame *frame);
/**
* Get a frame with filtered data from sink and put it in frame.
*
* @param ctx pointer to a context of a buffersink or abuffersink AVFilter.
* @param frame pointer to an allocated frame that will be filled with data.
* The data must be freed using av_frame_unref() / av_frame_free()
*
* @return
* - >= 0 if a frame was successfully returned.
* - AVERROR(EAGAIN) if no frames are available at this point; more
* input frames must be added to the filtergraph to get more output.
* - AVERROR_EOF if there will be no more output frames on this sink.
* - A different negative AVERROR code in other failure cases.
*/
int av_buffersink_get_frame(AVFilterContext *ctx, AVFrame *frame);
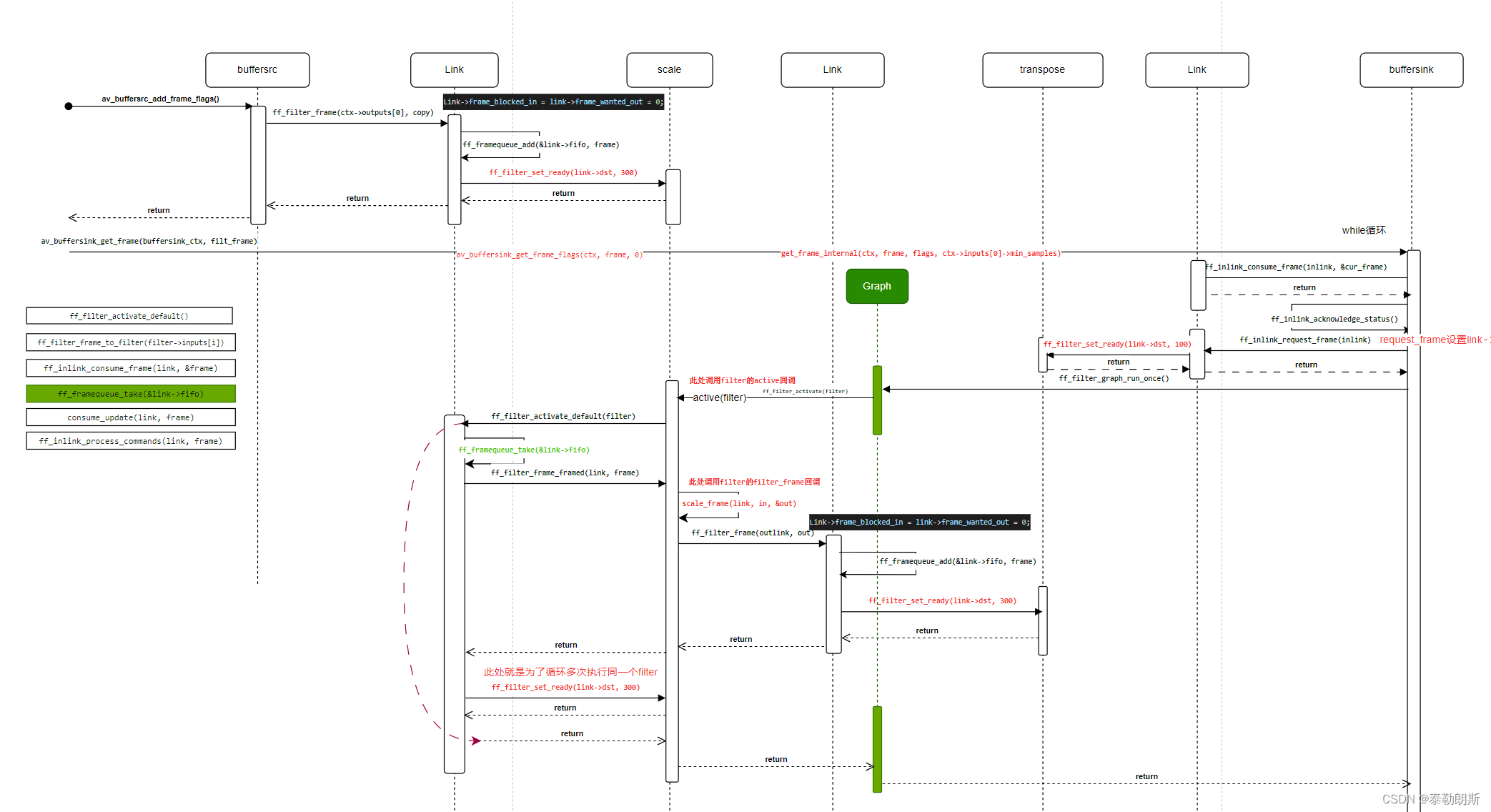
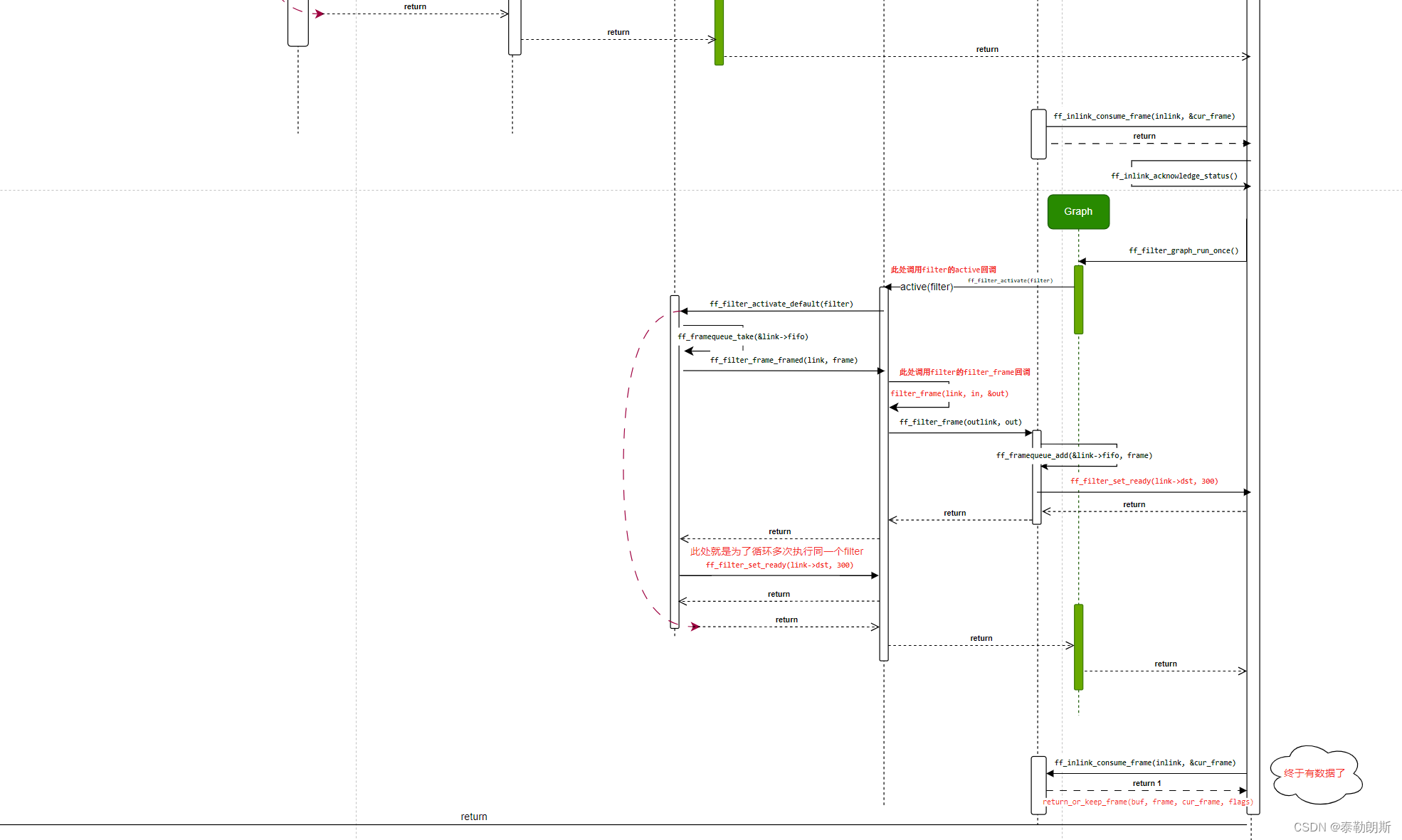
结构体
/** An instance of a filter */
struct AVFilterContext {
const AVClass *av_class; ///< needed for av_log() and filters common options
const AVFilter *filter; ///< the AVFilter of which this is an instance
char *name; ///< name of this filter instance
AVFilterPad *input_pads; ///< array of input pads
AVFilterLink **inputs; ///< array of pointers to input links
unsigned nb_inputs; ///< number of input pads
AVFilterPad *output_pads; ///< array of output pads
AVFilterLink **outputs; ///< array of pointers to output links
unsigned nb_outputs; ///< number of output pads
void *priv; ///< private data for use by the filter
struct AVFilterGraph *graph; ///< filtergraph this filter belongs to
/**
* Type of multithreading being allowed/used. A combination of
* AVFILTER_THREAD_* flags.
*
* May be set by the caller before initializing the filter to forbid some
* or all kinds of multithreading for this filter. The default is allowing
* everything.
*
* When the filter is initialized, this field is combined using bit AND with
* AVFilterGraph.thread_type to get the final mask used for determining
* allowed threading types. I.e. a threading type needs to be set in both
* to be allowed.
*
* After the filter is initialized, libavfilter sets this field to the
* threading type that is actually used (0 for no multithreading).
*/
int thread_type;
/**
* An opaque struct for libavfilter internal use.
*/
AVFilterInternal *internal;
struct AVFilterCommand *command_queue;
char *enable_str; ///< enable expression string
void *enable; ///< parsed expression (AVExpr*)
double *var_values; ///< variable values for the enable expression
int is_disabled; ///< the enabled state from the last expression evaluation
/**
* For filters which will create hardware frames, sets the device the
* filter should create them in. All other filters will ignore this field:
* in particular, a filter which consumes or processes hardware frames will
* instead use the hw_frames_ctx field in AVFilterLink to carry the
* hardware context information.
*/
AVBufferRef *hw_device_ctx;
/**
* Max number of threads allowed in this filter instance.
* If <= 0, its value is ignored.
* Overrides global number of threads set per filter graph.
*/
int nb_threads;
/**
* Ready status of the filter.
* A non-0 value means that the filter needs activating;
* a higher value suggests a more urgent activation.
*/
unsigned ready;
/**
* Sets the number of extra hardware frames which the filter will
* allocate on its output links for use in following filters or by
* the caller.
*
* Some hardware filters require all frames that they will use for
* output to be defined in advance before filtering starts. For such
* filters, any hardware frame pools used for output must therefore be
* of fixed size. The extra frames set here are on top of any number
* that the filter needs internally in order to operate normally.
*
* This field must be set before the graph containing this filter is
* configured.
*/
int extra_hw_frames;
};
下面结构体种含有若干回调,可以实现,不过实现的时候要注意一些特殊返回,用指定的函数去结束函数。
/**
* Filter definition. This defines the pads a filter contains, and all the
* callback functions used to interact with the filter.
*/
typedef struct AVFilter {
/**
* Filter name. Must be non-NULL and unique among filters.
*/
const char *name;
/**
* A description of the filter. May be NULL.
*
* You should use the NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL() macro to define it.
*/
const char *description;
/**
* List of static inputs.
*
* NULL if there are no (static) inputs. Instances of filters with
* AVFILTER_FLAG_DYNAMIC_INPUTS set may have more inputs than present in
* this list.
*/
const AVFilterPad *inputs;
/**
* List of static outputs.
*
* NULL if there are no (static) outputs. Instances of filters with
* AVFILTER_FLAG_DYNAMIC_OUTPUTS set may have more outputs than present in
* this list.
*/
const AVFilterPad *outputs;
/**
* A class for the private data, used to declare filter private AVOptions.
* This field is NULL for filters that do not declare any options.
*
* If this field is non-NULL, the first member of the filter private data
* must be a pointer to AVClass, which will be set by libavfilter generic
* code to this class.
*/
const AVClass *priv_class;
/**
* A combination of AVFILTER_FLAG_*
*/
int flags;
/*****************************************************************
* All fields below this line are not part of the public API. They
* may not be used outside of libavfilter and can be changed and
* removed at will.
* New public fields should be added right above.
*****************************************************************
*/
/**
* The number of entries in the list of inputs.
*/
uint8_t nb_inputs;
/**
* The number of entries in the list of outputs.
*/
uint8_t nb_outputs;
/**
* This field determines the state of the formats union.
* It is an enum FilterFormatsState value.
*/
uint8_t formats_state;
/**
* Filter pre-initialization function
*
* This callback will be called immediately after the filter context is
* allocated, to allow allocating and initing sub-objects.
*
* If this callback is not NULL, the uninit callback will be called on
* allocation failure.
*
* @return 0 on success,
* AVERROR code on failure (but the code will be
* dropped and treated as ENOMEM by the calling code)
*/
int (*preinit)(AVFilterContext *ctx);
/**
* Filter initialization function.
*
* This callback will be called only once during the filter lifetime, after
* all the options have been set, but before links between filters are
* established and format negotiation is done.
*
* Basic filter initialization should be done here. Filters with dynamic
* inputs and/or outputs should create those inputs/outputs here based on
* provided options. No more changes to this filter's inputs/outputs can be
* done after this callback.
*
* This callback must not assume that the filter links exist or frame
* parameters are known.
*
* @ref AVFilter.uninit "uninit" is guaranteed to be called even if
* initialization fails, so this callback does not have to clean up on
* failure.
*
* @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on failure
*/
int (*init)(AVFilterContext *ctx);
/**
* Should be set instead of @ref AVFilter.init "init" by the filters that
* want to pass a dictionary of AVOptions to nested contexts that are
* allocated during init.
*
* On return, the options dict should be freed and replaced with one that
* contains all the options which could not be processed by this filter (or
* with NULL if all the options were processed).
*
* Otherwise the semantics is the same as for @ref AVFilter.init "init".
*/
int (*init_dict)(AVFilterContext *ctx, AVDictionary **options);
/**
* Filter uninitialization function.
*
* Called only once right before the filter is freed. Should deallocate any
* memory held by the filter, release any buffer references, etc. It does
* not need to deallocate the AVFilterContext.priv memory itself.
*
* This callback may be called even if @ref AVFilter.init "init" was not
* called or failed, so it must be prepared to handle such a situation.
*/
void (*uninit)(AVFilterContext *ctx);
/**
* The state of the following union is determined by formats_state.
* See the documentation of enum FilterFormatsState in internal.h.
*/
union {
/**
* Query formats supported by the filter on its inputs and outputs.
*
* This callback is called after the filter is initialized (so the inputs
* and outputs are fixed), shortly before the format negotiation. This
* callback may be called more than once.
*
* This callback must set AVFilterLink.outcfg.formats on every input link
* and AVFilterLink.incfg.formats on every output link to a list of
* pixel/sample formats that the filter supports on that link. For audio
* links, this filter must also set @ref AVFilterLink.incfg.samplerates
* "in_samplerates" / @ref AVFilterLink.outcfg.samplerates "out_samplerates"
* and @ref AVFilterLink.incfg.channel_layouts "in_channel_layouts" /
* @ref AVFilterLink.outcfg.channel_layouts "out_channel_layouts" analogously.
*
* This callback must never be NULL if the union is in this state.
*
* @return zero on success, a negative value corresponding to an
* AVERROR code otherwise
*/
int (*query_func)(AVFilterContext *);
/**
* A pointer to an array of admissible pixel formats delimited
* by AV_PIX_FMT_NONE. The generic code will use this list
* to indicate that this filter supports each of these pixel formats,
* provided that all inputs and outputs use the same pixel format.
*
* This list must never be NULL if the union is in this state.
* The type of all inputs and outputs of filters using this must
* be AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.
*/
const enum AVPixelFormat *pixels_list;
/**
* Analogous to pixels, but delimited by AV_SAMPLE_FMT_NONE
* and restricted to filters that only have AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO
* inputs and outputs.
*
* In addition to that the generic code will mark all inputs
* and all outputs as supporting all sample rates and every
* channel count and channel layout, as long as all inputs
* and outputs use the same sample rate and channel count/layout.
*/
const enum AVSampleFormat *samples_list;
/**
* Equivalent to { pix_fmt, AV_PIX_FMT_NONE } as pixels_list.
*/
enum AVPixelFormat pix_fmt;
/**
* Equivalent to { sample_fmt, AV_SAMPLE_FMT_NONE } as samples_list.
*/
enum AVSampleFormat sample_fmt;
} formats;
int priv_size; ///< size of private data to allocate for the filter
int flags_internal; ///< Additional flags for avfilter internal use only.
/**
* Make the filter instance process a command.
*
* @param cmd the command to process, for handling simplicity all commands must be alphanumeric only
* @param arg the argument for the command
* @param res a buffer with size res_size where the filter(s) can return a response. This must not change when the command is not supported.
* @param flags if AVFILTER_CMD_FLAG_FAST is set and the command would be
* time consuming then a filter should treat it like an unsupported command
*
* @returns >=0 on success otherwise an error code.
* AVERROR(ENOSYS) on unsupported commands
*/
int (*process_command)(AVFilterContext *, const char *cmd, const char *arg, char *res, int res_len, int flags);
/**
* Filter activation function.
*
* Called when any processing is needed from the filter, instead of any
* filter_frame and request_frame on pads.
*
* The function must examine inlinks and outlinks and perform a single
* step of processing. If there is nothing to do, the function must do
* nothing and not return an error. If more steps are or may be
* possible, it must use ff_filter_set_ready() to schedule another
* activation.
*/
int (*activate)(AVFilterContext *ctx);
} AVFilter;
函数
/**
* Iterate over all registered filters.
*
* @param opaque a pointer where libavfilter will store the iteration state. Must
* point to NULL to start the iteration.
*
* @return the next registered filter or NULL when the iteration is
* finished
*/
const AVFilter *av_filter_iterate(void **opaque);
/**
* Get a filter definition matching the given name.
*
* @param name the filter name to find
* @return the filter definition, if any matching one is registered.
* NULL if none found.
*/
const AVFilter *avfilter_get_by_name(const char *name);
/**
* Initialize a filter with the supplied parameters.
*
* @param ctx uninitialized filter context to initialize
* @param args Options to initialize the filter with. This must be a
* ':'-separated list of options in the 'key=value' form.
* May be NULL if the options have been set directly using the
* AVOptions API or there are no options that need to be set.
* @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on failure
*/
int avfilter_init_str(AVFilterContext *ctx, const char *args);
/**
* Initialize a filter with the supplied dictionary of options.
*
* @param ctx uninitialized filter context to initialize
* @param options An AVDictionary filled with options for this filter. On
* return this parameter will be destroyed and replaced with
* a dict containing options that were not found. This dictionary
* must be freed by the caller.
* May be NULL, then this function is equivalent to
* avfilter_init_str() with the second parameter set to NULL.
* @return 0 on success, a negative AVERROR on failure
*
* @note This function and avfilter_init_str() do essentially the same thing,
* the difference is in manner in which the options are passed. It is up to the
* calling code to choose whichever is more preferable. The two functions also
* behave differently when some of the provided options are not declared as
* supported by the filter. In such a case, avfilter_init_str() will fail, but
* this function will leave those extra options in the options AVDictionary and
* continue as usual.
*/
int avfilter_init_dict(AVFilterContext *ctx, AVDictionary **options);
/**
* Free a filter context. This will also remove the filter from its
* filtergraph's list of filters.
*
* @param filter the filter to free
*/
void avfilter_free(AVFilterContext *filter);
/**
* Insert a filter in the middle of an existing link.
*
* @param link the link into which the filter should be inserted
* @param filt the filter to be inserted
* @param filt_srcpad_idx the input pad on the filter to connect
* @param filt_dstpad_idx the output pad on the filter to connect
* @return zero on success
*/
int avfilter_insert_filter(AVFilterLink *link, AVFilterContext *filt,
unsigned filt_srcpad_idx, unsigned filt_dstpad_idx);
案例
最后面还是贴个案例吧,想要说明一点的是,avfilter的最开始和结尾的filter一定要是
abuffer :it will be used for feeding the data into the graph
abuffersink:it will be used to get the filtered data out of the graph
下面这个案例非常具有代表性,真正作用的就一个filter“volume”。都是采用手动链接,链接后通过函数avfilter_graph_config再重新去协商,这个阶段会往pipeline张自动增加一些filter,最常用的就是csc,颜色空间转换,如果上下两个filter的pix_fmt不一致,那么就会自动增加一个filter。
其实就是这些函数族
int avfilter_graph_config(AVFilterGraph *graphctx, void *log_ctx)
{
int ret;
if ((ret = graph_check_validity(graphctx, log_ctx)))
return ret;
if ((ret = graph_config_formats(graphctx, log_ctx)))
return ret;
if ((ret = graph_config_links(graphctx, log_ctx)))
return ret;
if ((ret = graph_check_links(graphctx, log_ctx)))
return ret;
if ((ret = graph_config_pointers(graphctx, log_ctx)))
return ret;
return 0;
}
下面是代码全貌:
/*
* copyright (c) 2013 Andrew Kelley
*
* This file is part of FFmpeg.
*
* FFmpeg is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
*
* FFmpeg is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License along with FFmpeg; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
*/
/**
* @file
* libavfilter API usage example.
*
* @example filter_audio.c
* This example will generate a sine wave audio,
* pass it through a simple filter chain, and then compute the MD5 checksum of
* the output data.
*
* The filter chain it uses is:
* (input) -> abuffer -> volume -> aformat -> abuffersink -> (output)
*
* abuffer: This provides the endpoint where you can feed the decoded samples.
* volume: In this example we hardcode it to 0.90.
* aformat: This converts the samples to the samplefreq, channel layout,
* and sample format required by the audio device.
* abuffersink: This provides the endpoint where you can read the samples after
* they have passed through the filter chain.
*/
#include <inttypes.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "libavutil/channel_layout.h"
#include "libavutil/md5.h"
#include "libavutil/mem.h"
#include "libavutil/opt.h"
#include "libavutil/samplefmt.h"
#include "libavfilter/avfilter.h"
#include "libavfilter/buffersink.h"
#include "libavfilter/buffersrc.h"
#define INPUT_SAMPLERATE 48000
#define INPUT_FORMAT AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP
#define INPUT_CHANNEL_LAYOUT AV_CH_LAYOUT_5POINT0
#define VOLUME_VAL 0.90
static int init_filter_graph(AVFilterGraph **graph, AVFilterContext **src,
AVFilterContext **sink)
{
AVFilterGraph *filter_graph;
AVFilterContext *abuffer_ctx;
const AVFilter *abuffer;
AVFilterContext *volume_ctx;
const AVFilter *volume;
AVFilterContext *aformat_ctx;
const AVFilter *aformat;
AVFilterContext *abuffersink_ctx;
const AVFilter *abuffersink;
AVDictionary *options_dict = NULL;
uint8_t options_str[1024];
uint8_t ch_layout[64];
int err;
/* Create a new filtergraph, which will contain all the filters. */
filter_graph = avfilter_graph_alloc();
if (!filter_graph) {
fprintf(stderr, "Unable to create filter graph.\n");
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
/* Create the abuffer filter;
* it will be used for feeding the data into the graph. */
abuffer = avfilter_get_by_name("abuffer");
if (!abuffer) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not find the abuffer filter.\n");
return AVERROR_FILTER_NOT_FOUND;
}
abuffer_ctx = avfilter_graph_alloc_filter(filter_graph, abuffer, "src");
if (!abuffer_ctx) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate the abuffer instance.\n");
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
/* Set the filter options through the AVOptions API. */
av_get_channel_layout_string(ch_layout, sizeof(ch_layout), 0, INPUT_CHANNEL_LAYOUT);
av_opt_set (abuffer_ctx, "channel_layout", ch_layout, AV_OPT_SEARCH_CHILDREN);
av_opt_set (abuffer_ctx, "sample_fmt", av_get_sample_fmt_name(INPUT_FORMAT), AV_OPT_SEARCH_CHILDREN);
av_opt_set_q (abuffer_ctx, "time_base", (AVRational){ 1, INPUT_SAMPLERATE }, AV_OPT_SEARCH_CHILDREN);
av_opt_set_int(abuffer_ctx, "sample_rate", INPUT_SAMPLERATE, AV_OPT_SEARCH_CHILDREN);
/* Now initialize the filter; we pass NULL options, since we have already
* set all the options above. */
err = avfilter_init_str(abuffer_ctx, NULL);
if (err < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not initialize the abuffer filter.\n");
return err;
}
/* Create volume filter. */
volume = avfilter_get_by_name("volume");
if (!volume) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not find the volume filter.\n");
return AVERROR_FILTER_NOT_FOUND;
}
volume_ctx = avfilter_graph_alloc_filter(filter_graph, volume, "volume");
if (!volume_ctx) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate the volume instance.\n");
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
/* A different way of passing the options is as key/value pairs in a
* dictionary. */
av_dict_set(&options_dict, "volume", AV_STRINGIFY(VOLUME_VAL), 0);
err = avfilter_init_dict(volume_ctx, &options_dict);
av_dict_free(&options_dict);
if (err < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not initialize the volume filter.\n");
return err;
}
/* Create the aformat filter;
* it ensures that the output is of the format we want. */
aformat = avfilter_get_by_name("aformat");
if (!aformat) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not find the aformat filter.\n");
return AVERROR_FILTER_NOT_FOUND;
}
aformat_ctx = avfilter_graph_alloc_filter(filter_graph, aformat, "aformat");
if (!aformat_ctx) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate the aformat instance.\n");
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
/* A third way of passing the options is in a string of the form
* key1=value1:key2=value2.... */
snprintf(options_str, sizeof(options_str),
"sample_fmts=%s:sample_rates=%d:channel_layouts=0x%"PRIx64,
av_get_sample_fmt_name(AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16), 44100,
(uint64_t)AV_CH_LAYOUT_STEREO);
err = avfilter_init_str(aformat_ctx, options_str);
if (err < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not initialize the aformat filter.\n");
return err;
}
/* Finally create the abuffersink filter;
* it will be used to get the filtered data out of the graph. */
abuffersink = avfilter_get_by_name("abuffersink");
if (!abuffersink) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not find the abuffersink filter.\n");
return AVERROR_FILTER_NOT_FOUND;
}
abuffersink_ctx = avfilter_graph_alloc_filter(filter_graph, abuffersink, "sink");
if (!abuffersink_ctx) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate the abuffersink instance.\n");
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
/* This filter takes no options. */
err = avfilter_init_str(abuffersink_ctx, NULL);
if (err < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not initialize the abuffersink instance.\n");
return err;
}
/* Connect the filters;
* in this simple case the filters just form a linear chain. */
err = avfilter_link(abuffer_ctx, 0, volume_ctx, 0);
if (err >= 0)
err = avfilter_link(volume_ctx, 0, aformat_ctx, 0);
if (err >= 0)
err = avfilter_link(aformat_ctx, 0, abuffersink_ctx, 0);
if (err < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error connecting filters\n");
return err;
}
/* Configure the graph. */
err = avfilter_graph_config(filter_graph, NULL);
if (err < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Error configuring the filter graph\n");
return err;
}
*graph = filter_graph;
*src = abuffer_ctx;
*sink = abuffersink_ctx;
return 0;
}
/* Do something useful with the filtered data: this simple
* example just prints the MD5 checksum of each plane to stdout. */
static int process_output(struct AVMD5 *md5, AVFrame *frame)
{
int planar = av_sample_fmt_is_planar(frame->format);
int channels = av_get_channel_layout_nb_channels(frame->channel_layout);
int planes = planar ? channels : 1;
int bps = av_get_bytes_per_sample(frame->format);
int plane_size = bps * frame->nb_samples * (planar ? 1 : channels);
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < planes; i++) {
uint8_t checksum[16];
av_md5_init(md5);
av_md5_sum(checksum, frame->extended_data[i], plane_size);
fprintf(stdout, "plane %d: 0x", i);
for (j = 0; j < sizeof(checksum); j++)
fprintf(stdout, "%02X", checksum[j]);
fprintf(stdout, "\n");
}
fprintf(stdout, "\n");
return 0;
}
/* Construct a frame of audio data to be filtered;
* this simple example just synthesizes a sine wave. */
static int get_input(AVFrame *frame, int frame_num)
{
int err, i, j;
#define FRAME_SIZE 1024
/* Set up the frame properties and allocate the buffer for the data. */
frame->sample_rate = INPUT_SAMPLERATE;
frame->format = INPUT_FORMAT;
frame->channel_layout = INPUT_CHANNEL_LAYOUT;
frame->nb_samples = FRAME_SIZE;
frame->pts = frame_num * FRAME_SIZE;
err = av_frame_get_buffer(frame, 0);
if (err < 0)
return err;
/* Fill the data for each channel. */
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
float *data = (float*)frame->extended_data[i];
for (j = 0; j < frame->nb_samples; j++)
data[j] = sin(2 * M_PI * (frame_num + j) * (i + 1) / FRAME_SIZE);
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct AVMD5 *md5;
AVFilterGraph *graph;
AVFilterContext *src, *sink;
AVFrame *frame;
uint8_t errstr[1024];
float duration;
int err, nb_frames, i;
if (argc < 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <duration>\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
duration = atof(argv[1]);
nb_frames = duration * INPUT_SAMPLERATE / FRAME_SIZE;
if (nb_frames <= 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Invalid duration: %s\n", argv[1]);
return 1;
}
/* Allocate the frame we will be using to store the data. */
frame = av_frame_alloc();
if (!frame) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error allocating the frame\n");
return 1;
}
md5 = av_md5_alloc();
if (!md5) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error allocating the MD5 context\n");
return 1;
}
/* Set up the filtergraph. */
err = init_filter_graph(&graph, &src, &sink);
if (err < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Unable to init filter graph:");
goto fail;
}
/* the main filtering loop */
for (i = 0; i < nb_frames; i++) {
/* get an input frame to be filtered */
err = get_input(frame, i);
if (err < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error generating input frame:");
goto fail;
}
/* Send the frame to the input of the filtergraph. */
err = av_buffersrc_add_frame(src, frame);
if (err < 0) {
av_frame_unref(frame);
fprintf(stderr, "Error submitting the frame to the filtergraph:");
goto fail;
}
/* Get all the filtered output that is available. */
while ((err = av_buffersink_get_frame(sink, frame)) >= 0) {
/* now do something with our filtered frame */
err = process_output(md5, frame);
if (err < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error processing the filtered frame:");
goto fail;
}
av_frame_unref(frame);
}
if (err == AVERROR(EAGAIN)) {
/* Need to feed more frames in. */
continue;
} else if (err == AVERROR_EOF) {
/* Nothing more to do, finish. */
break;
} else if (err < 0) {
/* An error occurred. */
fprintf(stderr, "Error filtering the data:");
goto fail;
}
}
avfilter_graph_free(&graph);
av_frame_free(&frame);
av_freep(&md5);
return 0;
fail:
av_strerror(err, errstr, sizeof(errstr));
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", errstr);
return 1;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43360707/article/details/134943514
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!