Large Language Models Paper 分享
论文1:?ChatGPT's One-year Anniversary: Are Open-Source Large Language Models Catching up?
简介
2022年11月,OpenAI发布了ChatGPT,这一事件在AI社区甚至全世界引起了轰动。首次,一个基于应用的AI聊天机器人能够提供有帮助、安全和有用的答案,遵循人类指令,甚至承认并纠正之前的错误。作为第一个这样的应用,ChatGPT在其推出仅两个月内,用户数量就达到了1亿,远远快于其他流行应用如TikTok或YouTube。因此,它也吸引了巨额的商业投资,因为它有望降低劳动成本,自动化工作流程,甚至为客户带来新的体验。
但ChatGPT的闭源特性可能引发诸多问题。首先,由于不了解内部细节,比如预训练和微调过程,很难正确评估其潜在风险,尤其是考虑到大模型可能生成有害、不道德和虚假的内容。其次,有报道称ChatGPT的性能随时间变化,妨碍了可重复的结果。第三,ChatGPT经历了多次故障,仅在2023年11月就发生了两次重大故障,期间无法访问ChatGPT网站及其API。最后,采用ChatGPT的企业可能会关注API调用的高成本、服务中断、数据所有权和隐私问题,以及其他不可预测的事件,比如最近有关CEO Sam Altman被解雇并最终回归的董事会闹剧。
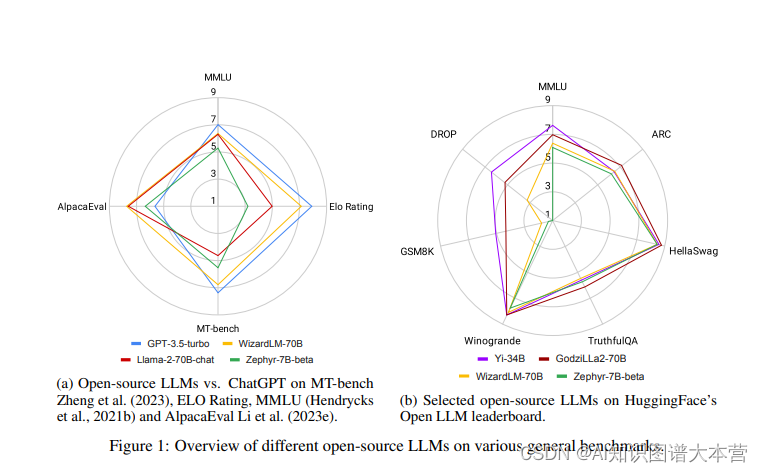
此时,开源大模型应运而生,社区一直在积极推动将高性能的大模型保持开源。然而,截至2023年末,大家还普遍认为类似Llama-2或Falcon这样的开源大模型在性能上落后于它们的闭源模型,如OpenAI的GPT3.5(ChatGPT)和GPT-4,Anthropic的Claude2或Google的Bard3,其中GPT-4通常被认为是最出色的。然而,令人鼓舞的是差距正在变得越来越小,开源大模型正在迅速赶上。
更有趣的 AI Agent
-
Generative Agents: Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.03442
-
RoleLLM: Benchmarking, Eliciting, and Enhancing Role-Playing Abilities of Large Language Models https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.00746
-
Role play with large language models https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06647-8
-
Exploring Large Language Models for Communication Games: An Empirical Study on Werewolf https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.04658
-
MemGPT: Towards LLMs as Operating Systems https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.08560
-
Augmenting Language Models with Long-Term Memory https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.07174
-
Do LLMs Possess a Personality? Making the MBTI Test an Amazing Evaluation for Large Language Models https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.16180.pdf
更有用的 AI Agent
-
The Rise and Potential of Large Language Model Based Agents: A Survey https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.07864
-
MetaGPT: Meta Programming for A Multi-Agent Collaborative Framework https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.00352
-
Communicative Agents for Software Development https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.07924.pdf
-
Large Language Models Can Self-Improve https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.11610
-
Evaluating Human-Language Model Interaction https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.09746
-
Large Language Models can Learn Rules https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.07064
-
AgentBench: Evaluating LLMs as Agents https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.03688
-
WebArena: A Realistic Web Environment for Building Autonomous Agents https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.13854
-
TableGPT: Towards Unifying Tables, Nature Language and Commands into One GPT https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.08674
任务规划与分解
-
Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.11903
-
Tree of Thoughts: Deliberate Problem Solving with Large Language Models https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.10601
-
Implicit Chain of Thought Reasoning via Knowledge Distillation https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.01460
-
ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.03629
-
ART: Automatic multi-step reasoning and tool-use for large language models https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.09014
-
Branch-Solve-Merge Improves Large Language Model Evaluation and Generation https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.15123
-
WizardLM: Empowering Large Language Models to Follow Complex Instructionshttps://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.12244.pdf
幻觉
-
Siren’s Song in the AI Ocean: A Survey on Hallucination in Large Language Modelshttps://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.01219.pdf
-
Check Your Facts and Try Again: Improving Large Language Models with External Knowledge and Automated Feedback https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.12813
-
SelfCheckGPT: Zero-Resource Black-Box Hallucination Detection for Generative Large Language Models https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.08896
-
WebBrain: Learning to Generate Factually Correct Articles for Queries by Grounding on Large Web Corpus https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.04358
多模态
-
Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision (CLIP) https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020
-
An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale (ViT): https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929
-
MiniGPT-v2: large language model as a unified interface for vision-language multi-task learninghttps://arxiv.org/abs/2310.09478
-
MiniGPT-4: Enhancing Vision-Language Understanding with Advanced Large Language Models https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.10592
-
NExT-GPT: Any-to-Any Multimodal LLM https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.05519.pdf
-
Visual Instruction Tuning (LLaVA) https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.08485.pdf
-
Improved Baselines with Visual Instruction Tuning (LLaVA-1.5) https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.03744
-
Sequential Modeling Enables Scalable Learning for Large Vision Models (LVM) https://arxiv.org/pdf/2312.00785.pdf
-
CoDi-2: In-Context, Interleaved, and Interactive Any-to-Any Generation https://arxiv.org/pdf/2311.18775.pdf
-
Neural Discrete Representation Learning (VQ-VAE) https://browse.arxiv.org/pdf/1711.00937.pdf
-
Taming Transformers for High-Resolution Image Synthesis (VQ-GAN) https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.09841
-
Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030
-
BLIP-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models https://browse.arxiv.org/pdf/2301.12597.pdf
-
InstructBLIP: Towards General-purpose Vision-Language Models with Instruction Tuning https://browse.arxiv.org/pdf/2305.06500.pdf
-
ImageBind: One Embedding Space To Bind Them All https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.05665
-
Meta-Transformer: A Unified Framework for Multimodal Learning https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.10802
图片/视频生成
-
High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models https://arxiv.org/pdf/2112.10752.pdf
-
Structure and Content-Guided Video Synthesis with Diffusion Models (RunwayML Gen1) https://browse.arxiv.org/pdf/2302.03011.pdf
-
Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents (DaLLE-2) https://arxiv.org/pdf/2204.06125.pdf
-
AnimateDiff: Animate Your Personalized Text-to-Image Diffusion Models without Specific Tuning https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.04725
-
Adding Conditional Control to Text-to-Image Diffusion Models (ControlNet) https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543
-
SDXL: Improving Latent Diffusion Models for High-Resolution Image Synthesishttps://arxiv.org/abs/2307.01952
-
Zero-1-to-3: Zero-shot One Image to 3D Object https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.11328
-
Scaling Vision Transformers to 22 Billion Parameters https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05442
-
Glow: Generative Flow with Invertible 1×1 Convolutions https://browse.arxiv.org/pdf/1807.03039.pdf
-
Language Model Beats Diffusion – Tokenizer is Key to Visual Generation https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.05737.pdf
-
InstaFlow: One Step is Enough for High-Quality Diffusion-Based Text-to-Image Generationhttps://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.06380.pdf
-
Perceptual Losses for Real-Time Style Transfer and Super-Resolution https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.08155.pdf
-
CogView: Mastering Text-to-Image Generation via Transformers https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.13290
-
Diffusion Models for Video Prediction and Infilling https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.07696
语音合成
-
Conditional Variational Autoencoder with Adversarial Learning for End-to-End Text-to-Speech (VITS)https://browse.arxiv.org/pdf/2106.06103.pdf
-
Neural Codec Language Models are Zero-Shot Text to Speech Synthesizers (VALL-E)https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.02111
-
Speak Foreign Languages with Your Own Voice: Cross-Lingual Neural Codec Language Modeling (VALL-E X) https://arxiv.org/pdf/2303.03926.pdf
-
MusicLM: Generating Music From Text https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.11325
大模型基础
-
Attention Is All You Need https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762
-
Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.3215
-
Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.0473
-
BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805
-
Scaling Laws for Neural Language Models https://arxiv.org/pdf/2001.08361.pdf
-
Emergent Abilities of Large Language Models https://openreview.net/pdf?id=yzkSU5zdwD
-
Training Compute-Optimal Large Language Models (ChinChilla scaling law) https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.15556
-
Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models https://arxiv.org/pdf/2210.11416.pdf
-
Direct Preference Optimization:
-
Your Language Model is Secretly a Reward Model https://arxiv.org/pdf/2305.18290.pdf
-
Progress measures for grokking via mechanistic interpretability https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.05217
-
Language Models Represent Space and Time https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.02207
-
GLaM: Efficient Scaling of Language Models with Mixture-of-Experts https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.06905
-
Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980
-
Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space (Word2Vec) https://arxiv.org/abs/1301.3781
-
Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality https://arxiv.org/abs/1310.4546
GPT
-
Language Models are Few-Shot Learners (GPT-3) https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.14165
-
Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners (GPT-2) https://d4mucfpksywv.cloudfront.net/better-language-models/language_models_are_unsupervised_multitask_learners.pdf
-
Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training (GPT-1) https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/openai-assets/research-covers/language-unsupervised/language_understanding_paper.pdf
-
Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback (InstructGPT)https://arxiv.org/pdf/2203.02155.pdf
-
Evaluating Large Language Models Trained on Code https://arxiv.org/pdf/2107.03374.pdf
-
Harnessing the Power of LLMs in Practice: A Survey on ChatGPT and Beyond https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.13712
-
Instruction Tuning with GPT-4 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.03277.pdf
-
The Dawn of LMMs: Preliminary Explorations with GPT-4V(ision) https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.17421
-
Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4 https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.12712
-
Weak-to-Strong Generalization: Eliciting Strong Capabilities With Weak Supervision https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.09390
开源大模型
-
LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.13971
-
Llama 2: Open Foundation and Fine-Tuned Chat Models https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.09288.pdf
-
Vicuna: An Open-Source Chatbot Impressing GPT-4 with 90%* ChatGPT Quality https://lmsys.org/blog/2023-03-30-vicuna/
-
LMSYS-Chat-1M: A Large-Scale Real-World LLM Conversation Dataset https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.11998
-
Judging LLM-as-a-Judge with MT-Bench and Chatbot Arena https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.05685
-
How Long Can Open-Source LLMs Truly Promise on Context Length? https://lmsys.org/blog/2023-06-29-longchat/
-
Mixtral of experts https://mistral.ai/news/mixtral-of-experts/
-
OpenChat: Advancing Open-source Language Models with Mixed-Quality Data https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.11235
-
RWKV: Reinventing RNNs for the Transformer Era https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.13048
-
Mamba: Linear-Time Sequence Modeling with Selective State Spaces https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/2312/2312.00752.pdf
-
Retentive Network: A Successor to Transformer for Large Language Models https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.08621
-
Baichuan 2: Open Large-scale Language Models https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.10305
-
GLM-130B: An Open Bilingual Pre-trained Model https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.02414
-
Qwen Technical Report https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.16609
-
Skywork: A More Open Bilingual Foundation Model https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.19341
微调
-
Learning to summarize from human feedback https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.01325
-
Self-Instruct: Aligning Language Model with Self Generated Instruction https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.10560
-
Scaling Down to Scale Up: A Guide to Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.15647
-
LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.09685
-
Vera: Vector-Based Random Matrix Adapation https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.11454.pdf
-
QLoRA: Efficient Finetuning of Quantized LLMs https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.14314
-
Chain of Hindsight Aligns Language Models with Feedback https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.02676
-
Beyond Human Data: Scaling Self-Training for Problem-Solving with Language Models https://arxiv.org/pdf/2312.06585.pdf
性能优化
-
Efficient Memory Management for Large Language Model Serving with PagedAttention (vLLM) https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.06180
-
FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14135
-
S-LoRA: Serving Thousands of Concurrent LoRA Adapters https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.03285
-
GPipe: Efficient Training of Giant Neural Networks using Pipeline Parallelism https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2019/file/093f65e080a295f8076b1c5722a46aa2-Paper.pdf
-
Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism https://arxiv.org/pdf/1909.08053.pdf
-
ZeRO: Memory Optimizations Toward Training Trillion Parameter Models https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.02054.pdf
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!