树——练习题
2023-12-23 20:44:46
1. ?二叉树的前序遍历
代码实现:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ #define MAX_NODE 100 // 递归 void pre_order1(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* returnSize) { if (root == NULL) { // 终止条件 return ; } res[(*returnSize)++] = root->val; pre_order1(root->left, res, returnSize); pre_order1(root->right, res, returnSize); } // 迭代(非递归) 深度优先搜索---借用栈 struct TreeNode* track[MAX_NODE]; int top = -1; void pre_order2(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* returnSize) { if (root == NULL) { return ; } track[++top] = root; while (top != -1) { // 栈不为空则执行while循环 struct TreeNode* r = track[top]; // 记录栈顶 res[(*returnSize)++] = r->val; top--; if (r->right) { // 右子树先进栈 track[++top] = r->right; } if (r->left) { track[++top] = r->left; } } } int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) { int* res = malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX_NODE); *returnSize = 0; pre_order1(root, res, returnSize); pre_order2(root, res, returnSize); return res; }
2. 二叉树的中序遍历
代码实现:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ #define MAX_NODE 100 // 递归 void mid_order1(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* returnSize) { if (root == NULL) { // 终止条件 return ; } mid_order1(root->left, res, returnSize); res[(*returnSize)++] = root->val; mid_order1(root->right, res, returnSize); } // 迭代(非递归) 深度优先搜索---借用栈 struct TreeNode* stack[MAX_NODE]; int top = -1; void mid_order2(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* returnSize) { if (root == NULL) { return ; } struct TreeNode* p = root; struct TreeNode* q = NULL; while (p || top != -1) { if (p) { stack[++top] = p; p = p->left; } else { q = stack[top]; res[(*returnSize)++] = q->val; top--; p = q->right; } } } int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) { int* res = malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX_NODE); *returnSize = 0; mid_order1(root, res, returnSize); mid_order2(root, res, returnSize); return res; }
3.?二叉树的后序遍历
代码实现:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ #define MAX_NODE 100 // 递归 void post_order1(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* returnSize) { if (root == NULL) { // 终止条件 return ; } post_order1(root->left, res, returnSize); post_order1(root->right, res, returnSize); res[(*returnSize)++] = root->val; } // 迭代(非递归) 深度优先搜索---借用栈 /* 第一种方法: 先序遍历是 中左右 --->调整代码左右循序--->中右左--->反转result数组--->左右中 后序遍历是 左右中 */ /* 第二种方法: 1、沿着根的左孩子,依次入栈,直到左孩子为空; 2、读栈顶元素进行判定,若右孩子不空且未被访问,将右孩子执行第一步; 3、栈顶元素出栈。 */ struct TreeNode* stack[MAX_NODE]; int top = -1; // 栈顶 void post_order2(struct TreeNode* root, int* res, int* returnSize) { struct TreeNode *p = root, *r = NULL; //r标记最近访问过的结点 while (p || top != -1) { if (p) { stack[++top] = p; p = p->left; } else { p = stack[top]; // 获取栈顶元素赋值给p // ?case one? if (p->right && p->right != r) { //若右孩子存在且未被访问 p = p->right; // 就让右孩子 stack[++top] = p; // 入栈 p = p->left; // 让右孩子向左 // 上面三句意思就是让右孩子的左孩子一直入栈,一直向左走 } else { // ?case two? res[(*returnSize)++] = stack[top--]->val; // 右孩子为空或未被访问过,就出栈 r = p; //r标记最近访问结点 p = NULL; //r置空 // 置空原因:因为这个结点已经出栈了 } } } } int* postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) { int* res = malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX_NODE); *returnSize = 0; post_order1(root, res, returnSize); post_order2(root, res, returnSize); return res; }
4. 二叉树的层序遍历
代码实现:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize. * The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array. * Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ // returnColumnSizes:用于存储每个数组中元素个数 int** levelOrder(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes) { *returnSize = 0; if (root == NULL) { return NULL; } int** res = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * 2000); *returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2000); struct TreeNode* queue[2001]; // 创建一个队列 注意:队头不放元素,长度须+1 int head = 0; // 队头 int tail = 0; // 队尾 queue[++tail] = root; //head:不存放数据,tail:存放数据 while (head < tail) { int colSize = 0, last = tail; res[*returnSize] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (last - head)); while (head < last) { struct TreeNode* node = queue[++head]; res[*returnSize][colSize++] = node->val; if (node->left != NULL) { queue[++tail] = node->left; } if (node->right != NULL) { queue[++tail] = node->right; } } (*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize] = colSize; (*returnSize)++; } return res; }
5. 二叉树的层序遍历||
思路:相对于102.二叉树的层序遍历,就是最后把res数组反转一下就可以了
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize. * The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array. * Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ // returnColumnSizes:用于存储每个数组中元素个数 int** levelOrderBottom(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes) { *returnSize = 0; if (root == NULL) { return NULL; } int** res = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * 2000); *returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2000); struct TreeNode* queue[2001]; // 创建一个队列 注意:队头不放元素,长度须+1 int head = 0; // 队头 int tail = 0; // 队尾 queue[++tail] = root; //head:不存放数据,tail:存放数据 while (head < tail) { int colSize = 0, last = tail; res[*returnSize] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (last - head)); while (head < last) { struct TreeNode* node = queue[++head]; res[*returnSize][colSize++] = node->val; if (node->left) { queue[++tail] = node->left; } if (node->right) { queue[++tail] = node->right; } } (*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize] = colSize; (*returnSize)++; } // 反转res数组 int** ret = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * (*returnSize)); int nums[*returnSize]; for (int i = 0; i < *returnSize; i++) { nums[i] = (*returnColumnSizes)[i]; } for (int i = 0; i < *returnSize; i++) { (*returnColumnSizes)[i] = nums[*returnSize - i - 1]; } for (int i = 0; i < *returnSize; i++) { ret[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * nums[*returnSize - i - 1]); for (int j = 0; j < nums[*returnSize - i - 1]; j++) { ret[i][j] = res[*returnSize - i - 1][j]; } } free(res); return ret; }
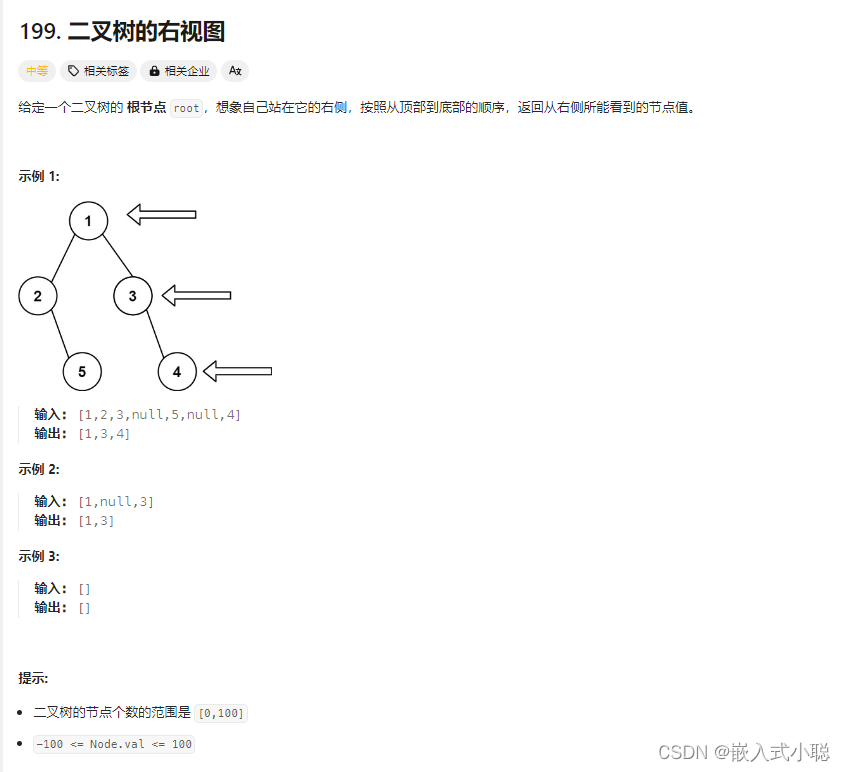
6.?二叉树的右视图
思路:层序遍历的时候,判断是否遍历到单层的最后面的元素,如果是,就放进result数组中,随后返回result就可以了
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ int* rightSideView(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) { int* ret = malloc(sizeof(int) * 100); memset(ret, 0, sizeof(int) * 100); *returnSize = 0; if (root == NULL) { return ret; } struct TreeNode* queue[101]; // 创建一个队列 int head = 0; // 对头 int tail = 0; // 队尾 queue[++tail] = root; //head:不存放数据,tail:存放数据 while (head < tail) { int last = tail; while (head < last) { struct TreeNode* node = queue[++head]; if (head == last) { ret[(*returnSize)++] = node->val; } if (node->left) { queue[++tail] = node->left; } if (node->right) { queue[++tail] = node->right; } } } return ret; } /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ double* averageOfLevels(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) { double* ret = malloc(sizeof(double) * 10000); memset(ret, 0, sizeof(int) * 10000); *returnSize = 0; if (root == NULL) { return ret; } int queue[10001]; // 创建一个队列 int head = 0; // 对头 int tail = 0; // 队尾 queue[++tail] = root; //head:不存放数据,tail:存放数据 while (head < tail) { int last = tail; double sum = 0; int size = tail - head; // 每层结点个数 while (head < last) { struct TreeNode* node = queue[++head]; sum += node->val; if (node->left) { queue[++tail] = node->left; } if (node->right) { queue[++tail] = node->right; } } ret[(*returnSize)++] = sum / size; } return ret; }
7. 二叉树的层平均值
代码实现:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ /** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */ double* averageOfLevels(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) { double* ret = malloc(sizeof(double) * 10000); memset(ret, 0, sizeof(int) * 10000); *returnSize = 0; if (root == NULL) { return ret; } struct TreeNode* queue[10001]; // 创建一个队列 int head = 0; // 对头 int tail = 0; // 队尾 queue[++tail] = root; //head:不存放数据,tail:存放数据 while (head < tail) { int last = tail; double sum = 0; int size = tail - head; // 每层结点个数 while (head < last) { struct TreeNode* node = queue[++head]; sum += node->val; if (node->left) { queue[++tail] = node->left; } if (node->right) { queue[++tail] = node->right; } } ret[(*returnSize)++] = sum / size; } return ret; }
8. N叉树的前序遍历
9. 在每个树行中找最大值 515
10. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 116
11.?填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针|| 117
12. 二叉树的最大深度? 104
13. 二叉树的最小深度 111
14. 翻转二叉树
思路:
- 在翻转时,需要从根节点往下先交换左右子树,然后再递归到左右子树进行相同的操作
? ? ? ? (前序遍历 and 层序遍历)
- 在翻转时,需要从下往上先交换左右子树,然后再递归到父节点进行交换(后序遍历)
- 中序遍历不可以(原因:先翻转左子树, 然后左右子树交换,这时候再翻转的右子树是之前的左子树)
层序遍历:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ // 交换左右子树 void swap(struct TreeNode* root) { struct TreeNode* l = root->left; struct TreeNode* r = root->right; root->left = r; root->right = l; } struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return root; } struct TreeNode* queue[101]; // 创建一个队列 int head = 0; // 队头 int tail = 0; // 队尾 queue[++tail] = root; // head:不存放数据,tail:存放数据 while (head < tail) { struct TreeNode* node = queue[++head]; swap(node); // 翻转 if (node->left) { queue[++tail] = node->left; } if (node->right) { queue[++tail] = node->right; } } return root; }前序遍历:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ // 交换左右子树 void swap(struct TreeNode* root) { struct TreeNode* l = root->left; struct TreeNode* r = root->right; root->left = r; root->right = l; } // 递归:先序遍历 void pre_order(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return ; } swap(root); // 交换 if (root->left) { pre_order(root->left); } if (root->right) { pre_order(root->right); } } struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return root; } pre_order(root); return root; }后序遍历:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */ // 交换左右子树 void swap(struct TreeNode* root) { struct TreeNode* l = root->left; struct TreeNode* r = root->right; root->left = r; root->right = l; } // 递归:后序遍历 void pre_order(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return ; } if (root->left) { pre_order(root->left); } if (root->right) { pre_order(root->right); } swap(root); // 交换 } struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) { return root; } pre_order(root); return root; }
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_68915288/article/details/135162274
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!