Netty Review - ByteBuf 读写索引 详解
2023-12-19 23:40:39

概念
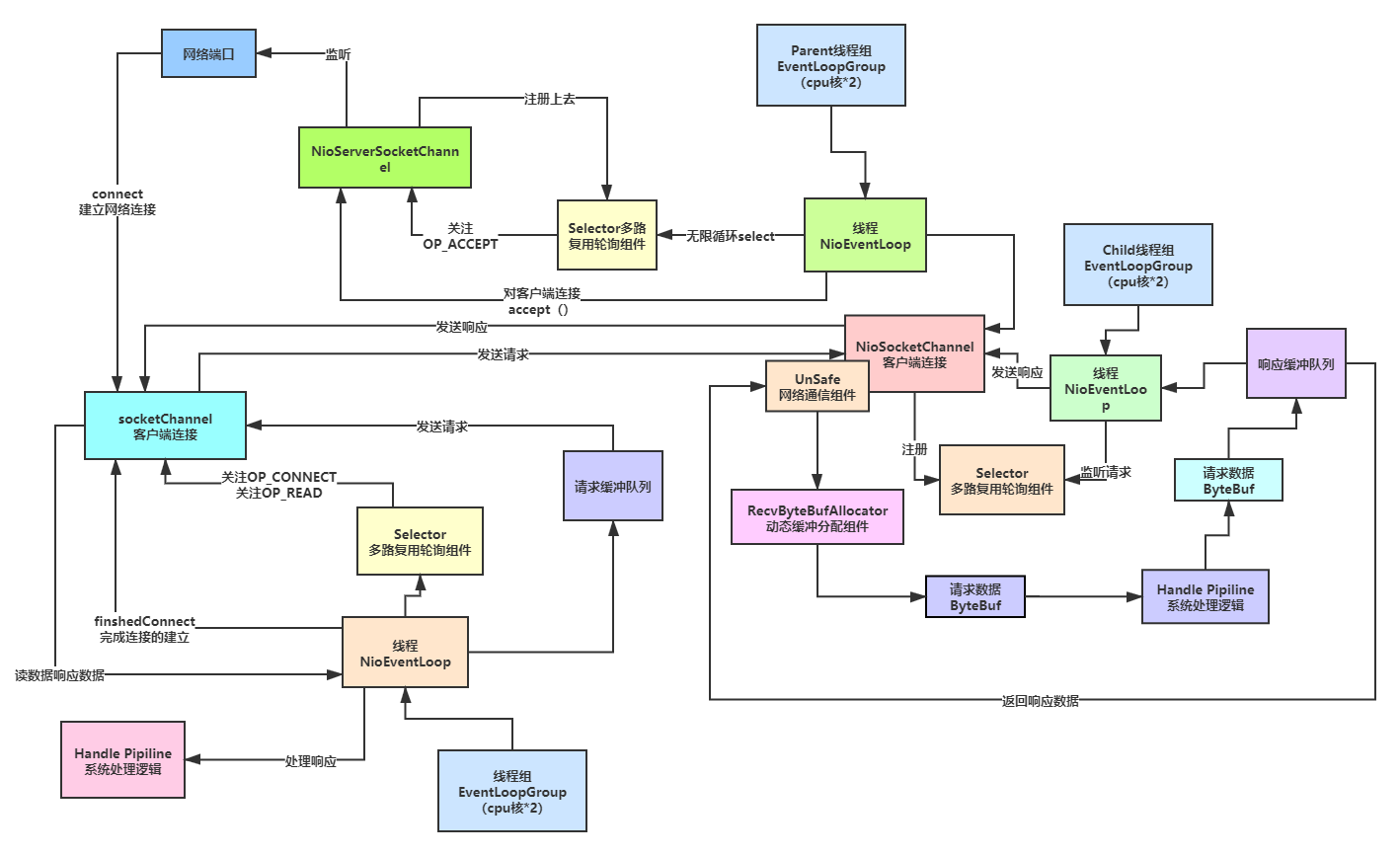
Pre
概述
Netty的ByteBuf是一个强大的字节容器,用于处理字节数据。它提供了比Java标准库中的ByteBuffer更灵活和高效的方式来操作字节数据。
ByteBuf简介
Netty的ByteBuf是一个字节容器,它提供了一种更灵活和高效的方式来操作字节数据。与ByteBuffer不同,ByteBuf具有可扩展的缓冲区,可以动态调整容量,而不需要创建新的缓冲区对象。
ByteBuf的主要特性
- 可读性和可写性: ByteBuf具有读和写两种模式。读操作和写操作是相互独立的,因此可以在不同的操作中使用同一段数据。
- 零拷贝: ByteBuf支持零拷贝操作,这意味着可以直接操作底层内存,而无需将数据复制到中间缓冲区。
- 引用计数: ByteBuf使用引用计数来跟踪对缓冲区的活动引用,这有助于防止内存泄漏。
结构
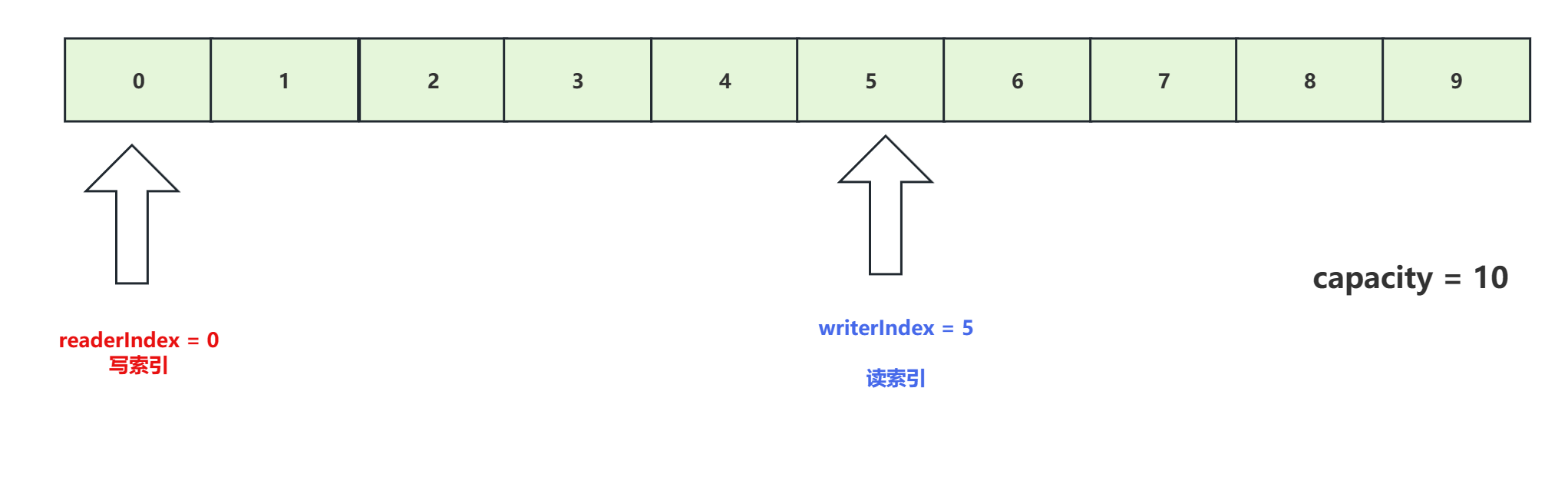
ByteBuf有三个关键的指针,分别是readerIndex、writerIndex和capacity。
- readerIndex表示读操作的起始位置,
- writerIndex表示写操作的起始位置,
- capacity表示ByteBuf的容量
-
从结构上来说,ByteBuf 由一串字节数组构成。数组中每个字节用来存放信息。
-
ByteBuf 提供了两个索引,一个用于读取数据,一个用于写入数据。这两个索引通过在字节数组中移动,来定位需要读或者写信息的位置。
读写操作: 通过readerIndex和writerIndex来进行读写操作,支持顺序读写和随机读写
-
当从 ByteBuf 读取时,它的 readerIndex(读索引)将会根据读取的字节数递增。
-
同样,当写 ByteBuf 时,它的 writerIndex 也会根据写入的字节数进行递增。
-
需要注意的是极限的情况是 readerIndex 刚好读到了 writerIndex 写入的地方。 如果 readerIndex 超过了 writerIndex 的时候,Netty 会抛出 IndexOutOf-BoundsException 异常。
API
ByteBuf的创建
ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.buffer(10); // 创建一个初始容量为10的ByteBuf
读写操作示例
// 写入数据
buffer.writeBytes("Hello".getBytes());
// 读取数据
byte[] data = new byte[buffer.readableBytes()];
buffer.readBytes(data);
System.out.println(new String(data));
引用计数操作
// 引用计数 +1
buffer.retain();
// 引用计数 -1,如果引用计数为0,则释放相关资源
buffer.release();
其他常用操作
- 获取和设置索引位置的字节值。
- 查找指定字节或字节数组的位置。
- 派发读/写索引而不实际移动数据。
Code 演示
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
public class NettyByteBuf {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建byteBuf对象,该对象内部包含一个字节数组byte[14]
// 通过readerindex和writerIndex和capacity,将buffer分成三个区域
// 已经读取的区域:[0,readerindex)
// 可读取的区域:[readerindex,writerIndex)
// 可写的区域: [writerIndex,capacity)
ByteBuf byteBuf = Unpooled.buffer(14);
System.out.println("byteBuf=" + byteBuf);
printBytebuf(byteBuf);
System.out.println("=================");
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
byteBuf.writeByte(i);
}
System.out.println("byteBuf=" + byteBuf);
printBytebuf(byteBuf);
System.out.println("=================");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(byteBuf.getByte(i));
}
System.out.println("byteBuf=" + byteBuf);
printBytebuf(byteBuf);
System.out.println("=================");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(byteBuf.readByte());
}
System.out.println("byteBuf=" + byteBuf);
printBytebuf(byteBuf);
System.out.println("=================");
//用Unpooled工具类创建ByteBuf
String text = "hello,artisan!" ;
ByteBuf byteBuf2 = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(text , CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
//使用相关的方法
if (byteBuf2.hasArray()) {
byte[] content = byteBuf2.array();
//将 content 转成字符串
System.out.println(new String(content, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("byteBuf2=" + byteBuf2);
printBytebuf(byteBuf2);
System.out.println("=================");
// 获取数组0这个位置的字符h的ascii码,h=104
System.out.println(byteBuf2.getByte(0));
System.out.println("=================");
//可读的字节数 14
int len = byteBuf2.readableBytes();
System.out.println("len=" + len);
printBytebuf(byteBuf2);
System.out.println("=================");
//使用for取出各个字节
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.println((char) byteBuf2.getByte(i));
}
printBytebuf(byteBuf2);
System.out.println("=================");
//范围读取
System.out.println(byteBuf2.getCharSequence(0, 6, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
printBytebuf(byteBuf2);
System.out.println("=================");
System.out.println(byteBuf2.getCharSequence(6, 8, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
printBytebuf(byteBuf2);
}
}
public static void printBytebuf(ByteBuf byteBuf){
System.out.println("readerIndex:" + byteBuf.readerIndex());
System.out.println("writerIndex:" + byteBuf.writerIndex());
System.out.println("capacity:" + byteBuf.capacity());
}
}
输出
byteBuf=UnpooledByteBufAllocator$InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 0, cap: 14)
readerIndex:0
writerIndex:0
capacity:14
=================
byteBuf=UnpooledByteBufAllocator$InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 8, cap: 14)
readerIndex:0
writerIndex:8
capacity:14
=================
0
1
2
3
4
byteBuf=UnpooledByteBufAllocator$InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 8, cap: 14)
readerIndex:0
writerIndex:8
capacity:14
=================
0
1
2
3
4
byteBuf=UnpooledByteBufAllocator$InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf(ridx: 5, widx: 8, cap: 14)
readerIndex:5
writerIndex:8
capacity:14
=================
hello,artisan!
byteBuf2=UnpooledByteBufAllocator$InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf(ridx: 0, widx: 14, cap: 42)
readerIndex:0
writerIndex:14
capacity:42
=================
104
=================
len=14
readerIndex:0
writerIndex:14
capacity:42
=================
h
e
l
l
o
,
a
r
t
i
s
a
n
!
readerIndex:0
writerIndex:14
capacity:42
=================
hello,
readerIndex:0
writerIndex:14
capacity:42
=================
artisan!
readerIndex:0
writerIndex:14
capacity:42

文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/yangshangwei/article/details/135095434
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!