反转链表、链表的中间结点、合并两个有序链表(leetcode 一题多解)
?一、反转链表
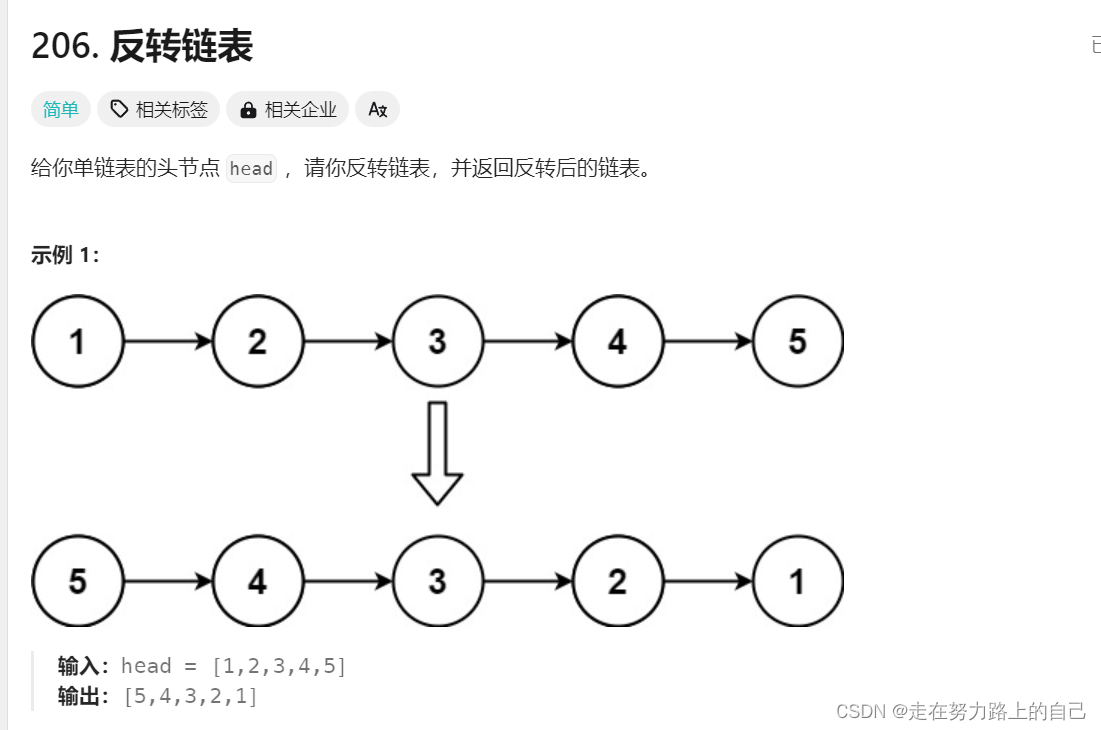
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
思路一:翻转单链表指针方向
这里解释一下三个指针的作用:
n1:记录上一个节点,如果是第一个就指向空
n2:记录此节点的位置
n3:记录下一个节点的位置,让翻转后能找到下一个节点,防止丢失指针的地址
/*
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//初始条件
struct ListNode* n1 = NULL,*n2 = head,*n3 = n2->next;
//结束条件
while(n2)
{
//迭代过程
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3)
n3 = n3->next;
}
return n1;
}
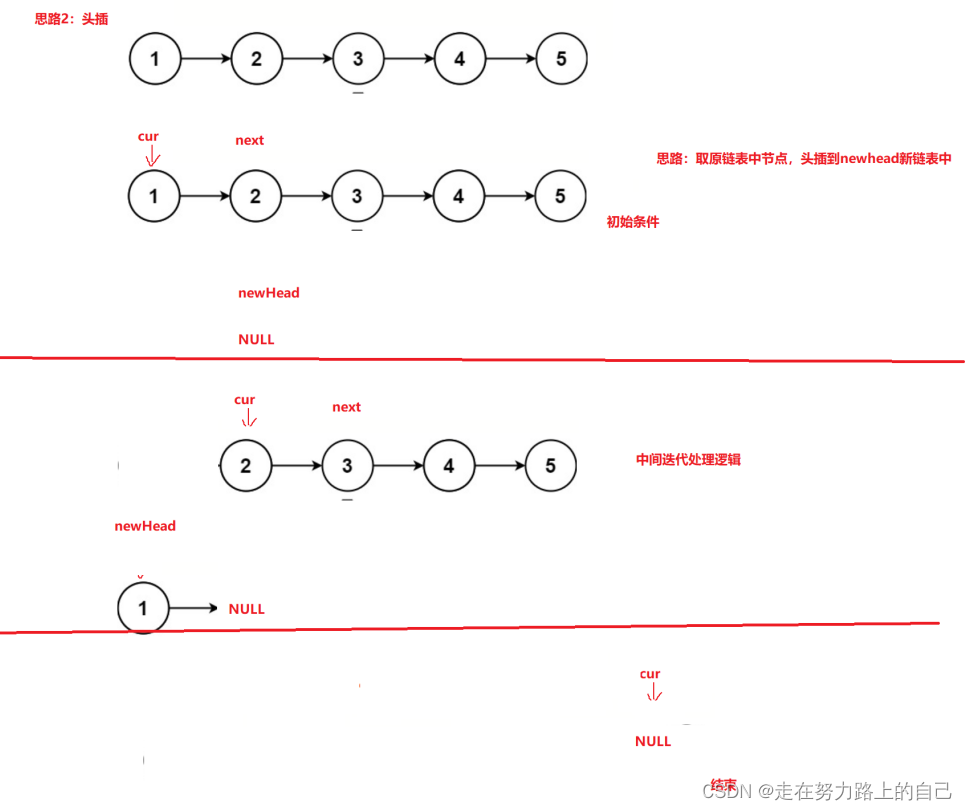
思路二:头插法
取原链表节点头插到新链表
/*
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* newHead = NULL;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
//头插
cur->next = newHead;
newHead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newHead;
}
二、链表的中间结点
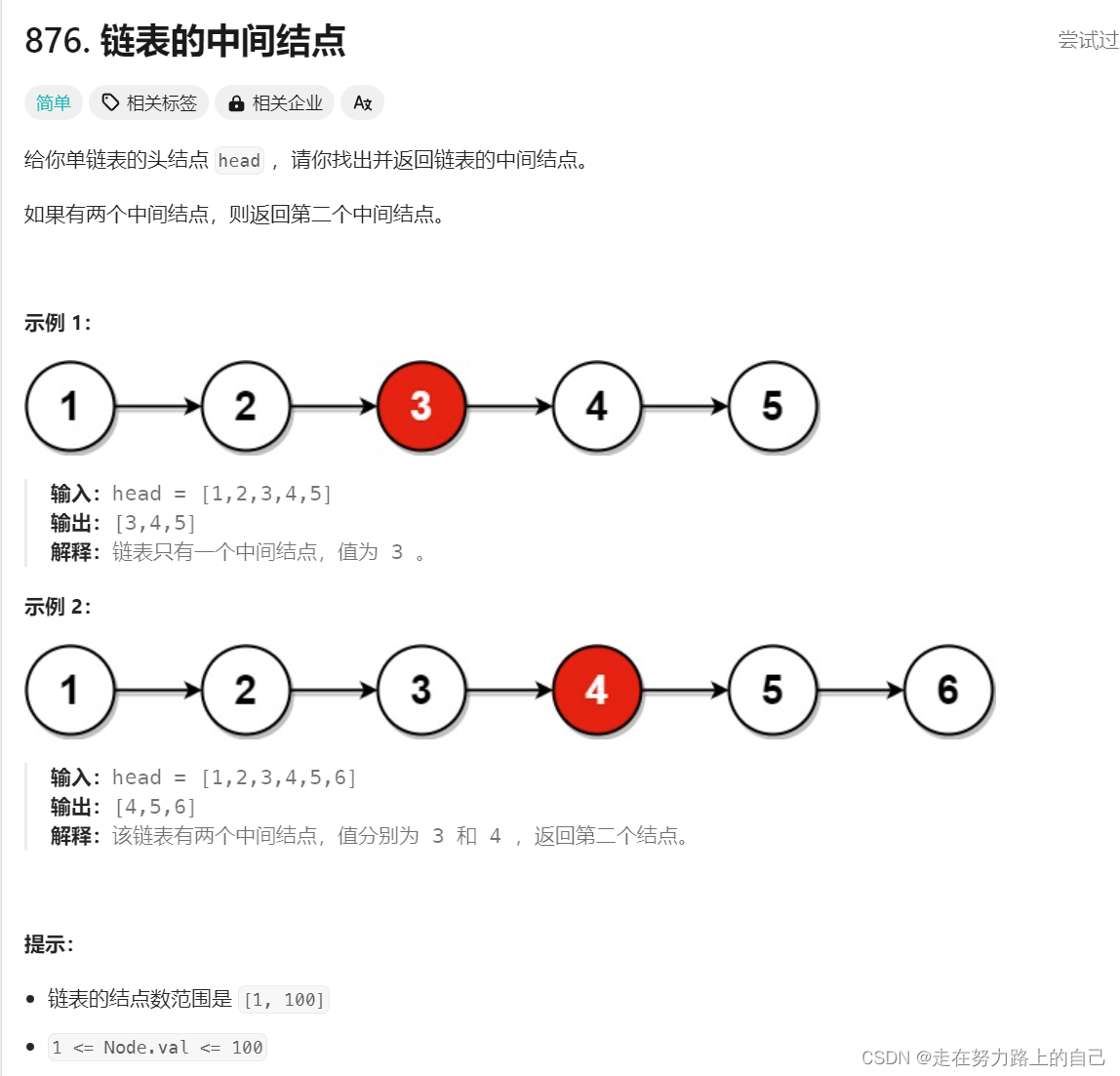
给你单链表的头结点 head ,请你找出并返回链表的中间结点。
如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
思路一:单指针法
-
时间复杂度:O(N*1.5),其中 N?是给定链表的结点数目。
-
空间复杂度:O(1),只需要常数空间存放变量和指针。
我们可以对链表进行两次遍历。第一次遍历时,我们统计链表中的元素个数 N;第二次遍历时,我们遍历到第 N/2 个元素(链表的首节点为第 0 个元素)时,将该元素返回即可。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
int n = 0;
struct ListNode*cur = head;
while(cur != NULL)
{
++n;
cur = cur->next;
}
int k = 0;
cur = head;
while(k < n/2)
{
++k;
cur = cur->next;
}
return cur;
}思路二:快慢指针法
-
时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 是给定链表的结点数目。
-
空间复杂度:O(1),只需要常数空间存放 slow 和 fast 两个指针。
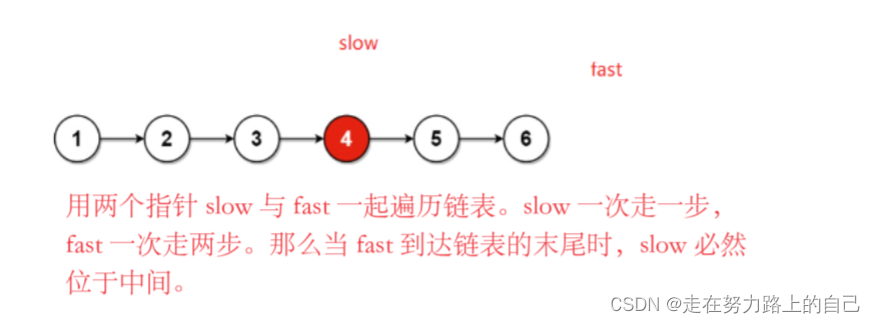
我们可以优化思路一,用两个指针 slow 与 fast 一起遍历链表。slow 一次走一步,fast 一次走两步。那么当 fast 到达链表的末尾时,slow 必然位于中间。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* slow = head,*fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}三、合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的?升序?链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。?
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
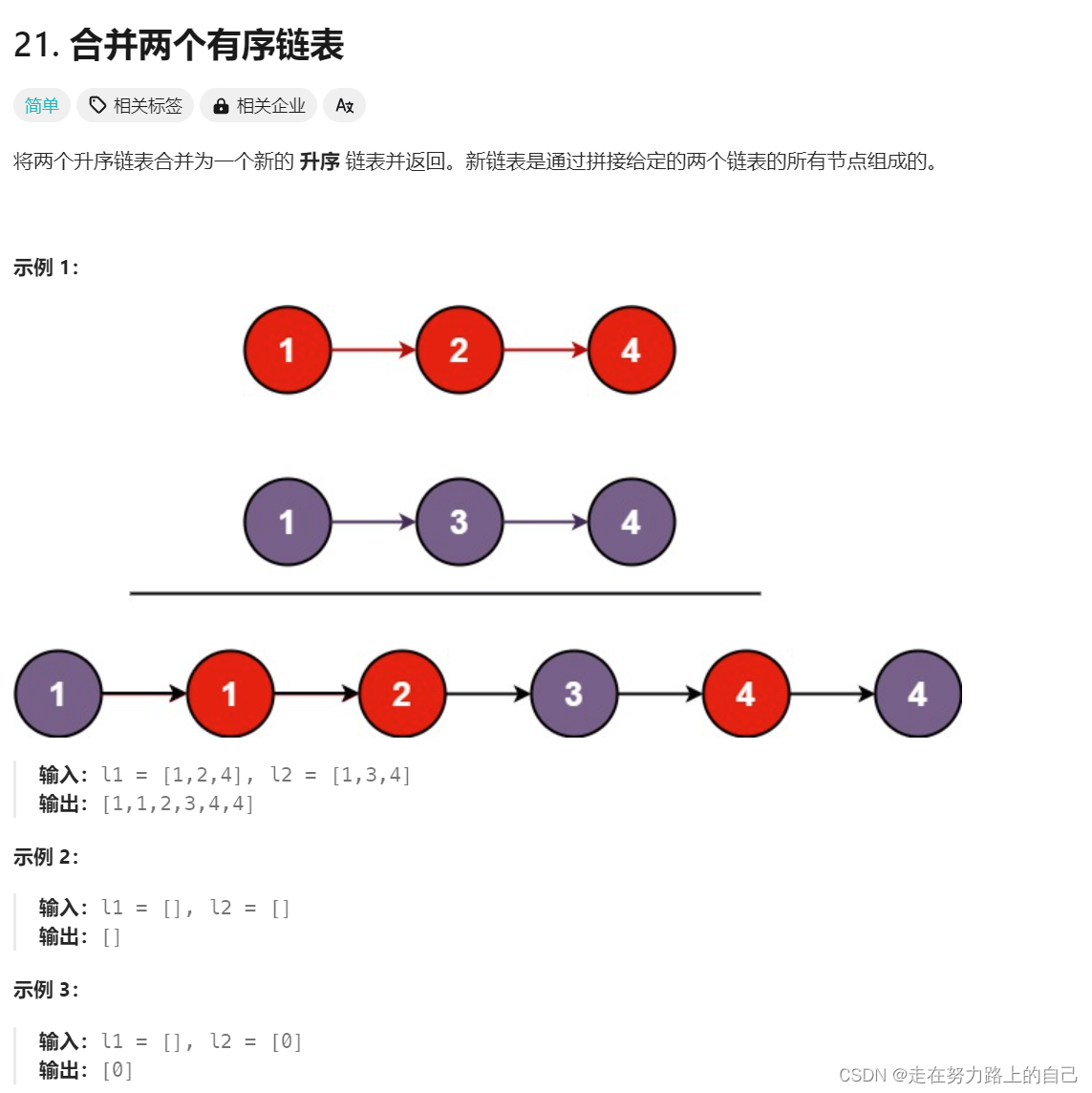
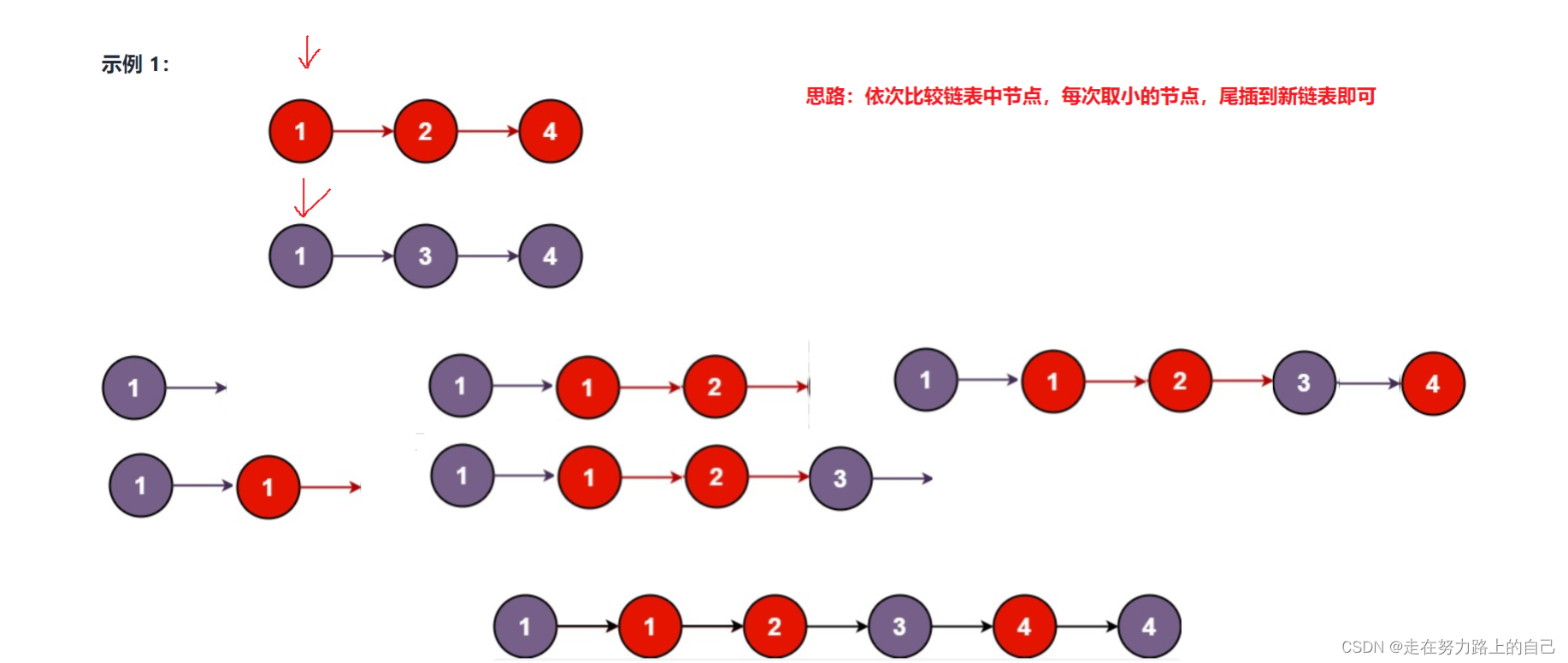
思路一(迭代法):
定义一个头指针和一个尾指针,从小到大依次尾插,直到一个链表为空时结束
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
if(l1 == NULL)
return l2;
if(l2 == NULL)
return l1;
struct ListNode* head = NULL, *tail = NULL;
while(l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL)
{
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
//尾插
if(tail == NULL)
{
head = tail = l1;
}
else{
tail->next = l1;
tail = tail->next;
}
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
if(tail == NULL)
{
head = tail = l2;
}
else{
tail->next = l2;
tail = tail->next;
}
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
if(l1)
tail->next= l1;
if(l2)
tail->next= l2;
return head;
}优化一:
先确定头结点,然后再循环判断val大小,尾插
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
if(l1 == NULL)
return l2;
if(l2 == NULL)
return l1;
struct ListNode* head = NULL, *tail = NULL;
//先确定头节点
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
head = tail =l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}else{
head = tail =l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
while(l1 && l2)
{
//尾插
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
tail->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
tail->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
if(l1)
tail->next= l1;
if(l2)
tail->next= l2;
return head;
}
优化二:
设置一个哨兵位的头节点,然后再去尾插。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
if(l1 == NULL)
return l2;
if(l2 == NULL)
return l1;
struct ListNode* head = NULL, *tail = NULL;
//哨兵位的头节点
head = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
while(l1 && l2)
{
//尾插
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{
tail->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
tail->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
if(l1)
tail->next= l1;
if(l2)
tail->next= l2;
struct ListNode* first = head->next;
free(head);
return first;
}
思路二(递归法):
(这是题解中大佬的一个解法)以迭代的思路写递归,尤为惊人!!!
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2){
/*if判断:
1.如果l1为空,返回l2
2.如果l2为空,返回l1
3.如果l1的值小于l2,比较l1的next值和l2,并把值赋给l1的下一个;返回l1
4.反之,比较l1和l2的next值,并把值赋给l2的下一个;返回l2
*/
if (l1 == NULL) {
return l2;
} else if (l2 == NULL) {
return l1;
} else if (l1->val < l2->val) {
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
}
因为有缓冲区的存在,C语言在操作文件的时候,需要做刷新缓冲区或者在文件操作结束的时候关闭文件。
如果不做,可能导致读写文件的问题。
今天就先到这了!!!

看到这里了还不给博主扣个:
?? 点赞??收藏 ?? 关注!
你们的点赞就是博主更新最大的动力!
有问题可以评论或者私信!!!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!