数据结构 模拟实现LinkedList单向不循环链表
目录
一、链表的简单介绍
概念:链表是一种物理存储结构不连续,逻辑上是连续的;链表类似现实中的火车,一节车厢连着一节车厢,而链表是通过链表之间的引用进行连接,构成一节一节的数据结构。如图:


二、链表的接口
代码如下:
public interface Ilist {
//头插法
void addFirst(int data);
//尾插法
void addLast(int data);
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
void addIndex(int index,int data);
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
boolean contains(int key);
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
void remove(int key);
//删除所有值为key的节点
void removeAllKey(int key);
//得到单链表的长度
int size();
void clear();
void display();
}
三、链表的方法实现
创建一个类,实现接口,重写方法,链表中的方法都在里面实现。类里面有链表类,也是内部类,有val值,next域,还有记录第一个节点的头结点,代码如下:
public class MyLinkedList implements Ilist{
public ListNode head;
static class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
}我们先创建一个方法,方法里面会创建几个节点,代码如下:
public void createList() {
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(34);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(45);
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(56);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node5;
this.head = node1;
}调用这个方法,就会创建出含有5个节点的链表,在test类里面创建main方法,调用此方法后的结果,结果如图:

(1)display方法
此方法可以显示链表中所有元素,也就是遍历一遍链表,打印val值,代码如下:
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}调用该方法执行结果如下: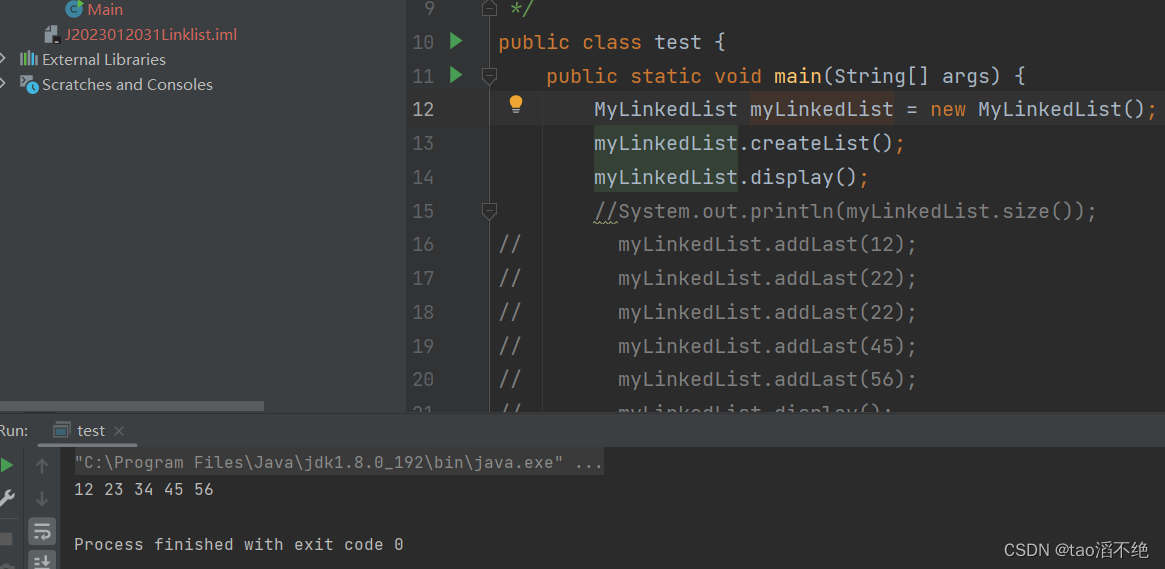
(2)size得到单链表的长度方法
要得到链表的长度,就要遍历一遍链表,定义一个变量进行统计个数,代码如下:
public int size() {
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}执行结果:

(3)addFirst头插方法
头插就要把要插入的节点当做头结点,要插入的元素next域指向当前头结点,再把头结点定成插入的元素。
代码:
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
}调用此方法,多条语句后的执行结果如下:
(4)addLast尾插方法
尾插就是要在链表的尾节点后插入节点,代码如下:
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}执行结果如下:

(5)addIndex指定位置插入方法
我们这里规定第一个节点的位置是0,第二个节点位置为1,依次往后推,我们要指定某一位置插入节点,先要检查插入位置是否合法,不合法抛出异常;合法在指定位置插入节点,如果指定位置是0,就是头插,指定位置是节点个数的size,就是尾插;中间位置,我们要找到指定位置的前一个节点,插入节点的next域指向前一个节点的next节点,前一个节点的next域指向插入节点,代码如下:
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
try {
if(index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new IndexException("下标异常,下标:" + index);
} else {
if(index == 0) {
//头插
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
//尾插
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
ListNode cur = searchPrev(index);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
} catch (IndexException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//找到链表前一个的位置
private ListNode searchPrev(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
int count = 0;
while (count != index - 1) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return cur;
}
public class IndexException extends RuntimeException{
public IndexException(String e) {
super(e);
}
}
(6)contains方法
查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中,遍历一遍链表,有该元素就返回true,没有就返回false,代码如下:
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}(7)remove删除第一个key值节点的方法
删除一个节点,先要判断该链表为不为空,为空就退出;不为空,看要删的节点是不是头结点,是头结点就直接把头结点改成头结点的next域;要删除的节点可能在中间,就要扎到要删除节点的前一个节点,把前一个节点的next域指向要删除节点的next域就好了,代码如下:
public void remove(int key) {
if(this.head == null) {
//一个节点都没有,无法删除
return;
}
if(this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = findPrev(key);
if(cur == null) {
System.out.println("没有要删除的点");
} else {
ListNode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
}
}
private ListNode findPrev(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if(cur.next.val == key) {
break;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur == this.head ? null : cur;
}执行结果如下:
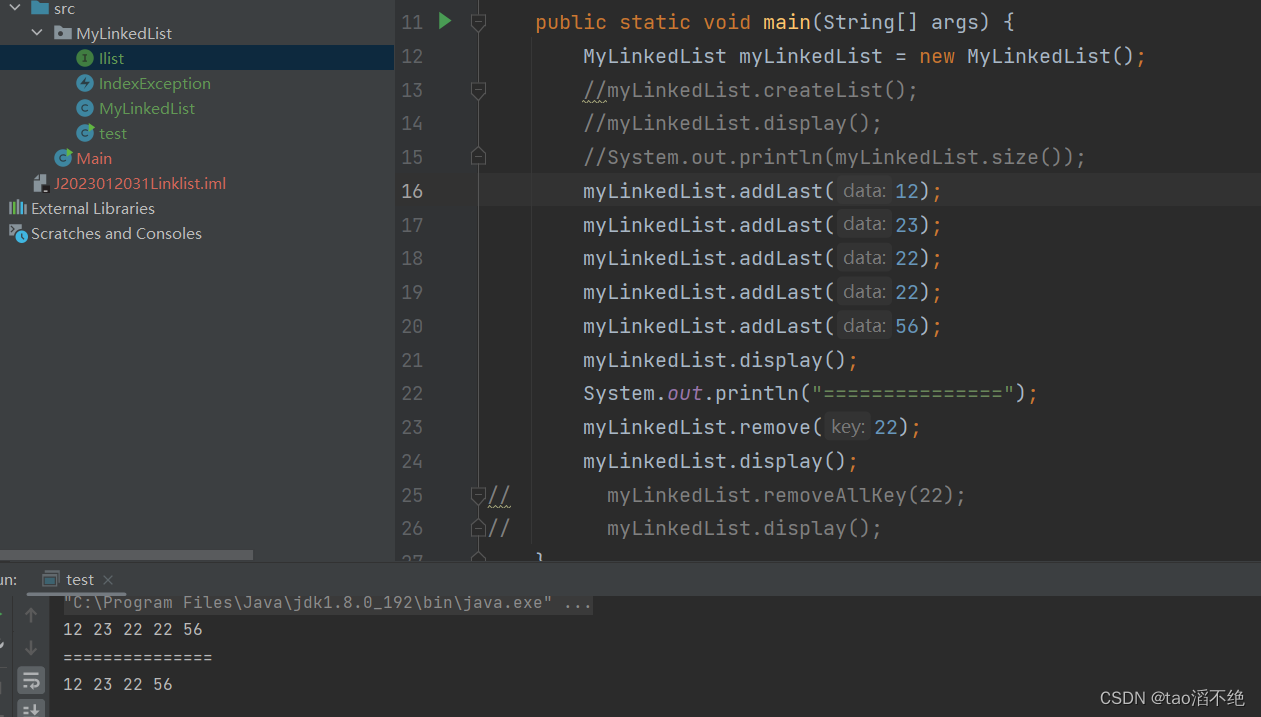
(8)removeAllKey删除所有值为key的方法
如果头结点是空的,就不用进行下面操作,直接返回。
两个节点,一个的前节点,一个是前节点的后一个节点,遍历后一个节点,判断后一个节点的val值是不是key,是key就把前一个节点的next域指向后一个节点的next域,后一个节点向后移,没有命中后一个节点==key这条件,前一个节点和后一个节点都要往后移动一步。
最后还要判断头结点的val值是否等于key值,是就要把head标记成head的next域。
代码入如下:
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if(this.head == null) {
return;
}
ListNode prev = this.head;
ListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
prev.next =cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
prev = prev.next;
}
}
if(this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
}执行结果如下:

(9)clear方法
清除所有节点,有两种解决方案,第一种是直接把头结点设为空,这种方法比较暴力;第二种是把每个节点的next域设为空,同时val也要设为空,因为这里的val类型是int,所以就设置不了空了,最后再把head节点设为空,代码如下:
public void clear() {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur = curNext;
}
head = null;
}执行结果如下:
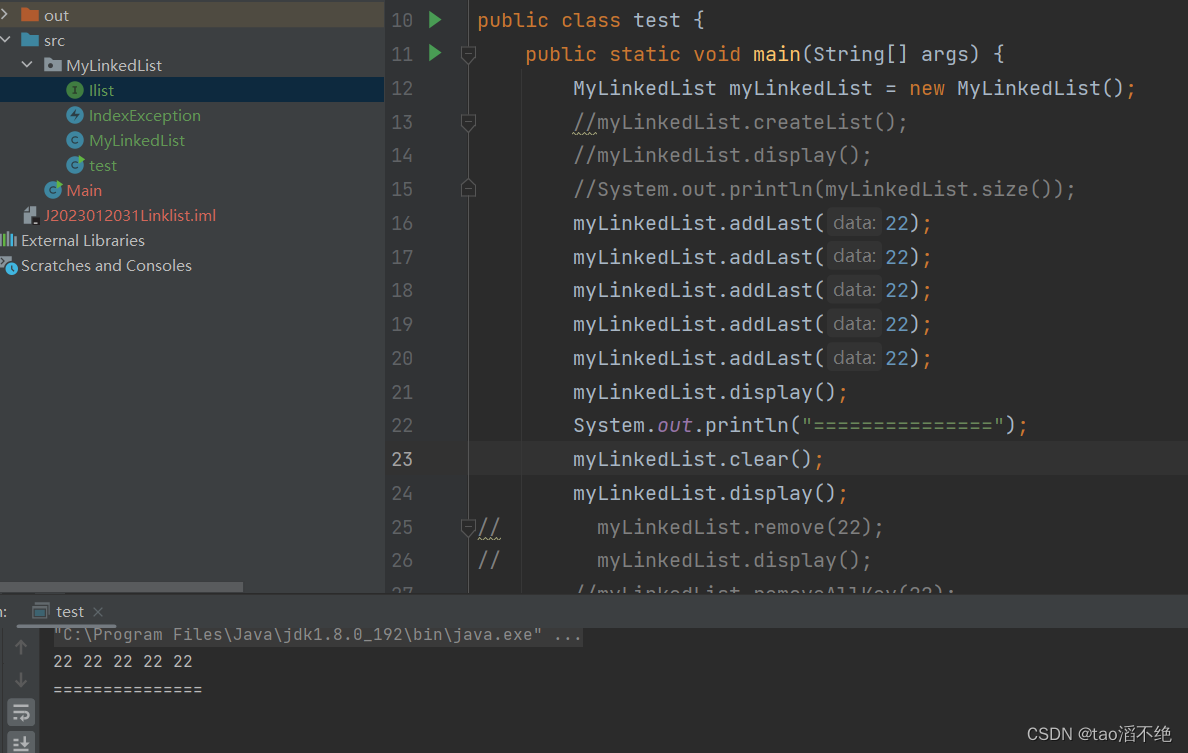
四、最终代码
public class MyLinkedList implements Ilist{
public ListNode head;
static class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public void createList() {
ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode node2 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode node3 = new ListNode(34);
ListNode node4 = new ListNode(45);
ListNode node5 = new ListNode(56);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node5;
this.head = node1;
}
@Override
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
}
@Override
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}
@Override
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
try {
if(index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new IndexException("下标异常,下标:" + index);
} else {
if(index == 0) {
//头插
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()) {
//尾插
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
ListNode cur = searchPrev(index);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
} catch (IndexException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//找到链表前一个的位置
private ListNode searchPrev(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
int count = 0;
while (count != index - 1) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return cur;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void remove(int key) {
if(this.head == null) {
//一个节点都没有,无法删除
return;
}
if(this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = findPrev(key);
if(cur == null) {
System.out.println("没有要删除的点");
} else {
ListNode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
}
}
private ListNode findPrev(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if(cur.next.val == key) {
break;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur == this.head ? null : cur;
}
@Override
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if(this.head == null) {
return;
}
ListNode prev = this.head;
ListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
prev.next =cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
prev = prev.next;
}
}
if(this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur = curNext;
}
head = null;
}
@Override
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//自定义异常类
public class IndexException extends RuntimeException{
public IndexException(String e) {
super(e);
}
}
点个赞再走吧,谢谢谢谢谢!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!