02-基于GEC6818开发板的画正方形、画圆的操作——使用mmap映射提高效率
2023-12-22 14:42:18
02-基于GEC6818开发板的画正方形、画圆的操作——使用mmap映射提高效率
本文主要是在01-基于粤嵌GEC6818实现屏幕的显示固定颜色进行自动切换-点击前往的基础上进行了进一步的更改,之前那个在切换时会有一定的花屏,是因为其效率低的原因,本文就对其将进行了优化。
包括实例:
1.使用mmap函数优化切换不同屏幕颜色的效率
2.在屏幕上画正方形
3.在屏幕上画一个圆形
文章目录
一、 效率提高
需要进行状态切换(内核态——应用态)以及需要从应用层到fb0到底层hardware,需要进行两次搬砖,所以导致效率低下,会在颜色切换的时候有异色横线。
解决方案:
映射
1.1 mmap 映射
NAME
mmap, munmap - map or unmap files or devices into memory
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/mman.h>
void *mmap(void *addr, size_t length, int prot, int flags,
int fd, off_t offset);
int munmap(void *addr, size_t length);
mmap函数:
- 功能:将一个文件或设备映射到进程的地址空间。
- 参数:
addr:期望的映射起始地址。通常设置为NULL,让系统选择一个合适的地址。(如果自己设计则需要选择内存为空闲的地址,自己难以知道确定)length:映射的长度。文件有多大就设置多大,注意要以页为单位,一页就是 4K。不足一页会补齐一页。prot:保护标志(权限)。指定了内存映射区域的保护模式,如读、写、执行等。一般这个权限要根据fd进行设置。
PROT_EXEC Pages may be executed.
PROT_READ Pages may be read.
PROT_WRITE Pages may be written.
PROT_NONE Pages may not be accessed.
- 续参数
flags:控制映射的各种属性,如共享性、映射标志等。- MAP_SHARED 公有映射-对内核的操作直接影响文件
- MAP_PRIVATE 私有映射-开辟一个自己的空间,不会影响文件
fd:文件描述符,指向要映射的文件。offset:文件中的偏移量,从这个偏移量开始映射。
- 返回值:成功后会返回映射后的首地址;失败返回NONE,同时Errno被设置。
1.2 munmap 取消映射
munmap函数:
- 功能:取消映射一个之前由
mmap创建的内存区域。 - 参数:
addr:要取消映射的内存区域的起始地址。length:要取消映射的长度。
使用mmap和munmap,您可以实现高效的文件和设备访问,同时还可以利用内存映射的特性,如零拷贝、共享内存等。
需要注意的是,使用这些函数时应谨慎处理,确保内存映射的正确性和安全性。在使用这些函数时,通常需要考虑与其他系统调用和操作系统接口的交互,以确保程序的正确性和稳定性。
二、 练习使用
2.1 练习1:使用mmap函数优化切换不同屏幕颜色的效率
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define WIDTH 800
#define HEIGHT 480
int main() {
int fd = open("/dev/fb0", O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open file error");
exit(1);
}
// 计算需要映射的大小
size_t screensize = WIDTH * HEIGHT * 4;
// 使用mmap映射到内核空间
int *fbp = (int *)mmap(0, screensize, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
if ((intptr_t)fbp == -1) {
perror("mmap error");
exit(1);
}
int color1[WIDTH * HEIGHT];
int color2[WIDTH * HEIGHT];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < WIDTH * HEIGHT; i++) {
color1[i] = 0x00FF00; // green
color2[i] = 0xFF0000; // red
}
while (1) {
// 将color1写入映射的内存
memcpy(fbp, color1, screensize);
sleep(1);
// 将color2写入映射的内存
memcpy(fbp, color2, screensize);
sleep(1);
}
// 取消映射并关闭文件描述符
munmap(fbp, screensize);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
2.2 练习2:在屏幕上画正方形
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int lcd_fd = -1;//全局的lcd描述符
unsigned int* plcd = NULL ;
void lcdinit()
{
lcd_fd = open("/dev/fb0", O_RDWR);
if (-1 == lcd_fd)
{
perror("open fb0 error");
exit(1);
}
plcd = mmap(NULL, 800*480*4, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, lcd_fd, 0);
if (plcd == MAP_FAILED) {
perror("mmap error");
return;
}
}
void lcd_destory()
{
munmap(plcd,800*400*4);
close(lcd_fd);
}
/*画点函数
* 传入参数:
* (x,y)需要画点的坐标
* color:(x,y)点的颜色
*/
void point(int x,int y, unsigned int color)
{
if(x>0&&x<800&&y>=0&&y<480)
{
*(plcd+y*800+x)=color;//给这个点赋值color
}
}
/*函数:画一个方块
* 传入参数:
* w: 正方形的宽
* h: 正方形的高
* x0: 需要画在x0的位置
* y0: 需要画在y0的位置
* color : 需要画的颜色
* 返回值:NULL
*/
void display_sql(int w,int h, int x0, int y0,int color)
{
int x,y;
for(y=0;y< h;y++)
{
for(x=0;x<w;x++)
{
point(x+x0,y+y0,color);//在x0,y0开始的位置开始画点
}
}
}
int main()
{
int r1,r2;
lcdinit();
//操作屏幕
display_sql(200,200,100,100,0xff0000);
display_sql(200,200,400,100,0xff);
lcd_destory();
return 0;
}
2.3 练习3: 在屏幕上画一个圆形
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
int lcd_fd = -1; // 全局的lcd描述符
unsigned int* plcd = NULL;
void lcdinit() {
lcd_fd = open("/dev/fb0", O_RDWR);
if (-1 == lcd_fd) {
perror("open fb0 error");
exit(1);
}
plcd = mmap(NULL, 800 * 480 * 4, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, lcd_fd, 0);
if (plcd == MAP_FAILED) {
perror("mmap error");
return;
}
}
void lcd_destory() {
munmap(plcd, 800 * 480 * 4);
close(lcd_fd);
}
void point(int x, int y, unsigned int color) {
if (x >= 0 && x < 800 && y >= 0 && y < 480) {
*(plcd + y * 800 + x) = color;
}
}
void display_sql(int w, int h, int x0, int y0, int color) {
int x, y;
for (y = 0; y < h; y++) {
for (x = 0; x < w; x++) {
point(x + x0, y + y0, color);
}
}
}
void fill_circle(int xc, int yc, int r, unsigned int color) {
int x = 0, y = r;
int d = 3 - 2 * r;
while (x <= y) {
// 画圆弧上的水平线
for (int i = xc - x; i <= xc + x; i++) {
point(i, yc - y, color);
point(i, yc + y, color);
}
// 画圆弧上的垂直线
for (int i = xc - y; i <= xc + y; i++) {
point(i, yc - x, color);
point(i, yc + x, color);
}
if (d < 0) {
d = d + 4 * x + 6;
} else {
d = d + 4 * (x - y) + 10;
y--;
}
x++;
}
}
int main() {
lcdinit();
display_sql(200, 200, 100, 100, 0xff0000);
display_sql(200, 200, 400, 100, 0xff);
// 画一个填充的黄色圆形
fill_circle(300, 240, 50, 0xffff00);
lcd_destory();
return 0;
}
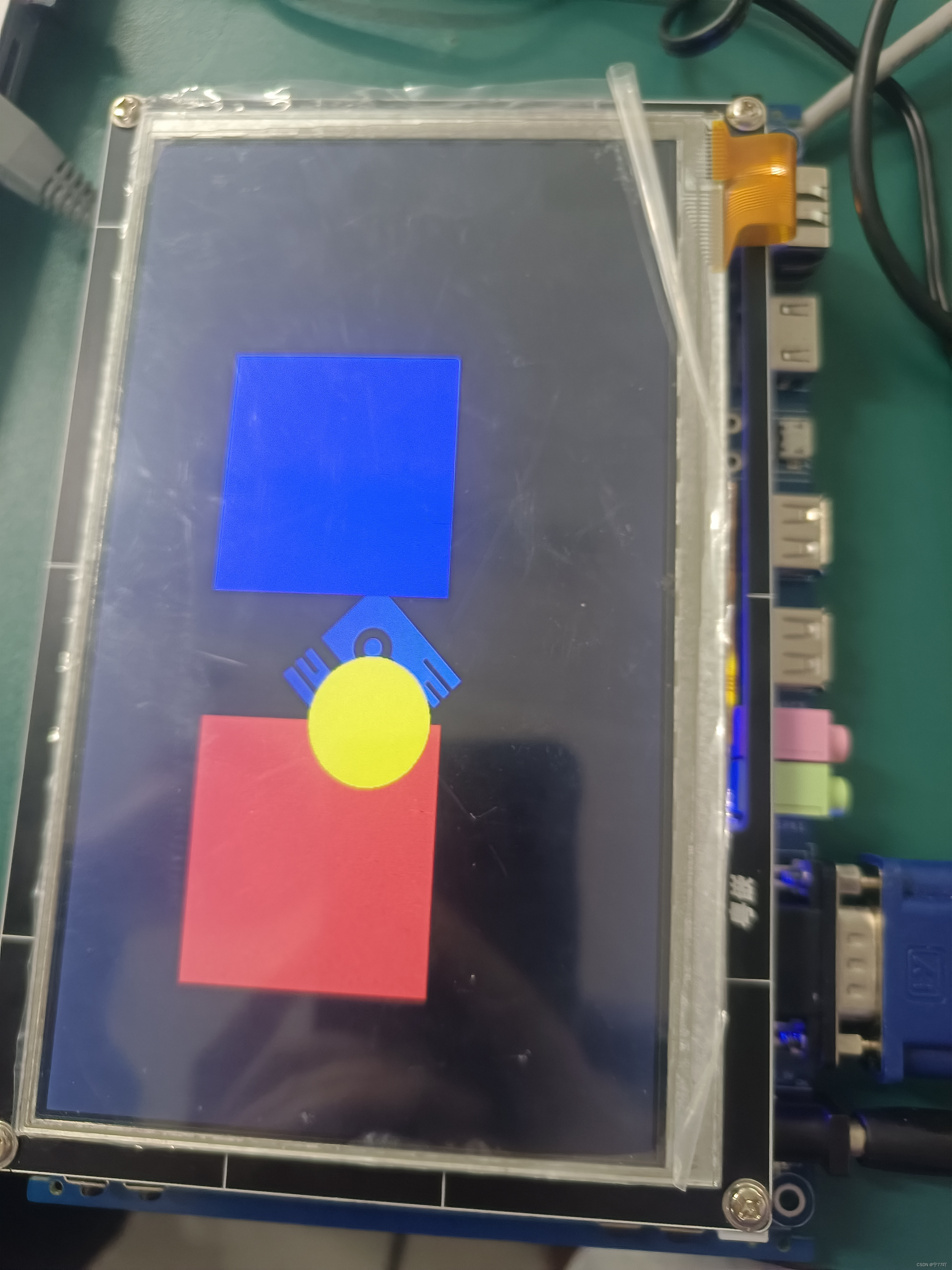
实现效果图
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_63831368/article/details/135151299
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!