EMT(light sr):Efficient Mixed Transformer for Single Image Super-Resolution
EMT
论文地址:Efficient Mixed Transformer for Single Image Super-Resolution
代码地址:Fried-Rice-Lab/EMT: Efficient Mixed Transformer for Single Image Super-Resolution (github.com)
摘要
? 最近,基于 Transformer 的方法在单图像超分辨率 (SISR) 中取得了令人印象深刻的结果。然而,局部性机表现不好和较高的模型复杂性限制了它们在超分辨率(SR)领域的应用。为了解决这些问题,提出了一种新的方法——高效混合Transformer(EMT)。具体来说,提出了由多个连续Transformer层组成的混合Transformer块(MTB),其中一些像素混合器(PM)被用来取代自注意机制(SA)。PM可以通过像素移位操作增强局部信息聚合。此外, 使用条带窗口,通过利用图像各向异性来获得有效的全局依赖建模。
现阶段问题
基于 Transformer 的 lightweight SR方法研究重点:如何在降低复杂度的同时能增强必要的局部性机制还能获得高效的全局依赖建模
贡献
- 对于局部性机制改进:开发了一个Pixel Mixer(PM),通过融合来自不同通道的相邻像素知识来改进局部性机制来扩展局部感受野.
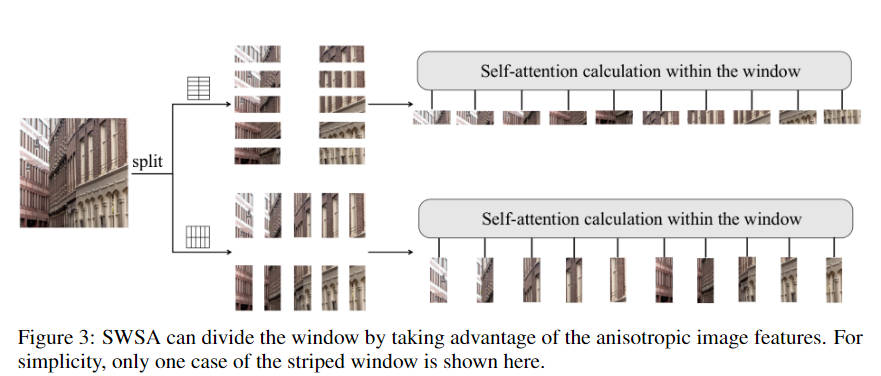
- 使用类似EDT的窗口计算attention(利用图像各向异性来获得有效的全局依赖建模),并简化了模型的计算复杂度
网络架构
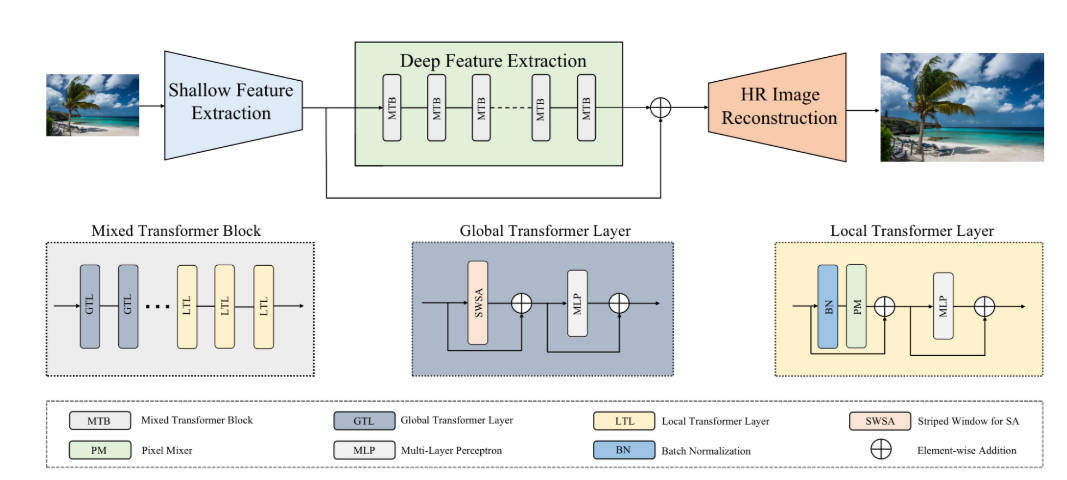
Mixed Transformer Block for SR
? 提出了混合Tranformer块(MTB),它由两种类型的Transformer层组成,即使用PixelMixer的局部Transformer(LTL)和使用window attention的全局Transformer层(GTL)。
Striped Window
该striped windows主要是在计算attn的时候,通过使用 Q T Q^T QT代替了 K K K,同时,在shift了window之后,没有进行mask操作,直接进行的attn的计算。通过这种方式,降低了计算复杂度。
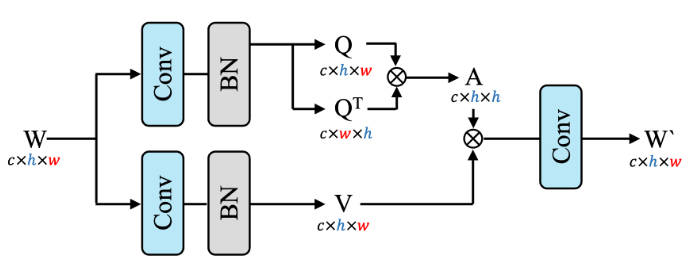
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor or tuple:
r"""
Args:
x: b c h w
Returns:
b c h w -> b c h w
"""
# attn_layer=[Conv2d1x1(dim, dim * 2),
# nn.BatchNorm2d(dim * 2)],
# proj_layer=[Conv2d1x1(dim, dim)],
# calculate qkv
qkv = self.attn(x)
_, C, _, _ = qkv.size()
# split channels
qkv_list = torch.split(qkv, [C // len(self.window_list)] * len(self.window_list), dim=1)
output_list = list()
if self.return_attns:
attn_list = list()
for attn_slice, window_size, shift_size in zip(qkv_list, self.window_list, self.shift_list):
_, _, h, w = attn_slice.size()
attn_slice = self.check_image_size(attn_slice, window_size)
# roooll!
if shift_size != (0, 0):
attn_slice = torch.roll(attn_slice, shifts=shift_size, dims=(2, 3))
# cal attn
_, _, H, W = attn_slice.size()
q, v = rearrange(attn_slice, 'b (qv head c) (nh ws1) (nw ws2) -> qv (b head nh nw) (ws1 ws2) c',
qv=2, head=self.num_heads,
ws1=window_size[0], ws2=window_size[1])
attn = (q @ q.transpose(-2, -1))
attn = f.softmax(attn, dim=-1)
if self.return_attns:
attn_list.append(attn.reshape(self.num_heads, -1,
window_size[0] * window_size[1],
window_size[0] * window_size[1])) # noqa
output = rearrange(attn @ v, '(b head nh nw) (ws1 ws2) c -> b (head c) (nh ws1) (nw ws2)',
head=self.num_heads,
nh=H // window_size[0], nw=W // window_size[1],
ws1=window_size[0], ws2=window_size[1])
# roooll back!
if shift_size != (0, 0):
output = torch.roll(output, shifts=(-shift_size[0], -shift_size[1]), dims=(2, 3))
output_list.append(output[:, :, :h, :w])
# proj output
output = self.proj(torch.cat(output_list, dim=1))
if self.return_attns:
return output, attn_list
else:
return output
Pixel Mixer
? Shift: A Zero FLOP, Zero Parameter Alternative to Spatial Convolutions通过提出移位卷积而不是空间卷积在网络中引入局部性。
神经网络轻量化改进之卷积结构设计_改进cnn_AI追随者的博客-CSDN博客
? 在此基础上我们通过改进它扩展了这个想法并开发了 PM。具体来说,PM首先将特征通道分成五个相等的组,然后将前四组的特征点按特定顺序(左、右、上、下)移动,并用超出范围的像素填充0。通过在相邻特征之间交换几个通道,将周围的知识混合,并将通道混合模块与感受野扩展,以快速捕获局部空间知识。此外,通过将边缘特征点与自注意机制中的每个输入窗口相关联的边缘特征点可以获得与其他源不同的知识。

#Algorithm 1: Pixel Mixer for EMT, PyTorch-like Code
import torch
class PixelMixer(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# list of shift rules
self.rule = [[-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [0, 0]]
def forward(self, x):
groups = torch.split(x, [x.shape[1]//5] * 5, dim=1)
# use different shift rules for each group
groups = [torch.roll(group, shifts=rule, dims=(2, 3))
for group, rule in zip(groups, self.rule)]
return torch.cat(groups, dim=1)
真实使用的PixelMixer
class PixelMixer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, planes: int, mix_margin: int = 1) -> None:
super(PixelMixer, self).__init__()
assert planes % 5 == 0
self.planes = planes
self.mix_margin = mix_margin # 像素的偏移量
self.mask = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((self.planes, 1, mix_margin * 2 + 1, mix_margin * 2 + 1)),
requires_grad=False)
# 左移一位
# [0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 0., 1.],
# [0., 0., 0.]
self.mask[0::5, 0, mix_margin, -1] = 1.
# 右移一位
# [0., 0., 0.],
# [1., 0., 0.],
# [0., 0., 0.]
self.mask[1::5, 0, mix_margin, 0] = 1.
# 上移一位
# [0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 1., 0.]
self.mask[2::5, 0, -1, mix_margin] = 1.
# 下移一位
# [0., 1., 0.],
# [0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 0., 0.]
self.mask[3::5, 0, 0, mix_margin] = 1.
# 不移动
# [0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 1., 0.],
# [0., 0., 0.]
self.mask[4::5, 0, mix_margin, mix_margin] = 1.
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
m = self.mix_margin
x = f.conv2d(input=f.pad(x, pad=(m, m, m, m), mode='circular'),
weight=self.mask, bias=None, stride=(1, 1), padding=(0, 0),
dilation=(1, 1), groups=self.planes)
return x
结论
? 本研究提出了一种用于 SISR 的 Efificint Mixed Transformer (EMT),它由浅层特征提取、深层特征提取和重建三个单元组成。深度特征提取单元使用混合Transformer块(MTB),每个块中全局Transformer层(GTL)和局部Transformer层(LTL)的混合。LTL 主要由像素混合器 (PM,移位卷积操作) 和多层感知器组成。PM通过通道分离和像素移位操作增强了网络的局部性机制,而不需要额外的复杂性。GTL中自注意(SWSA)的条纹窗口利用图像的各向异性来获得更有效的全局依赖建模。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!