[C++]:10.vector使用
vector使用
一.vector使用
1.构造函数:
void text_1()
{
//0.类型的重定义:
//typedef T value_type
//typedef value_type* iterator
//1.无参:vector<>()
vector<int> v_1;
//2.构造并且初始化n个val:
//vector<> (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type())
vector<int> v_2(10, 2);
//3.拷贝构造:vector<> (const vector& x);
vector<int> v_3(v_2);
//4.迭代器进行初始化构造:vector<> (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
vector<int> v_4(v_2.begin(), v_2.end());
}
补充:
1.迭代器可以是其他任意类型在这个地方发生的是隐式类型的转换:
2.使用迭代器进行初始化构造的时候一定是一个已经实例化好的对象的迭代器。
3.注意数值的类型:
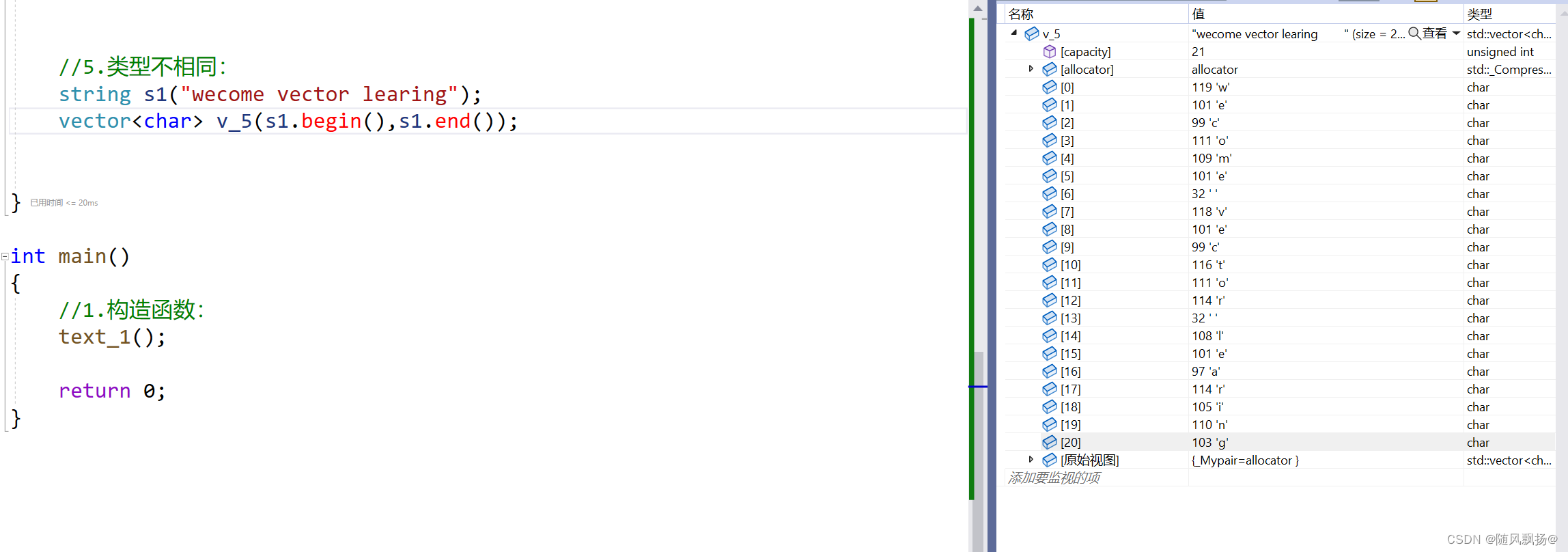
2.迭代器+遍历数据:
//2.迭代器+数据遍历
void text_2()
{
//1.列表初始化:
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 };
//2.迭代器遍历:
vector<int>::iterator it_1 = v1.begin();
while (it_1 != v1.end())
{
cout << *it_1 << " ";
it_1++;
}
cout << endl;
}
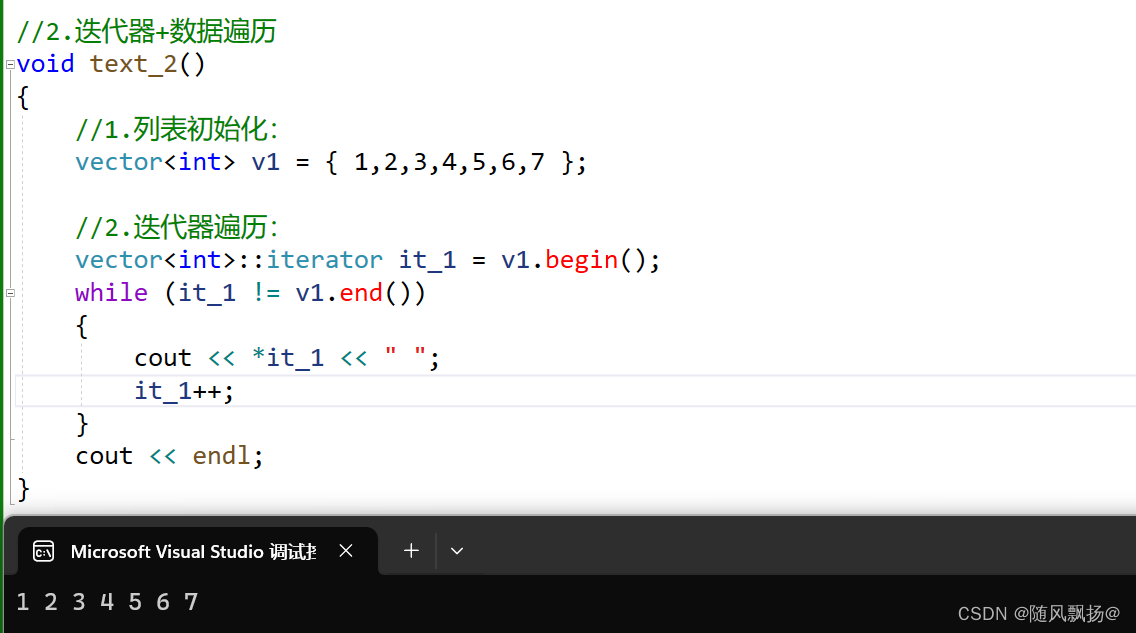
补充迭代器的空间结构:
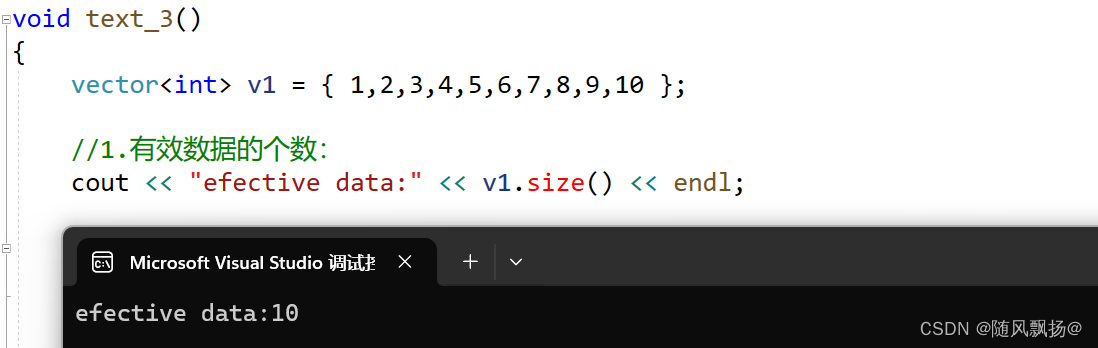
3.空间问题:
1.size():返回有效数据个数:
void text_3()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
//1.有效数据的个数:
cout << "efective data:" << v1.size() << endl;
}
2.capacity():返回容量大小:
void text_3()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
//2.容量的大小:
cout << "capacity : " << v1.capacity() << endl;
}
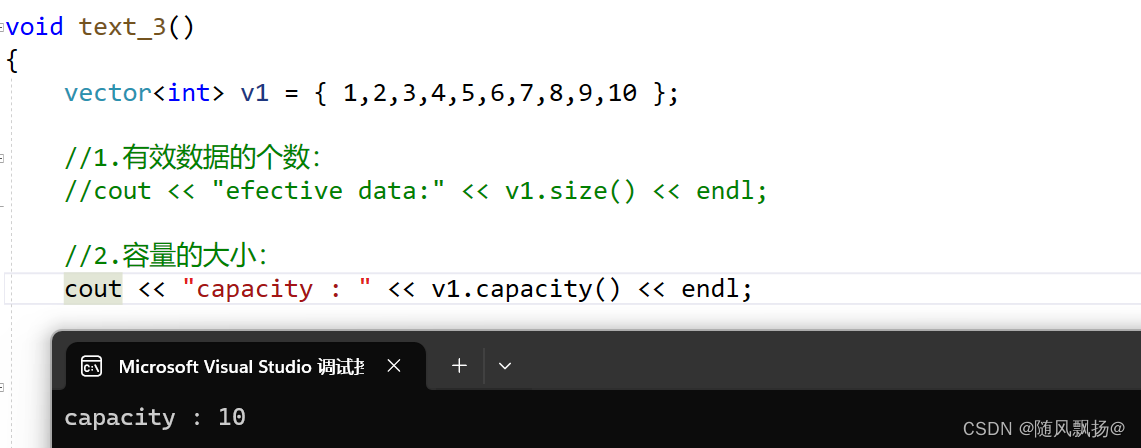
3.容量检测:
void text_3()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
int cat = 100;
int flag = 0;
while (cat--)
{
v1.push_back(cat);
flag++;
if (flag == 10)
{
cout << "efective data:" << v1.size();
cout << "capacity : " << v1.capacity() << endl;
flag = 0;
}
}
}
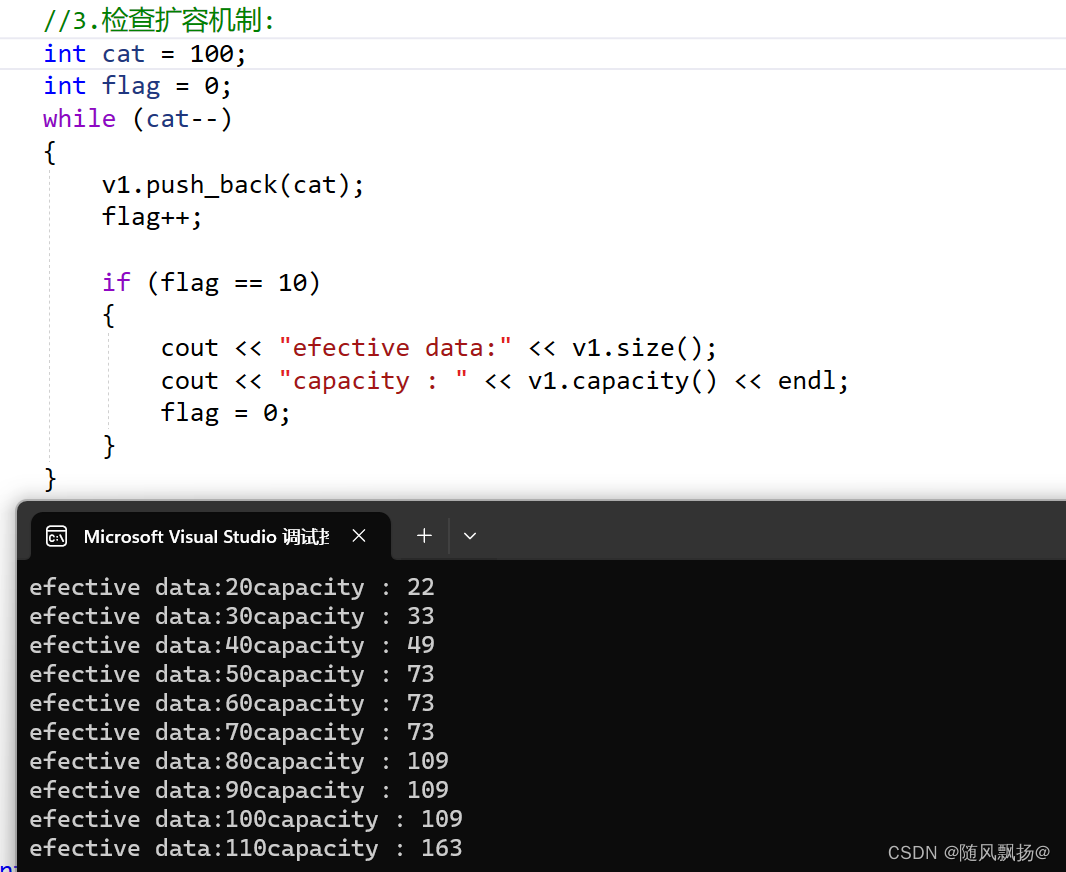
1.在vs下容量的扩容是1.5倍的进行扩容。
2.在SGI下是2倍进行扩容操作。
4.emptr():判断顺序表是否为空:
void text_3()
{
//4.判断vector是否为空:
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
vector<int> v2;
if (v2.empty())
{
cout << "v2 is empty!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "v2 not empty!" << endl;
}
if (v1.empty())
{
cout << "v1 is empty!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "v1 not empty!" << endl;
}
}
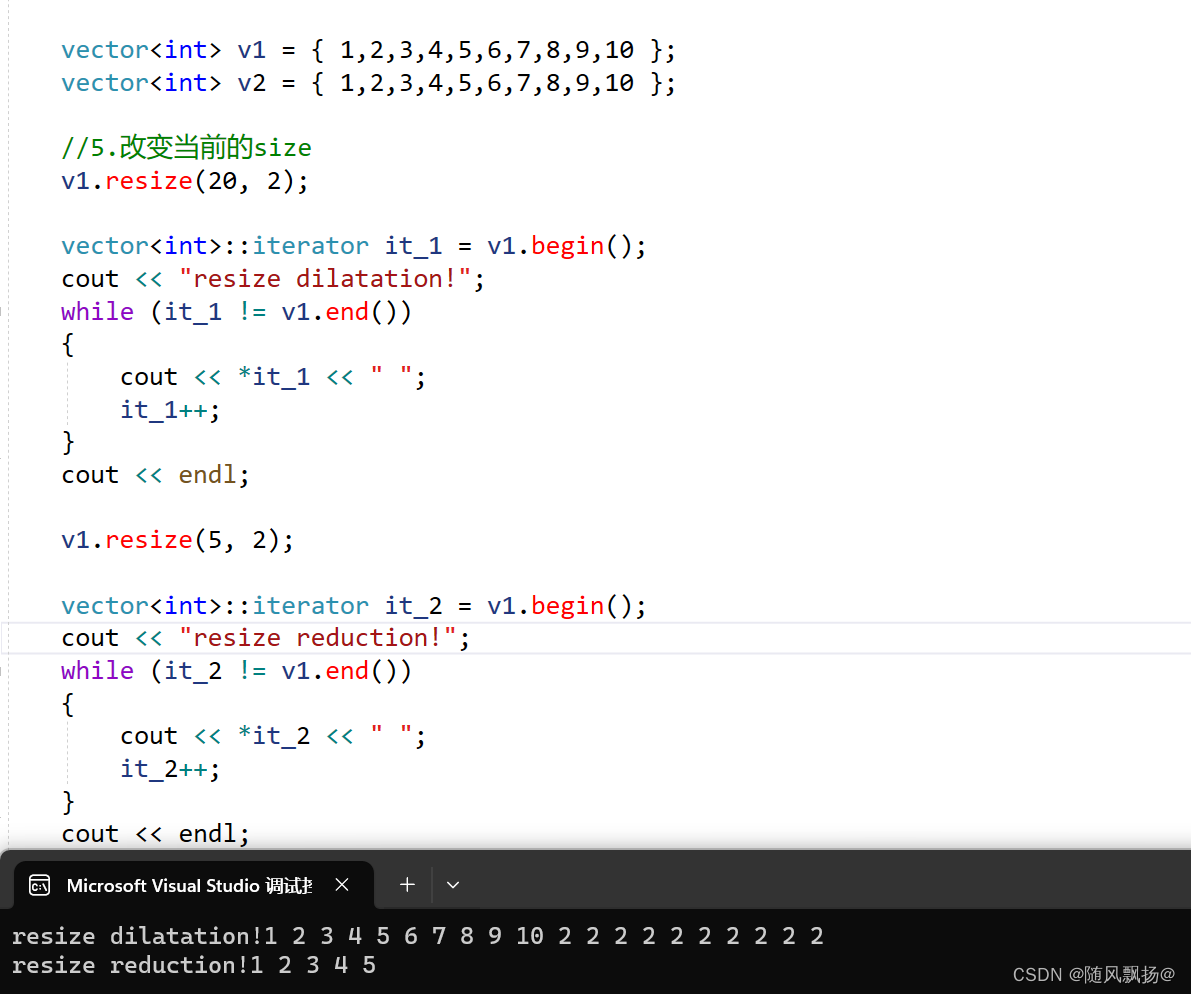
5.resize():改变vector的size
//void resize (size_type n, value_type val = value_type());
//我们通过上面的代码发现resize改变size的大小同时是会去初始化这些空间的!
void text_3()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
vector<int> v2 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
//5.改变当前的size
v1.resize(20, 2);
vector<int>::iterator it_1 = v1.begin();
cout << "resize dilatation!";
while (it_1 != v1.end())
{
cout << *it_1 << " ";
it_1++;
}
cout << endl;
v1.resize(5, 2);
vector<int>::iterator it_2 = v1.begin();
cout << "resize reduction!";
while (it_2 != v1.end())
{
cout << *it_2 << " ";
it_2++;
}
cout << endl;
}
6.reserve():改变vector的capacity
//void reserve (size_type n);
//我们通过上面的代码发现reserve适用于知道需要多少空间的情况并且这些空间不需要当前就去初始化
void text_3()
{
//6.改变当前的capacity
vector<int> v1;
v1.reserve(100);
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
flag++;
if (flag == 10)
{
cout << "new capacity:" << v1.capacity() << endl;
flag = 0;
}
}
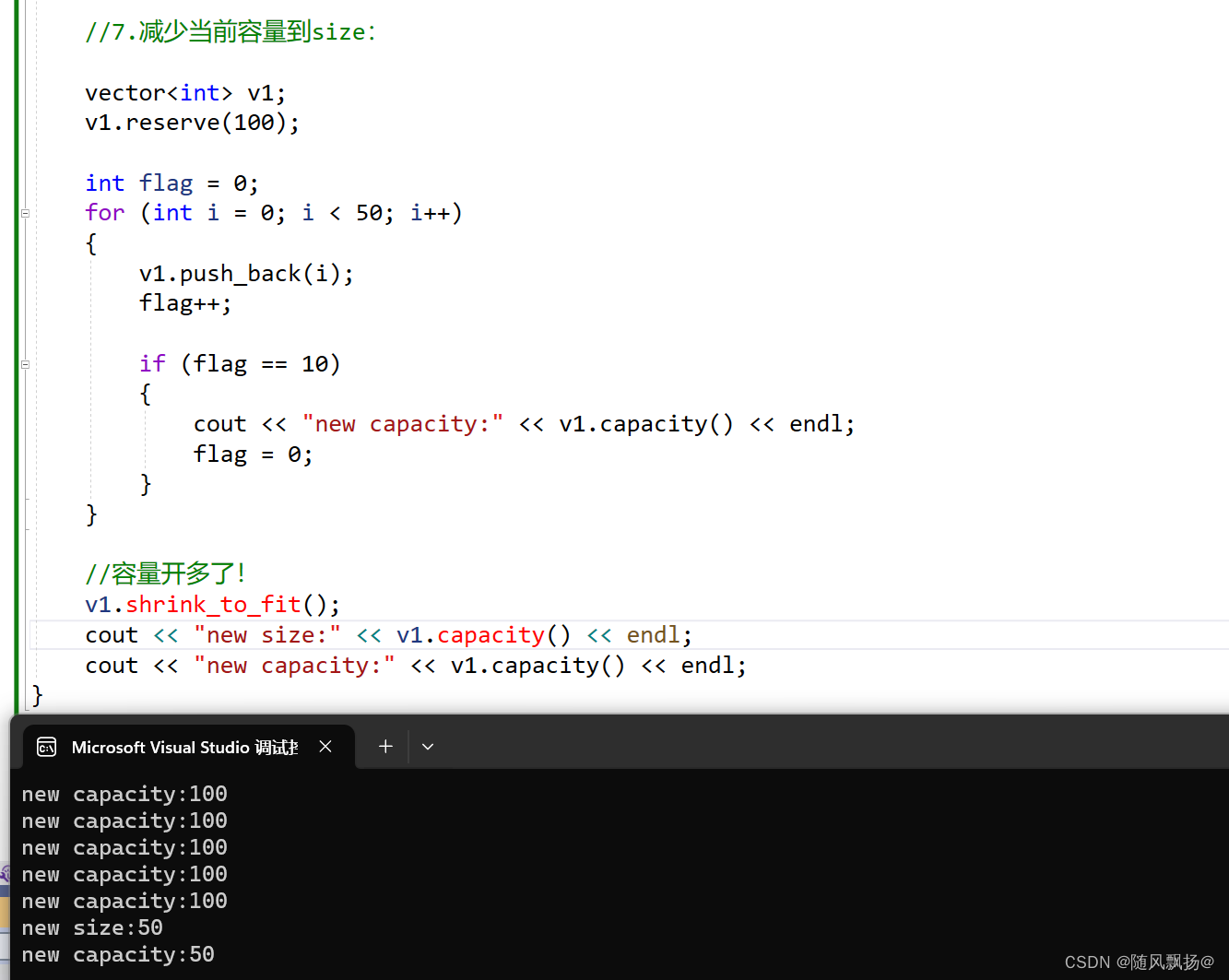
}
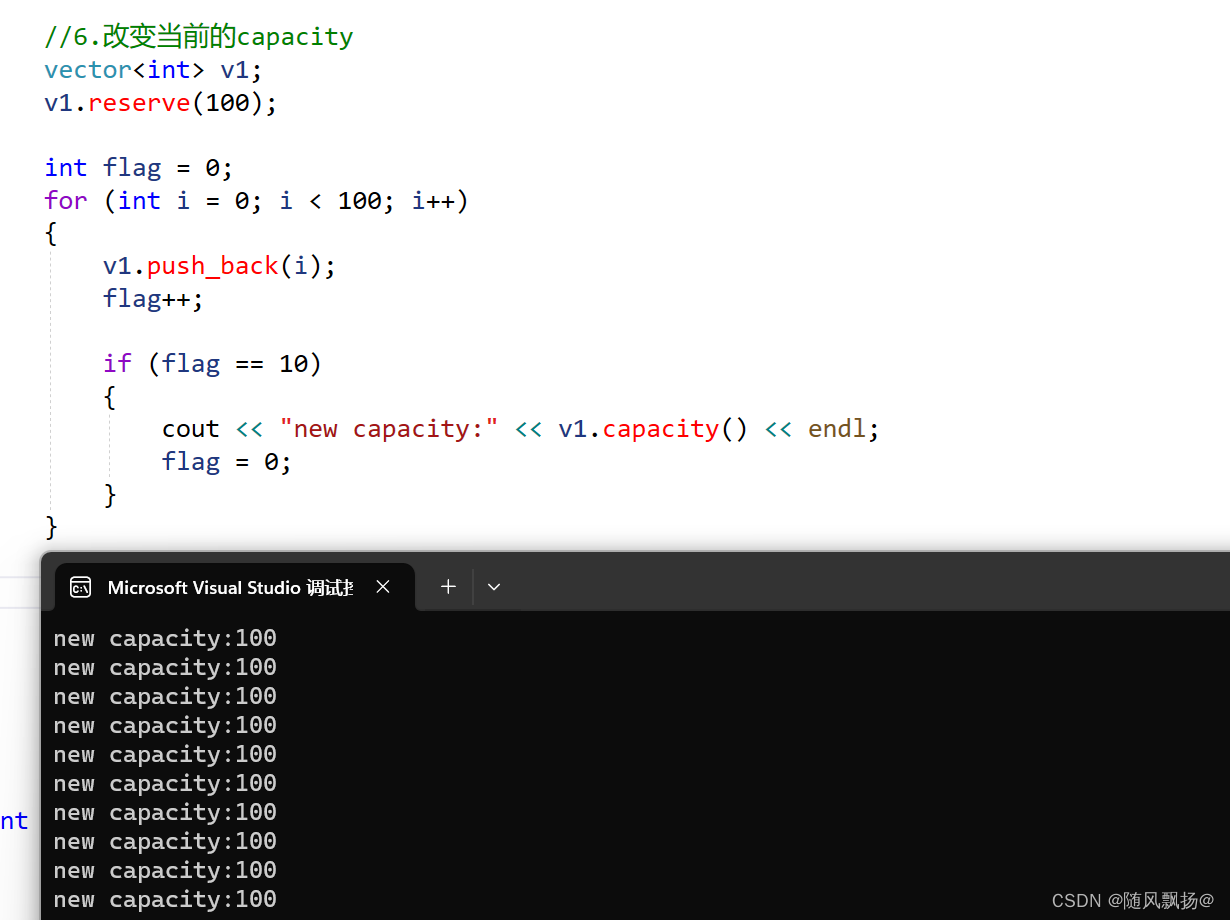
7.shrink_to_fit(): 减少当前容量到size的大小:
shrink_to_fit() C++ 11 新增内容
我们当前的capacity比较大当前情况以后都不会扩容不需要额外的空间了在这个情况下可以使用shrink_to_fit()进行减少容量到当前的size!
void text_3()
{
//7.减少当前容量到size:
vector<int> v1;
v1.reserve(100);
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
flag++;
if (flag == 10)
{
cout << "new capacity:" << v1.capacity() << endl;
flag = 0;
}
}
//容量开多了!
v1.shrink_to_fit();
cout << "new size:" << v1.capacity() << endl;
cout << "new capacity:" << v1.capacity() << endl;
}
4.增删查改:
1.operator[] 和 at:


1.使用和string中的[] 和at的使用是相同的!
2.operator[] 是断言检查直接报错
3.at 是 抛异常的进行检查!比较温柔!
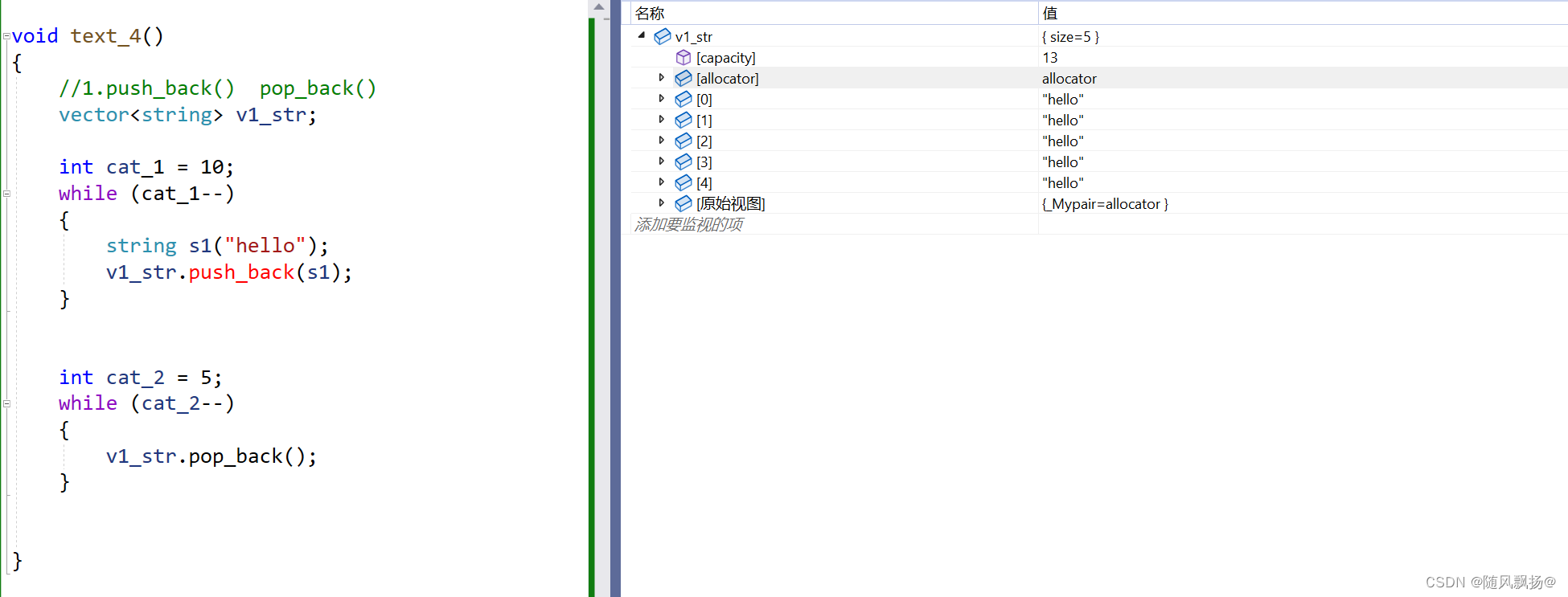
2.push_back() 和 pop_back()


void text_4()
{
//1.push_back() pop_back()
vector<string> v1_str;
int cat_1 = 10;
while (cat_1--)
{
string s1("hello");
v1_str.push_back(s1);
}
int cat_2 = 5;
while (cat_2--)
{
v1_str.pop_back();
}
}
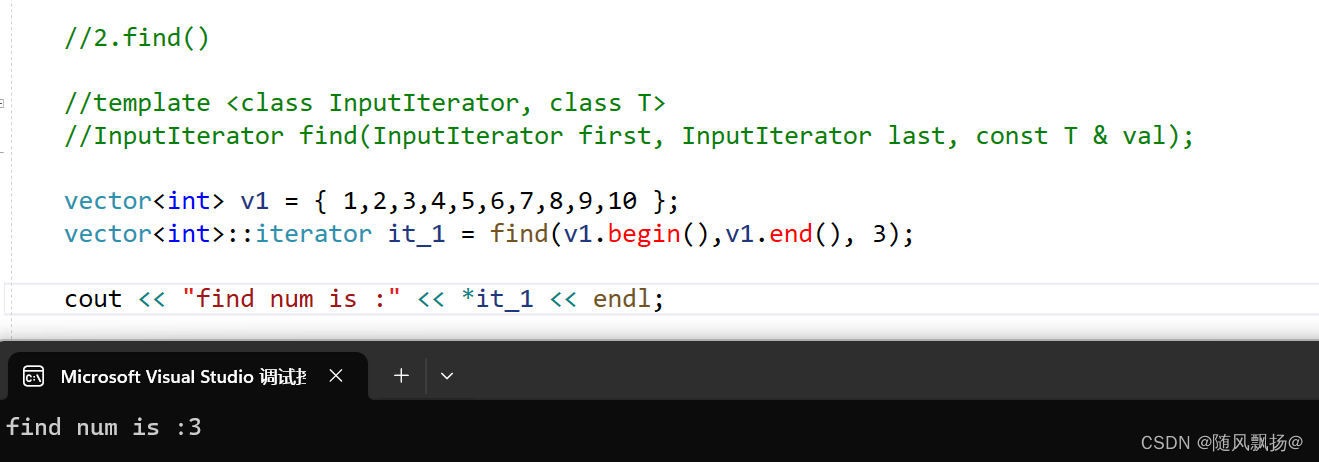
3.find()

1.find在一个迭代器范围内寻找想要找到的值并且返回迭代器。
void text_4()
{
//2.find()
//template <class InputIterator, class T>
//InputIterator find(InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const T & val);
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
vector<int>::iterator it_1 = find(v1.begin(),v1.end(), 3);
cout << "find num is :" << *it_1 << endl;
}
4.insert 和 erase


1.insert和erase 通常是和find()在一起使用:
2.insert 在postion位置之前插入一个数据因为插入数据需要把后面的数据向会移动。
3.erase是删除postion位置的数据并且后面的数据需要向前面覆盖。
4.注意:每次插入或者删除数据迭代器的值会更新!
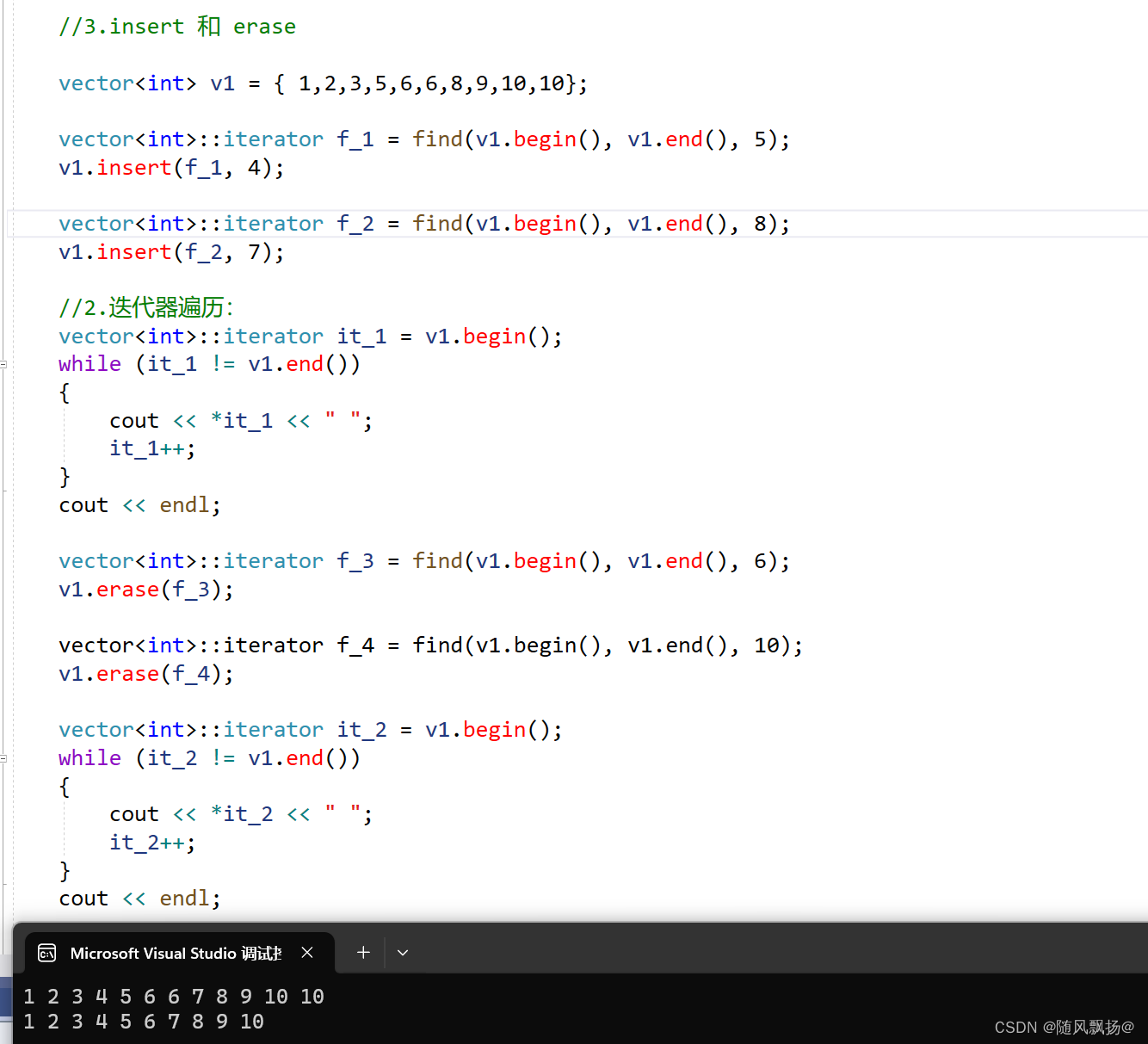
void text_4()
{
//3.insert 和 erase
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,5,6,6,8,9,10,10};
vector<int>::iterator f_1 = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 5);
v1.insert(f_1, 4);
vector<int>::iterator f_2 = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 8);
v1.insert(f_2, 7);
//2.迭代器遍历:
vector<int>::iterator it_1 = v1.begin();
while (it_1 != v1.end())
{
cout << *it_1 << " ";
it_1++;
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator f_3 = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 6);
v1.erase(f_3);
vector<int>::iterator f_4 = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 10);
v1.erase(f_4);
vector<int>::iterator it_2 = v1.begin();
while (it_2 != v1.end())
{
cout << *it_2 << " ";
it_2++;
}
cout << endl;
}
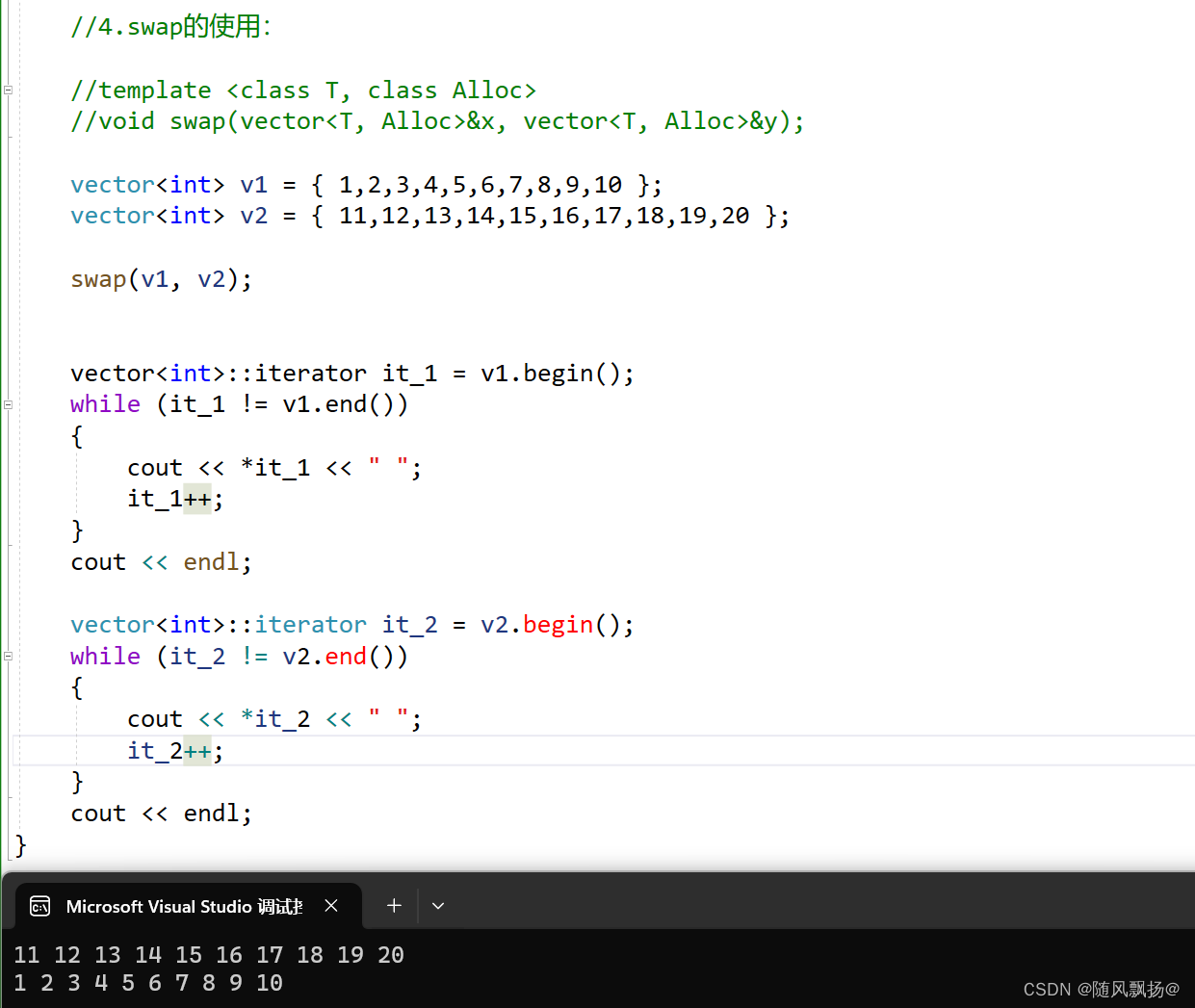
5.swap()

void text_4()
{
//4.swap的使用:
//template <class T, class Alloc>
//void swap(vector<T, Alloc>&x, vector<T, Alloc>&y);
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
vector<int> v2 = { 11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20 };
swap(v1, v2);
vector<int>::iterator it_1 = v1.begin();
while (it_1 != v1.end())
{
cout << *it_1 << " ";
it_1++;
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it_2 = v2.begin();
while (it_2 != v2.end())
{
cout << *it_2 << " ";
it_2++;
}
cout << endl;
}
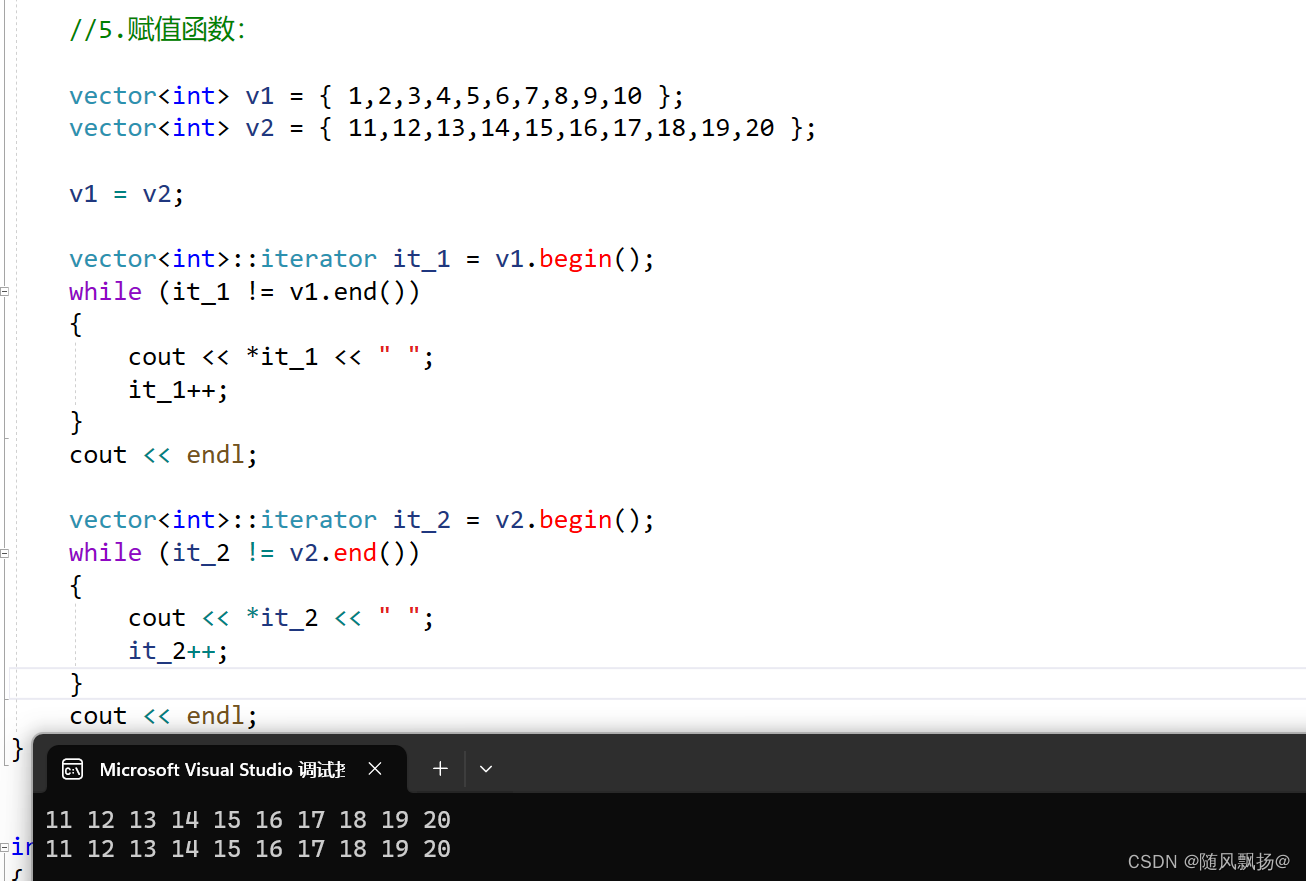
5.赋值函数 和 拷贝构造函数:
1.给一个对象初始化赋值其实是拷贝构造:
2.给两个已经初始化好的数据进行赋值才是赋值
//5.赋值函数:
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
vector<int> v2 = { 11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20 };
v1 = v2;
vector<int>::iterator it_1 = v1.begin();
while (it_1 != v1.end())
{
cout << *it_1 << " ";
it_1++;
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it_2 = v2.begin();
while (it_2 != v2.end())
{
cout << *it_2 << " ";
it_2++;
}
cout << endl;
二.练习题:
1.只出现一次的数字_1

1-1:GIF 题目解析
思路一:1.使用异或思路把所有数据遍历异或一边。
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
int value = 0;
for(auto num:nums)
{
value^=num;
}
return value;
}
};
2.只出现一次的数字_2

思路一:排序+三指针遍历
1.因为排完序,不同的那个数始终出现在第一个指针位置:
2.特殊情况有两个:
2-1:只有一个数子直接返回
2-2:排序之后单个数字在最后中间指针和末尾下标的越界问题要考虑到!
2-1:GIF 题目解析
class Solution {
public:
int singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size()==1)
return nums[0];
//1.排序
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
//2.三指针遍历数据:
int l = 0;
int m = 1;
int r = 2;
while(l < nums.size())
{
if( m >= nums.size() && r >= nums.size())
{
return nums[l];
}
if(nums[m] == nums[r] && nums[m] != nums[l])
{
return nums[l];
}
else
{
l+=3;
m+=3;
r+=3;
}
}
return 0;
}
};
3.只出现一次的数字_3


3-1:GIF 题目解析

class Solution {
public:
vector<int> singleNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
//0.特殊情况:
int n = nums.size();
if(n==2)
return nums;
//1.排序
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
//2.创建双指针分析各种情况解决方案:
int left = 0;
int right = 1;
vector<int> vv ;
while(left<n && right<=n)
{
//情况1: 1 1 2 3 3 4 4 5
if(right == n)
{
vv.push_back(nums[left]);
break;
}
if(nums[left]==nums[right])
{
left+=2;
right+=2;
}
else
{
vv.push_back(nums[left]);
left+=1;
right+=1;
}
}
return vv;
}
};
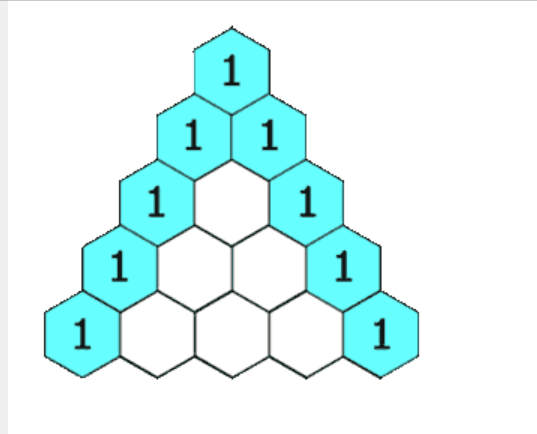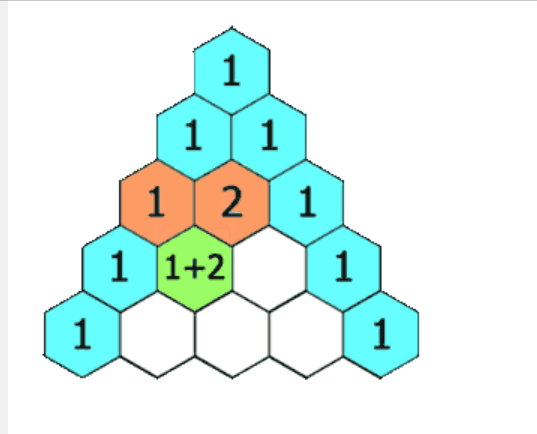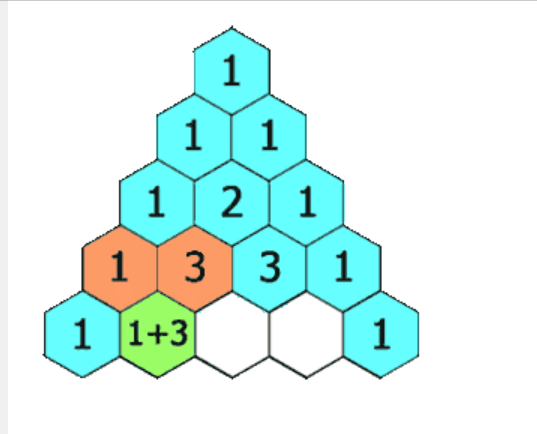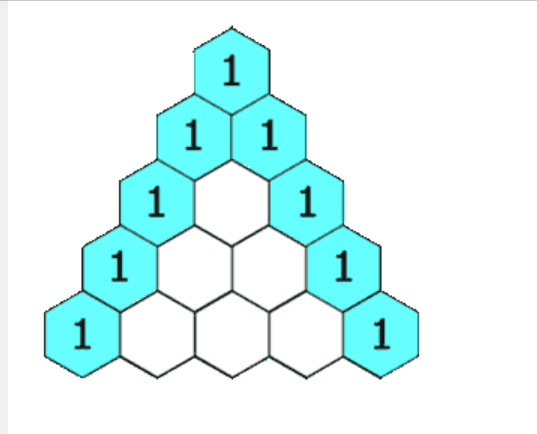
4.杨辉三角

class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> generate(int numRows) {
vector<vector<int>> vv(numRows);
for (size_t i = 0; i < numRows; i++)
{
vv[i].reserve(i + 1);
vv[i].resize(i + 1, 0);
vv[i][0] = 1;
vv[i][i] = 1;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < vv.size(); i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < vv[i].size(); j++)
{
if (vv[i][j] == 0)
{
vv[i][j] = vv[i - 1][j] + vv[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
}
return vv;
}
};
4-1:GIF 题目解析
5.删除有序数组中的重复项
思路一:
1.记住两个指针进行遍历数据:
2.同时进行判断:
2-1:数据相同:删除后面的那个it_2 更新:
2-1:数据不同:it_1++ it_2++
5-1:GIF 题目解析

class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int>::iterator it_1 = nums.begin();
vector<int>::iterator it_2 = nums.begin() + 1;
int count = 0;
while (it_2 != nums.end())
{
if (*it_1 == *it_2)
{
nums.erase(it_2);
it_2 = it_1 + 1;
//更新因为删除数据导致的迭代器的变化
}
else if (*it_1 != *it_2)
{
it_1++;
it_2++;
}
}
return nums.size();
}
};
6.数字中出现次数超过一半的数字

思路一:
6-1:GIF 题目解析

#include <iostream>
class Solution {
public:
int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int>& numbers)
{
// write code here
if (numbers.size() == 1)
{
return numbers[0];
}
//1.遍历寻找众数:
vector<int>::iterator it_1 = numbers.begin();
int cnt = 0;
int count = -1;
while (it_1 != numbers.end())
{
if (cnt == 0)
{
count = *it_1;
cnt++;
}
else if (cnt > 0)
{
if (count == *it_1)
{
cnt++;
}
else
{
cnt--;
}
}
it_1++;
}
cout << cnt << ":" << count << endl;
//2.确定是不是重数:
cnt = 0;
for (const int num : numbers)
{
if (num == count)
{
cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt > (numbers.size() / 2))
{
return count;
}
return 0;
}
};
7.电话号码的字母组合

方法一:循环方法:
1.一个vector< string > 类型的顺序表保存数据通过下标对应字符串
2.因为输入的数字字符串是有长度限制的所以暴力的方法就是。
3.从输入数字字符串长度为2到4进行多次的循环遍历数据。
4.在for的最深处进行const char* 的定义通过string进行转化:
5.在for外面先转化为const char* 类型方便循环的遍历数据!
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
vector<string> tem;
tem.push_back("");
tem.push_back("");
tem.push_back("abc");
tem.push_back("def");
tem.push_back("ghi");
tem.push_back("jkl");
tem.push_back("mno");
tem.push_back("pqrs");
tem.push_back("tuv");
tem.push_back("wxyz");
int size_d = (int)digits.size();
const char* num = digits.c_str();
vector<string> buffer;
if (size_d == 0)
{
return buffer;
}
if (size_d == 1)
{
int pos = num[0] - 48;
int size = (int)tem[pos].size();
const char* arr = tem[pos].c_str();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
char ch = arr[i];
string tmp(1,ch);
buffer.push_back(tmp);
}
}
else if (size_d > 1)
{
if (size_d == 2)
{
int pos_1 = num[0] - 48;
int pos_2 = num[1] - 48;
int size_1 = (int)tem[pos_1].size();
int size_2 = (int)tem[pos_2].size();
const char* arr_1 = tem[pos_1].c_str();
const char* arr_2 = tem[pos_2].c_str();
for (int i = 0; i < size_1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size_2; j++)
{
const char arr[3] = { arr_1[i],arr_2[j],'\0' };
string s1(arr);
buffer.push_back(s1);
}
}
}
if (size_d == 3)
{
int pos_1 = num[0] - 48;
int pos_2 = num[1] - 48;
int pos_3 = num[2] - 48;
int size_1 = (int)tem[pos_1].size();
int size_2 = (int)tem[pos_2].size();
int size_3 = (int)tem[pos_3].size();
const char* arr_1 = tem[pos_1].c_str();
const char* arr_2 = tem[pos_2].c_str();
const char* arr_3 = tem[pos_3].c_str();
for (int i = 0; i < size_1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size_2; j++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < size_3; x++)
{
const char arr[4] = { arr_1[i],arr_2[j],arr_3[x],'\0' };
string s1(arr);
buffer.push_back(s1);
}
}
}
}
if (size_d == 4)
{
int pos_1 = num[0] - 48;
int pos_2 = num[1] - 48;
int pos_3 = num[2] - 48;
int pos_4 = num[3] - 48;
int size_1 = (int)tem[pos_1].size();
int size_2 = (int)tem[pos_2].size();
int size_3 = (int)tem[pos_3].size();
int size_4 = (int)tem[pos_4].size();
const char* arr_1 = tem[pos_1].c_str();
const char* arr_2 = tem[pos_2].c_str();
const char* arr_3 = tem[pos_3].c_str();
const char* arr_4 = tem[pos_4].c_str();
for (int i = 0; i < size_1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size_2; j++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < size_3; x++)
{
for (int y = 0; y < size_4; y++)
{
const char arr[5] = { arr_1[i],arr_2[j],arr_3[x],arr_4[y],'\0' };
string s1(arr);
buffer.push_back(s1);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return buffer;
}
};
方法二:dfs方法:

class Solution {
public:
vector<string> tem = {"","","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"};
void combine(string& num, size_t di , string com_str , vector<string>& vv)
{
if(di==num.size())
{
vv.push_back(com_str);
return;
}
int pos = num[di] - '0';
int len = tem[pos].size();
string s1 = tem[pos];
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
combine(num,di+1,com_str+s1[i],vv);
}
}
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
vector<string> vv;
if(digits.size()==0)
return vv;
combine(digits,0,"",vv);
return vv;
}
};
7-1:GIF 题目解析
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!

