2807. Insert Greatest Common Divisors in Linked List
2024-01-07 17:36:26
Given the head of a linked list?head, in which each node contains an integer value.
Between every pair of adjacent nodes, insert a new node with a value equal to the?greatest common divisor?of them.
Return?the linked list after insertion.
The?greatest common divisor?of two numbers is the largest positive integer that evenly divides both numbers.
Example 1:
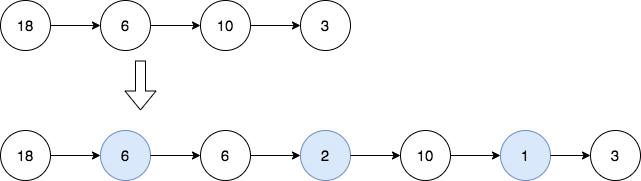
Input: head = [18,6,10,3] Output: [18,6,6,2,10,1,3] Explanation: The 1st diagram denotes the initial linked list and the 2nd diagram denotes the linked list after inserting the new nodes (nodes in blue are the inserted nodes). - We insert the greatest common divisor of 18 and 6 = 6 between the 1st and the 2nd nodes. - We insert the greatest common divisor of 6 and 10 = 2 between the 2nd and the 3rd nodes. - We insert the greatest common divisor of 10 and 3 = 1 between the 3rd and the 4th nodes. There are no more adjacent nodes, so we return the linked list.
Example 2:

Input: head = [7] Output: [7] Explanation: The 1st diagram denotes the initial linked list and the 2nd diagram denotes the linked list after inserting the new nodes. There are no pairs of adjacent nodes, so we return the initial linked list.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range?
[1, 5000]. 1 <= Node.val <= 1000
法一:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* insertGreatestCommonDivisors(ListNode* head) {
int count = 1;
while(head->next == nullptr){
return head;
}
ListNode * node = head;
while(node -> next != nullptr){
int a,b;
if(node -> val >= node -> next -> val){
a = node -> val;
b = node -> next -> val;
}
else{
a = node -> next -> val;
b = node -> val;
}
int temp;
while(b!= 0){
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp%b;
}
node -> next = new ListNode(a,node->next);
node = node -> next -> next;
}
return head;
}
};法二:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* insertGreatestCommonDivisors(ListNode* head) {
while(head->next == nullptr){
return head;
}
ListNode * node = head;
while(node -> next != nullptr){
node -> next = new ListNode(std::__gcd(node->val, node->next->val),node->next);
node = node -> next -> next;
}
return head;
}
};
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/Recursions/article/details/135430266
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!