MapReduce序列化实例代码
2023-12-17 22:33:40
1 )需求:统计每个学号该月的超市消费、食堂消费、总消费2 )输入数据格式序号 学号 超市消费 食堂消费18 202200153105 8.78123 )期望输出格式key (学号) value ( bean 对象)202200153105 8.78 12 20.78
代码一定要自己打,并且知道每一步的含义,在写代码时我也遇到了各种问题,比如不知道Bean对象怎么写,怎么实现序列化反序列化,以及对应的包导错导致一直运行不出来,前一段时间一直在准备六级考试,导致很多课程都落下好多,接下来有时间继续更新
1.
序列化概述
(
1
)什么是序列化
序列化就是把内存中的对象,转换成字节序列(或其他数据传输协议)以便于存储到磁盘(持久化)和网络传输。
反序列化就是将收到字节序列(或其他数据传输协议)或者是磁盘的持久化数据,转换成内存中的对象。
(
2
)为什么要序列化
对象只生存在内存里,关机断电就没有了。而且“活的”对象只能由本地的进程使用,不能被发送到网络上的另外一台计算机。 然而序列化可以存储“活的”对象,可以将“活的”对象发送到远程计算机。
(
3
)为什么不用
Java
的序列化
Java
的序列化是一个重量级序列化框架(
Serializable
),一个对象被序列化后,会附带很多额外的信息(各种校验信息,Header
,继承体系等),不便于在网络中高效传输。所以,Hadoop
自己开发了
一套序列化机制(Writable)
。
(4)Hadoop序列化特点
1
)紧凑 :高效使用存储空间。
2
)快速:读写数据的额外开销小。
3
)互操作:支持多语言的交互
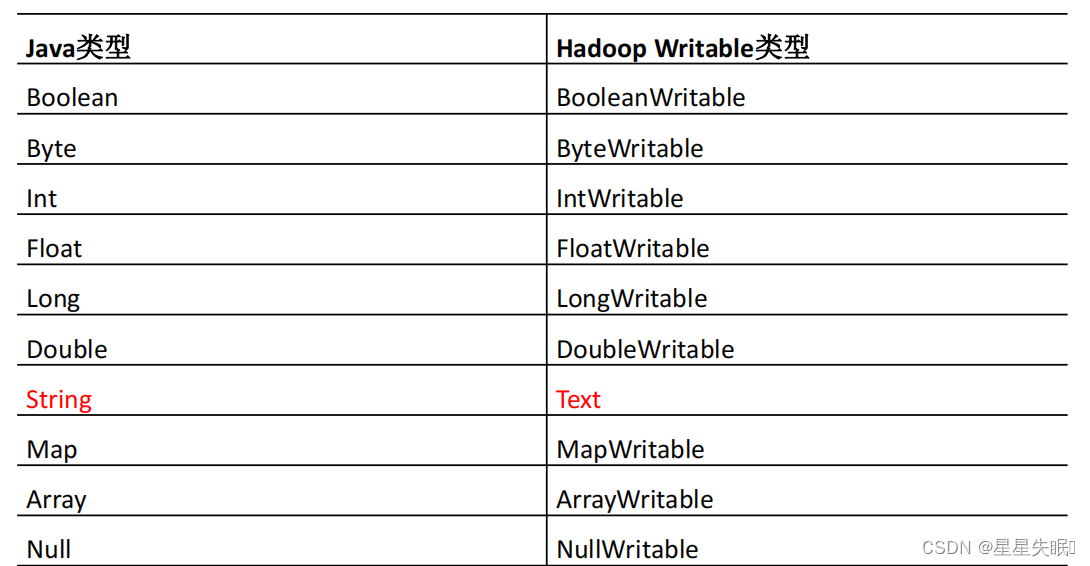
自定义序列化
实际开发过程中,基本序列化类型不能满足所有需求,比如在 Hadoop 框架内部 传递一个bean 对象,那么该对象就需要实现序列化接口。
package com.nefu.zhangna.maxcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
public class StudentBean implements Writable {
private double foodFee;
private double maketFee;
private double totalFee;
public StudentBean(){ //反序列化必须调用空参构造函数
}
public double getFoodFee() {
return foodFee;
}
public void setFoodFee(double foodFee) {
this.foodFee = foodFee;
}
public double getMaketFee() {
return maketFee;
}
public void setMaketFee(double maketFee) {
this.maketFee = maketFee;
}
public double getTotalfee() {
return totalFee;
}
public void setTotalfee(double totalfee) {
this.totalFee = totalfee;
}
public void setTotalFee(){
this.totalFee=this.foodFee+this.maketFee;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeDouble(foodFee);
out.writeDouble(maketFee);
out.writeDouble(totalFee);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.foodFee=in.readDouble();
this.maketFee=in.readDouble();
this.totalFee=in.readDouble();
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return this.foodFee+"\t"+this.maketFee+"\t"+this.totalFee;
}
}
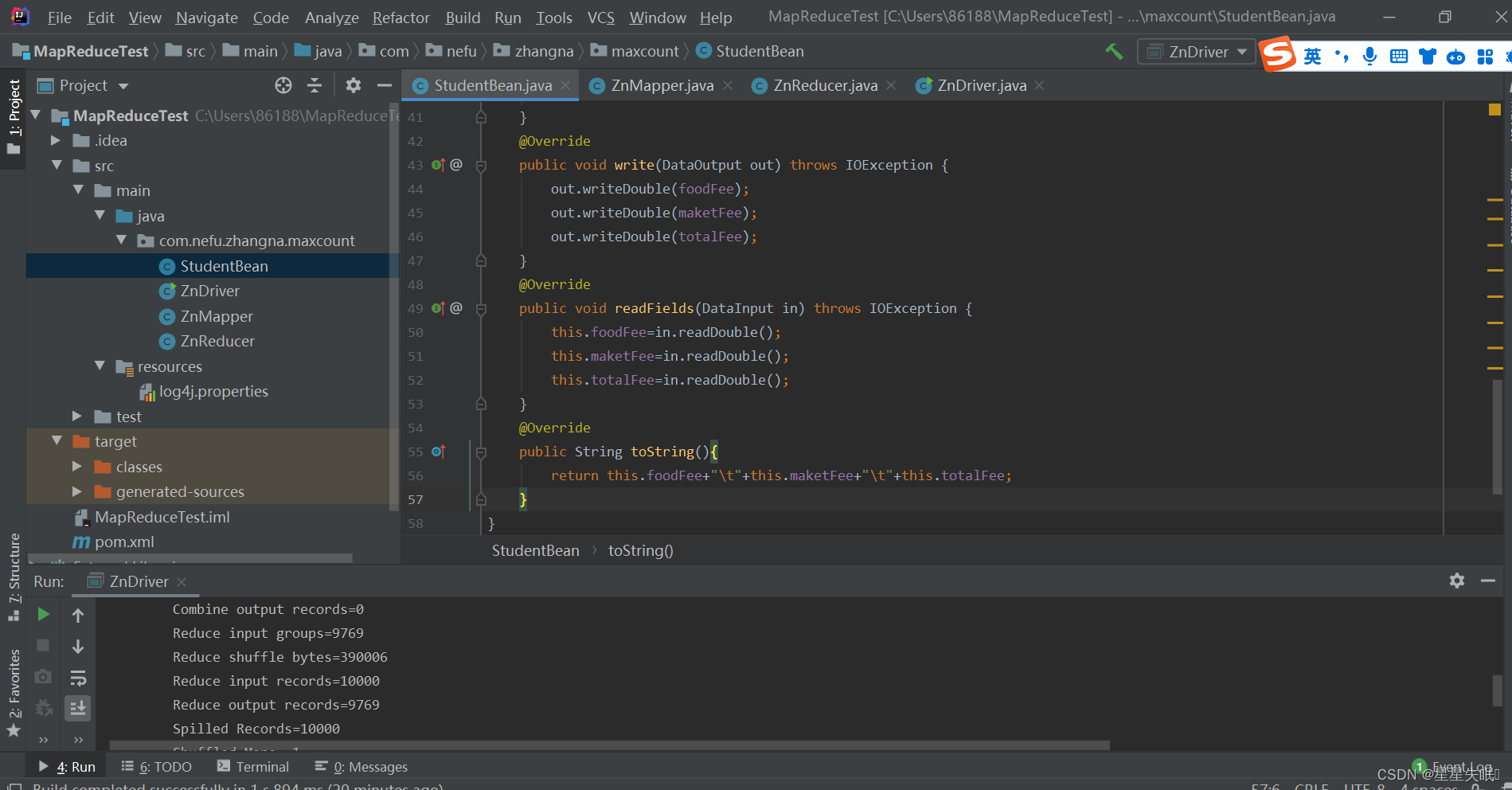
Map阶段( 1 )读取一行数据,切分字段( 2 )抽取超市消费、食堂消费( 3 )以学号为 key , bean 对象为 value 输出, context.write( 学号, bean)( 4 ) bean 对象能够传输的前提是实现序列化接口 Writable
package com.nefu.zhangna.maxcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ZnMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text,Text,StudentBean> {
private Text outk=new Text();
private StudentBean outv=new StudentBean();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key,Text value,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line=value.toString();
String[] content=line.split("\t");
String schoolnumber=content[1];
String foodFee=content[2];
String marketFee=content[3];
outk.set(schoolnumber);
outv.setFoodFee(Double.parseDouble(foodFee));
outv.setMaketFee(Double.parseDouble(marketFee));
outv.setTotalFee();
context.write(outk,outv);
}
}
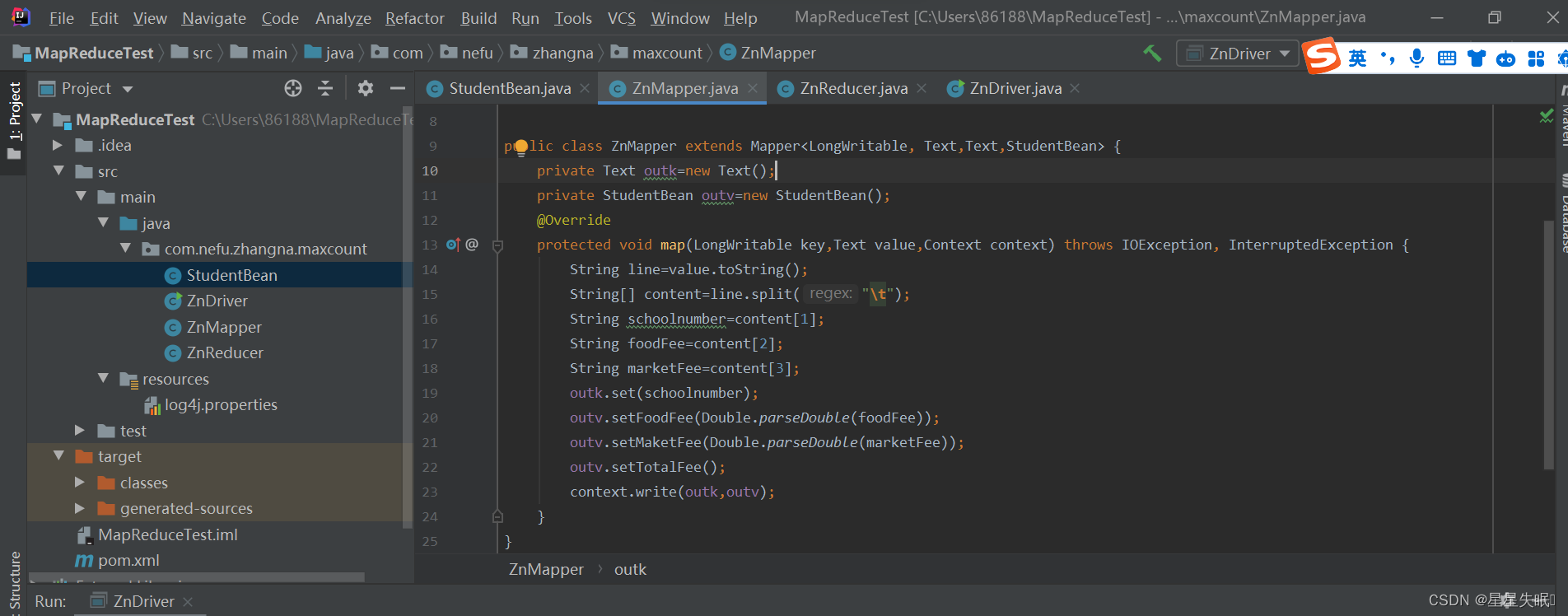
Reduce( 1 )累加每个 key (学号)对应的 foodfee marketfee totalfee
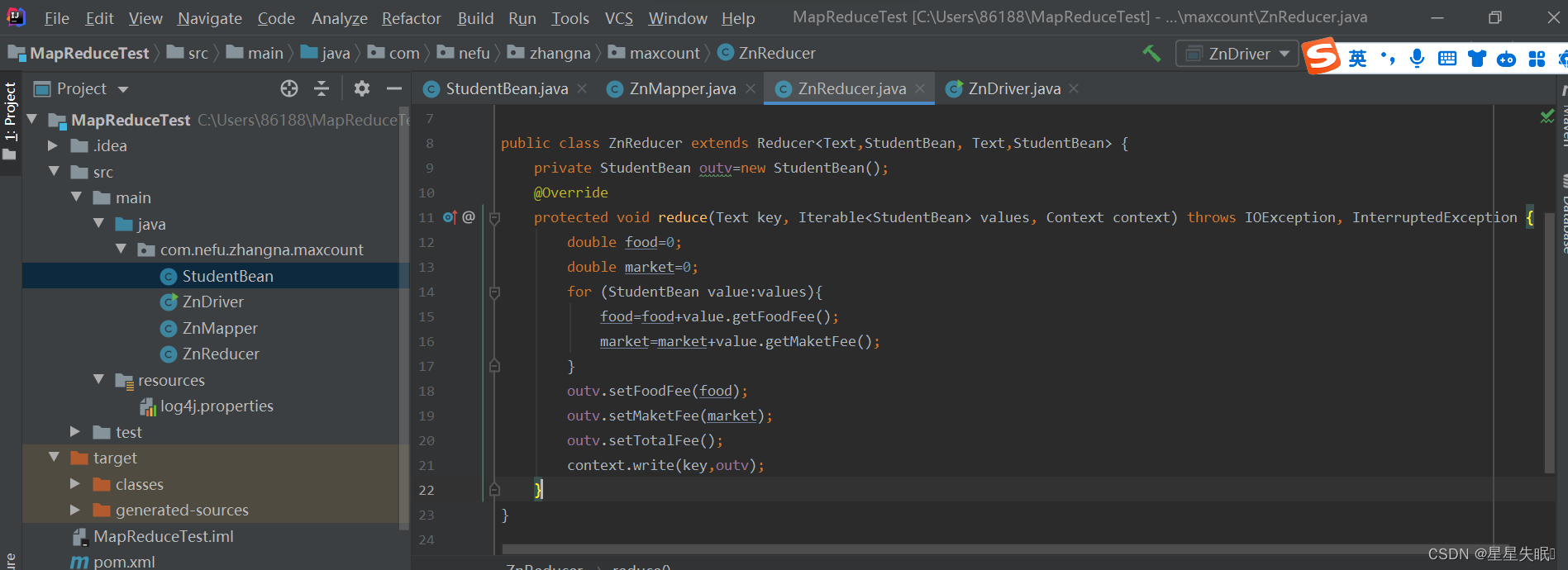
package com.nefu.zhangna.maxcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ZnReducer extends Reducer<Text,StudentBean, Text,StudentBean> {
private StudentBean outv=new StudentBean();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<StudentBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
double food=0;
double market=0;
for (StudentBean value:values){
food=food+value.getFoodFee();
market=market+value.getMaketFee();
}
outv.setFoodFee(food);
outv.setMaketFee(market);
outv.setTotalFee();
context.write(key,outv);
}
}
package com.nefu.zhangna.maxcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ZnDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration configuration=new Configuration();
Job job=Job.getInstance(configuration);
job.setJarByClass(ZnDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(ZnMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(ZnReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(StudentBean.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,new Path("D:\\mydata.txt"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("D:\\cluster\\studentbean"));
boolean result=job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(result?0:1);
}
}


原始数据

经过map-reduce之后


文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/zn2021220822/article/details/135051135
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!