android之Handler详解
2023-12-24 18:32:53
一,Handler实现每一秒打印一次
第一种实现
该实现是从1秒的开始进行计时
public class TimerThread extends Thread {
private H mH;
private int timerMills = 1000;
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
Looper.prepare();
mH = new H();
mH.sendMessageDelayed(mH.obtainMessage(), timerMills);
Looper.loop();
}
class H extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
Log.e("TimerThread", "M---------------------------------");
mH.sendMessageDelayed(mH.obtainMessage(), timerMills - System.currentTimeMillis() % timerMills);
}
}
public void setTimerMills(int timerMills) {
this.timerMills = timerMills;
}
public void quit() {
Looper.myLooper().quit();
}
}
代码打印如下,明显一
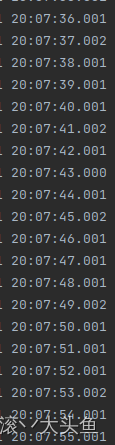
第二种实现
该方法是从一秒内随意位置进行计时打印
public class TimerThread extends Thread {
private H mH;
private int timerMills = 1000;
private long oldTime;
private long diffTime;
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
Looper.prepare();
mH = new H();
oldTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
mH.sendMessageDelayed(mH.obtainMessage(), timerMills);
Looper.loop();
}
class H extends Handler {
@Override
public void handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
long newTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long diff = newTime - oldTime;
oldTime = newTime;
long startTIme;
if (diff > timerMills) {
diffTime += diff % timerMills;
} else if (diff < timerMills) {
diffTime += diff - timerMills;
}
startTIme = timerMills - diffTime;
Log.e("TimerThread", "-------" + timerMills + "------" + diff + "-------" + diffTime + "-------" + startTIme + "------");
mH.sendMessageDelayed(mH.obtainMessage(), startTIme);
}
}
public void setTimerMills(int timerMills) {
this.timerMills = timerMills;
}
public void quit() {
Looper.myLooper().quit();
}
}
打印如下
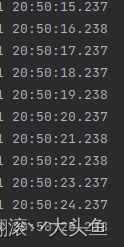
二,源码解析
Looper.prepare()
1,保存创建的Looper到ThreadLocal
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}
2,创建MessageQueue,活动当前线程
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}Message创建,获取了一个native方法
MessageQueue(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQuitAllowed = quitAllowed;
mPtr = nativeInit();
}2,Looper.loop()出队列
public static void loop() {
//获取当前线程
final Looper me = myLooper();
//进行死循环获取消息
for (;;) {
if (!loopOnce(me, ident, thresholdOverride)) {
return;
}
}
} private static boolean loopOnce(final Looper me,
final long ident, final int thresholdOverride) {
//从MessageQueuq中拿出Message
Message msg = me.mQueue.next(); // might block
//如果messagequeue中没有消息了,退出循环
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return false;
}
try {
//拿出message中的Handler,执行它的ddispatchMessage;
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
} catch (Exception exception) {
} finally {
}
//message释放
msg.recycleUnchecked();
return true;
}
1,MessageQueue.next()出队
Message next() {
// Return here if the message loop has already quit and been disposed.
// This can happen if the application tries to restart a looper after quit
// which is not supported.
final long ptr = mPtr;
if (ptr == 0) {
return null;
}
int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iteration
int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
for (;;) {
if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) {
Binder.flushPendingCommands();
}
//在没有消息的时候,会阻塞在这里,等待唤醒
nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);
synchronized (this) {
// Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found.
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
Message prevMsg = null;
//头部消息赋值给msg
Message msg = mMessages;
//当前消息不为空并且消息的handler是空的
if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {
// Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue.
do {
prevMsg = msg;
msg = msg.next;
} while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());
}
//当前消息不为空
if (msg != null) {
//当前实际小于msg的时间
if (now < msg.when) {
// Next message is not ready. Set a timeout to wake up when it is ready.
//计算这条消息在当前时间需要多久才执行
nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} else {
//正常执行该条消息秒,
// Got a message.
mBlocked = false;
//prevMsg.next等于下一条消息
if (prevMsg != null) {
prevMsg.next = msg.next;
} else {
//该消息等于消息队列的下一条消息
mMessages = msg.next;
}
//第一个消息从消息链表中断开
msg.next = null;
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Returning message: " + msg);
msg.markInUse();
return msg;
}
} else {
// No more messages.
//消息队列没有消息了
nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;
}
// Process the quit message now that all pending messages have been handled.
//退出消息循环,退出loop循环
if (mQuitting) {
dispose();
return null;
}
// If first time idle, then get the number of idlers to run.
// Idle handles only run if the queue is empty or if the first message
// in the queue (possibly a barrier) is due to be handled in the future.
if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0
&& (mMessages == null || now < mMessages.when)) {
pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size();
}
//当没有消息后,进入下一次循环,消息机制以便于阻塞等待
if (pendingIdleHandlerCount <= 0) {
// No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more.
mBlocked = true;
continue;
}
if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) {
mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)];
}
mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers);
}
// Run the idle handlers.
// We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration.
for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) {
final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i];
mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handler
boolean keep = false;
try {
keep = idler.queueIdle();
} catch (Throwable t) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "IdleHandler threw exception", t);
}
if (!keep) {
synchronized (this) {
mIdleHandlers.remove(idler);
}
}
}
// Reset the idle handler count to 0 so we do not run them again.
pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0;
// While calling an idle handler, a new message could have been delivered
// so go back and look again for a pending message without waiting.
nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
}
}2,Message.target.dispatchMessage(msg)执行消息回调
3,Hanler.dispatchMessage
对应方法是不是以为空,不为空就执行对应的数据
public void dispatchMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
//初始化handler的时候创建
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
//如果没有创建,直接调用handler中的方法,该方法是一个空方法
handleMessage(msg);
}
}msg.callback
Message类中创建
public static Message obtain(Handler h, Runnable callback) {
Message m = obtain();
m.target = h;
m.callback = callback;
return m;
}?
3,入队
1,Handler创建
public Handler(@Nullable Callback callback, boolean async) {
//获取消息队列
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
//获取传入的caollback
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}2,Handler.sendMessage
Handler的所有senndMessage方法最总都会调用
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(@NonNull Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
//创建handler的时候获取到队列
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
}3,Handler.enqueueMessage
private boolean enqueueMessage(@NonNull MessageQueue queue, @NonNull Message msg,
long uptimeMillis) {
//赋值message的handler,这里message会持有handler的对象,内存泄漏的最初位置
msg.target = this;
msg.workSourceUid = ThreadLocalWorkSource.getUid();
if (mAsynchronous) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}4,MessageQueue.queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis)
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {
if (msg.target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Message must have a target.");
}
//加锁,放在反复加入
synchronized (this) {
if (msg.isInUse()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(msg + " This message is already in use.");
}
//如果退出了,释放该message,退出
if (mQuitting) {
IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException(
msg.target + " sending message to a Handler on a dead thread");
Log.w(TAG, e.getMessage(), e);
msg.recycle();
return false;
}
msg.markInUse();
msg.when = when;
Message p = mMessages;
boolean needWake;
//将message加入到第一个位置
if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) {
// New head, wake up the event queue if blocked.
msg.next = p;
mMessages = msg;
needWake = mBlocked;
} else {
// Inserted within the middle of the queue. Usually we don't have to wake
// up the event queue unless there is a barrier at the head of the queue
// and the message is the earliest asynchronous message in the queue.
needWake = mBlocked && p.target == null && msg.isAsynchronous();
Message prev;
//循环遍历将传入的message放在对应时间点的位置
for (;;) {
prev = p;
p = p.next;
if (p == null || when < p.when) {
break;
}
if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) {
needWake = false;
}
}
msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.next
prev.next = msg;
}
// We can assume mPtr != 0 because mQuitting is false.
//如果消息队列在阻塞,就唤醒消息队列进行数据处理
if (needWake) {
nativeWake(mPtr);
}
}
return true;
}
这样handler的流程就走完了
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/luck_xiang/article/details/135139299
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!