linux系统和网络(三):IO,信号,信号量,线程
? ? ? ? 本文主要探讨linux的IO,信号,信号量,线程相关知识,详细知识可参考本博客其他文章。
信号(可参考本博客其他文章)
????????信号是内容受限的异步通信机制,硬件异常后统内核发出信号
?????????alarm产生SIGALARM信号,读端关闭后管道write产生SIGPIPE信号
常见信号
SIGINT?? ??? ??? ? 2?? ??? ? Ctrl+C(前台进程组中每个进程)
SIGABRT?? ??? ??? ?6?? ??? ? 异常终止
SIGPOLL?? SIGIO?? ?8?? ??? ? 异步IO
SIGKILL?? ??? ??? ?9?? ??? ? 杀死进程
SIGSEGV?? ??? ??? ?11?? ??? ?无效存储访问信号
SIGPIPE?? ??? ??? ?13?? ??? ?管道,socket
SIGALARM?? ??? ? 14?? ??? ?alarm
SIGTERM?? ??? ??? ?15?? ??? ?kill命令默认
SIGCHLD?? ??? ??? ?17?? ??? ?子进程终止(父进程接收信号)
SIGUSR1?? ??? ??? ?10?? ??? ?自定义信号
SIGUSR2?? ??? ??? ?12 ?? ??? 自定义信号????????信号处理
typedef void (*sighandler_t)(int);
sighandler_t signal(int signum, sighandler_t handler);
默认处理SIG_DFL
忽略处理SIG_IGN
捕获处理handler
返回出错为SIG_ERRint sigaction(int signum, const struct sigaction *act,struct sigaction *oldact);
struct sigaction {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?void ? ? (*sa_handler)(int);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?void ? ? (*sa_sigaction)(int, siginfo_t *, void *);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?sigset_t ? sa_mask;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?int ? ? ? ?sa_flags;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?void ? ? (*sa_restorer)(void);
? ? ? ? ? ?};????????sigaction可设置新捕获函数和获取旧的捕获函数,signal须在新捕获函数中获取旧捕获函数
????????alarm和pause
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? alarm内核提供闹钟的API
unsigned int alarm(unsigned int seconds);int pause(void);????????????????内核挂起,进程暂停运行,交出CPU给其他进程(阻塞住),需被信号唤醒
信号量(可参考本博客其他文章)
sem_t sem;
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);
sem:信号量,pshared:0线程间非0用于进程,value:信号量初值IO
????????阻塞IO:wait、pause、sleep、read、write等
????????非阻塞IO访问:添加O_NONBLOCK模式(fd调用fcntl)
????????select和poll(多路复用IO):外部阻塞式,内部非阻塞式自动轮询多路阻塞式IO
int poll(struct pollfd *fds, nfds_t nfds, int timeout);
struct pollfd {
int fd; /* 文件描述符*/
short events; /* 监控事件 */
short revents; /* 监控事件中满足条件的返回事件*/
};
POLLIN普通或带外优先数据可读,即POLLRDNORM | POLLRDBAND
POLLRDNORM 数据可读
POLLRDBAND 优先级带数据可读
POLLPRI 高优先级可读数据
POLLOUT普通或带外数据可写
POLLWRNORM 数据可写
POLLWRBAND 优先级带数据可写
POLLERR 发生错误
POLLHUP 发生挂起
POLLNVAL 描述字不是一个打开的文件
nfds:监控文件描述符个数
timeout:等待(ms),-1阻塞等,0:不阻塞进程,>0等待指定毫秒数int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds,fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
nfds:监控文件描述符个数
struct timeval {
long tv_sec; /* seconds */
long tv_usec; /* microseconds */
};
and
struct timespec {
long tv_sec; /* seconds */
long tv_nsec; /* nanoseconds */
};
FD_ZERO(fd_set* fdset): 将fd_set位初始化为0
FD_SET(int fd, fd_set* fdset):注册文件描述符fd信息
FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set* fdset):清除文件描述符fd信息
FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set* fdset):fd_set包含文件描述符fd信息返回真????????异步IO(操作系统中断)
????????存储映射IO(mmap):共享内存,提高效率(LCD显示和IPC间共享内存)
线程(可参考本博客其他文章)
????????进程:CPU时分复用,实现多任务系统需求,进程间切换开销大,通信效率低
????????线程间通信效率高且可多任务
????????线程函数
????????????????线程创建,退出,回收,分离,id
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
void pthread_exit(void *retval);
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);
int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);
pthread_t pthread_self(void);
线程退出后,主线程pthread_join回收子线程,pthread_detach是线程分离,子线程自回收?
????????????????取消线程
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);
线程取消状态
int pthread_setcancelstate(int state, int *oldstate);
PTHREAD_CANCEL_ENABLE:线程可取消(默认值)
PTHREAD_CANCEL_DISABLE:线程不可取消,取消请求挂起至线程状态为 PTHREAD_CANCEL_ENABLE
线程取消性类型
int pthread_setcanceltype(int type, int *oldtype);
PTHREAD_CANCEL_DEFERRED:取消请求到达,线程继续运行,取消请求挂起,直到线程到达取消点(默认)
PTHREAD_CANCEL_ASYNCHRONOUS:立即取消
线程清理函数中添加和移除清理函数
void pthread_cleanup_push(void (*routine)(void *),void *arg);
void pthread_cleanup_pop(int execute);
routine:清理函数,arg给清理函数传参
execute为0清理函数不调用且清理函数栈中最顶层函数移除,非0还清除清理该函数
线程清理函数中添加(入栈)和清理(出栈)次数相同????????????????互斥量(代码保护)
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr);
????????????????线程条件
pthread_cond_t ?cond;
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,const struct timespec *restrict abstime);
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);demo1:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? linux的sleep命令
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
void func(int sig)
{
}
void my_sleep(unsigned int sec)
{
struct sigaction act = {0};
act.sa_handler = func;
sigaction(SIGALRM, &act, NULL);
alarm(sec);
pause();
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
if(argc != 2)
printf("ex: ./a.out sec");
printf("my_sleep start\n");
my_sleep(atoi(argv[1]));
printf("my_sleep end\n");
return 0;
}结果显示:??
demo2:?
? ? ? ? 多路io(poll)监控鼠标和键盘
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <poll.h>
int main(void)
{
int fd;
int ret;
char buf[256];
struct pollfd fds[2] = {0};
fd = open("/dev/input/mouse0", O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
fds[0].fd = 0;
fds[0].events = POLLIN;
fds[1].fd = fd;
fds[1].events = POLLIN;
ret = poll(fds,2, 10000);
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("poll");
return -1;
}
else if (ret == 0)
{
printf("timeout\n");
}
else
{
if (fds[0].events == fds[0].revents)
{
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
read(0, buf, 5);
printf("keyboard:%s\n", buf);
}
if (fds[1].events == fds[1].revents)
{
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
read(fd, buf, 50);
printf("mouse:%s\n", buf);
}
}
return 0;
}结果显示:

????????多路io(select)监控鼠标和键盘?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
int main()
{
int fd;
int ret;
char buf[256];
fd_set set;
struct timeval tm;
fd = open("/dev/input/mouse0", O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open:");
return -1;
}
FD_ZERO(&set);
FD_SET(fd, &set);
FD_SET(0, &set);
tm.tv_sec = 10;
tm.tv_usec = 0;
ret = select(fd+1, &set, NULL, NULL, &tm);
if (ret < 0)
{
perror("select");
return -1;
}
else if (ret == 0)
{
printf("timeout\n");
}
else
{
if (FD_ISSET(0, &set))
{
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
read(0, buf, 5);
printf("keyboard:%s\n", buf);
}
if (FD_ISSET(fd, &set))
{
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
read(fd, buf, 50);
printf("mouse:%s\n", buf);
}
}
return 0;
}结果显示:
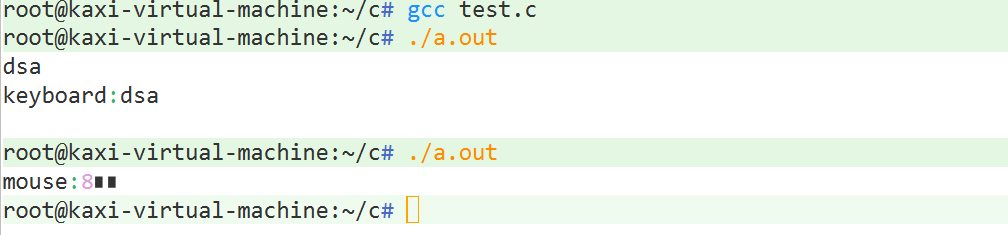
? ? ? ? 异步IO监控鼠标和键盘?(可配合poll.selectshi用)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
int mouse_fd;
void func(int sig)
{
char buf[200] = {0};
if (sig != SIGIO)
return;
read(mouse_fd, buf, 50);
if(strlen(buf))
printf("mouse:%s\n", buf);
}
int main()
{
char buf[200];
int flag = -1;
mouse_fd = open("/dev/input/mouse0", O_RDONLY);
if (mouse_fd < 0)
{
perror("open:");
return -1;
}
//获取 mouse_fd
flag = fcntl(mouse_fd, F_GETFL);
//add O_ASYNC(异步)
flag |= O_ASYNC;
//重写 mouse_fd
fcntl(mouse_fd, F_SETFL, flag);
//设置 mouse_fd 接收SIGIO/SIGURG信号且与进程绑定
fcntl(mouse_fd, F_SETOWN, getpid());
signal(SIGIO, func);
while (1)
{
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
read(0, buf, 5);
if(strlen(buf))
printf("keyboard:%s\n", buf);
}
return 0;
}结果显示:
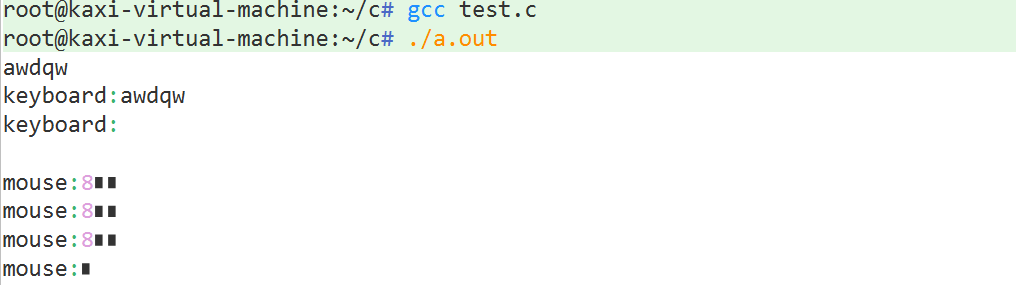
demo3:?
? ? ? ? 字符输入和个数计算(线程+信号量)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
char buf[256] = {0};
sem_t sem;
unsigned int flag = 0;
void *func(void *arg)
{
sem_wait(&sem);
while (flag == 0)
{
printf("the num of string :%ld\n", strlen(buf));
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
sem_wait(&sem);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(void)
{
int ret;
pthread_t th;
sem_init(&sem, 0, 0);
ret = pthread_create(&th, NULL, func, NULL);
if (ret != 0)
{
printf("pthread_create error\n");
exit(-1);
}
printf("input string:\n");
while (scanf("%s", buf))
{
if (!strncmp(buf, "end", 3))
{
printf("process end\n");
flag = 1;
sem_post(&sem);
break;
}
sem_post(&sem);
}
ret = pthread_join(th, NULL);
if (ret != 0)
{
printf("join error\n");
exit(-1);
}
printf("join sucess\n");
sem_destroy(&sem);
return 0;
}结果显示:

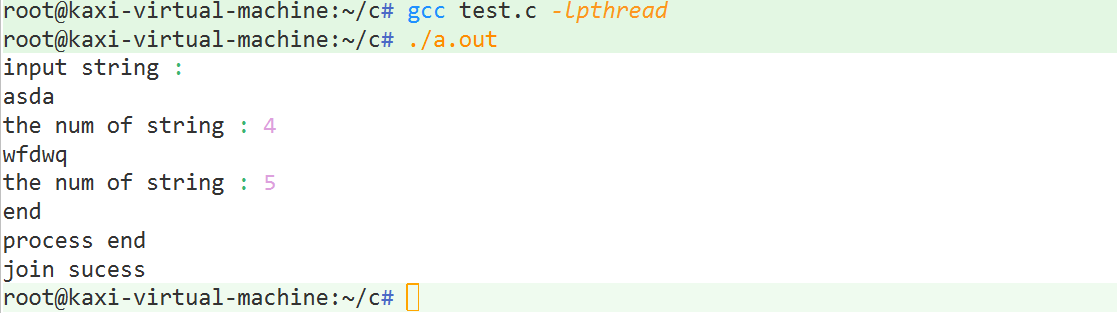
? ? ? ? ?字符输入和个数计算(线程条件)
结果显示:?
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!