MIT6.5840-2023-Lab4A: Sharded K/V Service-The Shard controller
实验内容
实现一个分片 k/v 存储系统,分片指如所有以“a”开头的键可能是一个分片,所有以 “b”开头的键可能是另一个分片。每个副本组仅处理几个分片的 Put、Append 操作,实现并行操作,系统总吞吐量(单位时间的放入和获取)与组的数量成正比。
分片 k/v 存储系统由多个副本组和一个分片控制器组成,分片控制器管理配置信息,决定哪个副本组为哪个分片服务。
某些组的负载可能远高于其他组,实现在多个副本组之间转移分片,以达到负载均衡。同时可能会添加新的副本组以增加容量,或者现有的副本组可能会脱机以进行修复,因此必须移动分片以继续满足要求。
主要挑战是处理重新配置,即将分片重新分配给副本组。在单个副本组中, 所有组成员必须就客户端的 Put/Append/Get 请求在进行重新配置时达成一致。如 Put 可能与重新配置同时到达,重新配置导致副本组不再对 Put 的 key 对应的分片负责。所以组中的所有副本必须就 Put 发生在重新配置之前还是之后达成一致。若在重新配置之前,则 Put 应生效,并且该分片的新所有者需要看到生效效果;若在重新配置之后,Put 将不会生效,客户必须重新请求该 key 的新所有者。
推荐的方法是让每个副本组使用 Raft 不仅记录请求的ID,还记录重新配置的ID。需要确保任何时间最多只有一个副本组为一个分片提供服务。
重新配置还涉及到副本组之间的交互,如在配置 10 中,组 G1 负责分片 S1,在配置 11 中,组 G2 负责分片 S1;在 10 到 11 的重新配置期间,G1 和 G2 必须使用 RPC 将分片 S1 的内容(键/值对)从 G1 移动到 G2。
实验环境
OS:WSL-Ubuntu-18.04
golang:go1.17.6 linux/amd64
Part A: The Shard controller
Impl:shardctrler/server.go and client.go
ShardCtrler 管理一系列配置,每个配置都描述了每个分片由哪个副本组管理以及每个副本组包含哪些服务器的信息;每当需要更改分片分配信息时,ShardCtrler 都会创建新配置,当键/值客户端和服务器想要了解当前或过去的配置时,它们会请求 ShardCtrler。
大部分类似 lab3,只是实现细节不同
rpc及其他格式
// The number of shards.
const NShards = 10
// A configuration -- an assignment of shards to groups.
// Please don't change this.
type Config struct {
Num int // config number
Shards [NShards]int // shard -> gid
Groups map[int][]string // gid -> servers[]
}
const (
OK = "OK"
)
type Err string
type JoinArgs struct {
Servers map[int][]string // new GID -> servers mappings
ClientId int64
ReqId int64
}
type JoinReply struct {
WrongLeader bool
Err Err
}
type LeaveArgs struct {
GIDs []int
ClientId int64
ReqId int64
}
type LeaveReply struct {
WrongLeader bool
Err Err
}
type MoveArgs struct {
Shard int
GID int
ClientId int64
ReqId int64
}
type MoveReply struct {
WrongLeader bool
Err Err
}
type QueryArgs struct {
Num int // desired config number
ClientId int64
ReqId int64
}
type QueryReply struct {
WrongLeader bool
Err Err
Config Config
}
type Clerk struct {
servers []*labrpc.ClientEnd
// Your data here.
ClientId int64
ReqId int64
}
type ShardCtrler struct {
mu sync.Mutex
me int
rf *raft.Raft
applyCh chan raft.ApplyMsg
// Your data here.
dead int32
waitCh map[int]chan *Op
lastReq map[int64]int64
timeout time.Duration
configs []Config // indexed by config num
}
type Op struct {
// Your data here.
ClientId int64
ReqId int64
OpType string
Servers map[int][]string
GIDs []int // Leave
Shard int // Move
GID int // Join\Move
Num int // Query
Config Config
}
client
参照lab3,代码略。
rpc响应
同样类似lab3。
join执行
添加新的副本组。
func (sc *ShardCtrler) execJoin(op *Op) {
n := len(sc.configs) // config num
newGroups := sc.copyGroups() // gid -> servers[]
newShards := sc.configs[n-1].Shards // shard -> gid
for gid, servers := range op.Servers {
newGroups[gid] = servers
}
sc.balance(newGroups, &newShards)
sc.configs = append(sc.configs, Config{
Num: sc.configs[n-1].Num + 1,
Shards: newShards,
Groups: newGroups,
})
}
func (sc *ShardCtrler) balance(newGroups map[int][]string, newShards *[NShards]int) {
if len(newGroups) == 0 {
return
}
cnt := map[int][]int{} // shard ids in each gid
for gid := range newGroups {
cnt[gid] = make([]int, 0)
}
for shardId, gid := range newShards {
cnt[gid] = append(cnt[gid], shardId)
}
for {
maxGID, maxNum, minGID, minNum := sc.findMinMaxGID(cnt)
if maxGID != 0 && maxNum <= minNum+1 {
return
}
cnt[minGID] = append(cnt[minGID], cnt[maxGID][0])
cnt[maxGID] = cnt[maxGID][1:]
newShards[cnt[minGID][len(cnt[minGID])-1]] = minGID
}
}
func (sc *ShardCtrler) findMinMaxGID(cnt map[int][]int) (int, int, int, int) {
minGID, maxGID := -1, -1
minNum, maxNum := math.MaxInt, math.MinInt
gids := []int{}
for gid := range cnt {
gids = append(gids, gid)
}
sort.Ints(gids)
for _, gid := range gids {
n := len(cnt[gid]) // shard num
if maxGID != 0 &&
((gid == 0 && n > 0) || (gid != 0 && n > maxNum)) {
maxGID = gid
maxNum = n
}
if gid != 0 && n < minNum {
minGID = gid
minNum = n
}
}
return maxGID, maxNum, minGID, minNum
}
leave执行
删除 GIDs 副本组。
func (sc *ShardCtrler) execLeave(op *Op) {
n := len(sc.configs) // config num
newGroups := sc.copyGroups() // gid -> servers[]
newShards := sc.configs[n-1].Shards // shard -> gid
for _, gid := range op.GIDs {
for shardId, tmpgid := range newShards {
if gid == tmpgid {
newShards[shardId] = 0 // wait for allocation
}
}
delete(newGroups, gid)
}
sc.balance(newGroups, &newShards)
sc.configs = append(sc.configs, Config{
Num: sc.configs[n-1].Num + 1,
Shards: newShards,
Groups: newGroups,
})
}
move执行
将指定分片移到指定副本组。
func (sc *ShardCtrler) execMove(op *Op) {
n := len(sc.configs) // config num
newGroups := sc.copyGroups() // gid -> servers[]
newShards := sc.configs[n-1].Shards // shard -> gid
newShards[op.Shard] = op.GID
sc.configs = append(sc.configs, Config{
Num: sc.configs[n-1].Num + 1,
Shards: newShards,
Groups: newGroups,
})
}
query执行
查询第num个配置信息,包括Num、Shards(shard -> gid)、Groups(gid -> servers[])。
func (sc *ShardCtrler) execQuery(op *Op) {
n := len(sc.configs) // config num
num := op.Num
if num == -1 || num >= n {
op.Config = sc.configs[n-1]
} else {
op.Config = sc.configs[num]
}
}
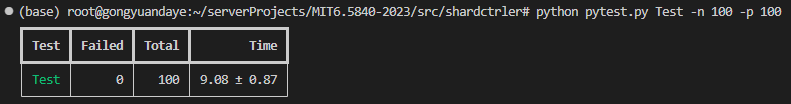
实验结果
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!