C++相关闲碎记录(9)
2023-12-13 21:12:00
1、非修改型算法
| for_each() | 对每个元素执行某种操作 |
| count() | 返回元素个数 |
| count_if() | 返回满足某一条件的元素的个数 |
| min_element() | 返回最小值元素 |
| max_element() | 返回最大值元素 |
| minmax_element() | 返回最小值和最大值元素 |
| find() | 查找某个数值 |
| find_if() | 查找满足条件的元素 |
| find_if_not() | 查找不满足条件的第一个元素 |
| search_n() | 查找具备某特性的之前n个连续元素 |
| search() | 查找某个子区间第一个出现的元素 |
| find_end() | 查找某个区间最后一次出现的位置 |
| find_first_of() | 查找数个可能元素中的第一个出现者 |
| adjacent_find() | 查找连续两个相等或者说符合特定准则的元素 |
| equal() | 判断两区间是否相等 |
| is_permutation() | 两个不定序区间是否含有相等元素 |
| mismatch() | 返回两个序列的各组对应元素中的第一对不相等元素 |
| lexicographical_compare() | 判断字典序下某个序列是否小于另外一个序列 |
| is_sorted() | 返回区间元素是否已经排序 |
| is_sorted_until() | 返回区间内第一个未遵循排序准则的元素 |
| is_partitioned() | 返回区间内的元素是否基于某准则被分割为两组 |
| partition_point() | 返回区间内的一个分割元素,它把元素切割为两组,其中第一组满足某个predicate,另一组不然 |
| is_heap() | 返回区间元素是否形成一个heap |
| is_heap_until() | 返回区间内第一个未遵循heap排序准则的元素 |
| all_of() | 返回是否所有元素都吻合某准则 |
| any_of() | 返回是否至少有一个元素吻合 |
| none_of() | 返回是否无任何元素吻合 |

?2、修改型算法

3、移除型算法
?不可以使用在关联型容器和无序容器中,这些容器的元素是被视为常量,移除型算法只是逻辑上移除元素,手段是将不应该移除的元素往前覆盖应该被移除的元素,因此不改变操作区间元素的个数,返回的是逻辑上的新终点位置。
4、变序型算法
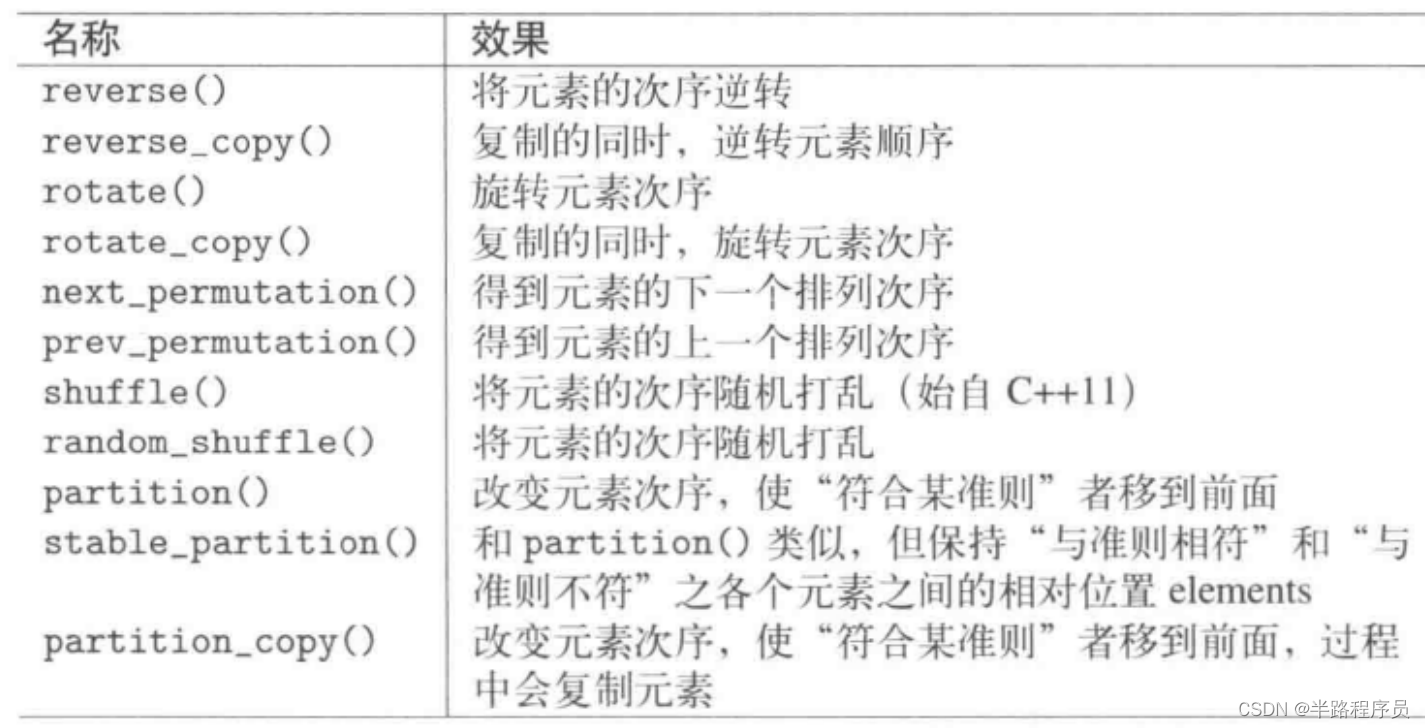
?5、排序算法

?6、检查是否排序
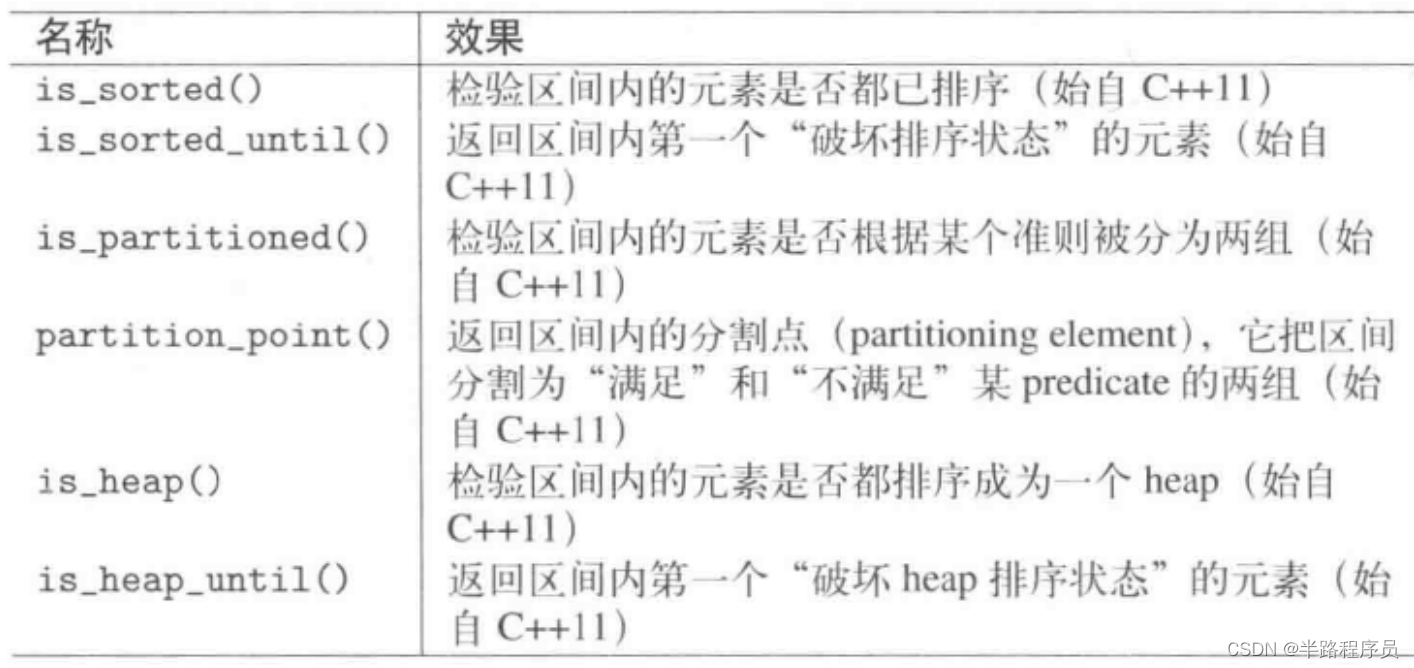
?7、已排序区间算法

?8、数值算法

?9、辅助函数
#ifndef ALGOSTUFF_HPP
#define ALGOSTUFF_HPP
#include <array>
#include <vector>
#include <deque>
#include <list>
#include <forward_list>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
// INSERT_ELEMENTS (collection, first, last)
// - fill values from first to last into the collection
// - NOTE: NO half-open range
template <typename T>
inline void INSERT_ELEMENTS (T& coll, int first, int last)
{
for (int i=first; i<=last; ++i) {
coll.insert(coll.end(),i);
}
}
// PRINT_ELEMENTS()
// - prints optional string optcstr followed by
// - all elements of the collection coll
// - separated by spaces
template <typename T>
inline void PRINT_ELEMENTS (const T& coll,
const std::string& optcstr="")
{
std::cout << optcstr;
for (auto elem : coll) {
std::cout << elem << ' ';
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// PRINT_MAPPED_ELEMENTS()
// - prints optional string optcstr followed by
// - all elements of the key/value collection coll
// - separated by spaces
template <typename T>
inline void PRINT_MAPPED_ELEMENTS (const T& coll,
const std::string& optcstr="")
{
std::cout << optcstr;
for (auto elem : coll) {
std::cout << '[' << elem.first
<< ',' << elem.second << "] ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
#endif /*ALGOSTUFF_HPP*/10、for_each()
#include "algostuff.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> coll;
INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll,1,9);
// add 10 to each element
for_each (coll.begin(), coll.end(), // range
[](int& elem){ // operation
elem += 10;
});
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);
// add value of first element to each element
// 这里必须使用=捕获,是为了后面加第一个元素
for_each (coll.begin(), coll.end(), // range
[=](int& elem){ // operation
elem += *coll.begin();
});
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);
}#include "algostuff.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> coll;
INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll,1,9);
// add 10 to each element
for_each (coll.begin(), coll.end(), // range
[](int& elem){ // operation
elem += 10;
});
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll); // 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
// add value of first element to each element
// 这里必须使用=捕获,是为了后面加第一个元素
// for_each (coll.begin(), coll.end(), // range
// [=](int& elem){ // operation
// elem += *coll.begin();
// }); //
// PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll); // 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
for_each(coll.begin(), coll.end(),
[&](int& elem) { // 这里捕获用的引用,会导致*coll.begin() 在第一次被修改之后,后面会被使用修改之后的元素
elem += *coll.begin();
});
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll); // 22 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41
}11、search_n()
#include "algostuff.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
deque<int> coll;
coll = { 1, 2, 7, 7, 6, 3, 9, 5, 7, 7, 7, 3, 6 };
PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);
// find three consecutive elements with value 7
deque<int>::iterator pos;
pos = search_n (coll.begin(), coll.end(), // range
3, // count
7); // value
// print result
if (pos != coll.end()) {
cout << "three consecutive elements with value 7 "
<< "start with " << distance(coll.begin(),pos) +1
<< ". element" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "no four consecutive elements with value 7 found"
<< endl;
}
// find four consecutive odd elements
pos = search_n (coll.begin(), coll.end(), // range
4, // count
0, // value
[](int elem, int value){ // criterion
return elem%2==1;
});
// print result
if (pos != coll.end()) {
cout << "first four consecutive odd elements are: ";
for (int i=0; i<4; ++i, ++pos) {
cout << *pos << ' ';
}
}
else {
cout << "no four consecutive elements with value > 3 found";
}
cout << endl;
}
输出:
1 2 7 7 6 3 9 5 7 7 7 3 6
three consecutive elements with value 7 start with 9. element
first four consecutive odd elements are: 3 9 5 7
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/wj617906617/article/details/134957130
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
