egen3 rowwise().maxCoeff()的使用
2023-12-14 04:12:17
1、安装eigen3?

2、引用头文件
3、代码测试
MatrixXf aaa(2, 4);
aaa << 1, 2, 3, 4,
5, 6, 7, 8;
Vector2f diff(10, 20);
aaa.colwise() += diff;
std::cout << "new_aaa : " << aaa << endl;
?
全部代码:
int main()
{
MatrixXf mat(2, 4);
mat << -1, 2, 6, 19, //19+6+2-1= 26
3, 1, 7, -2; // 3+1+7-2=9
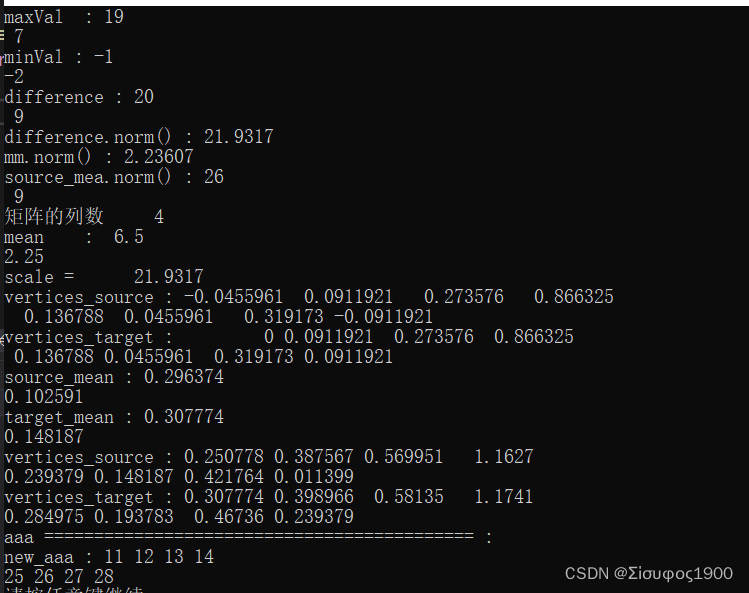
VectorXf maxVal = mat.rowwise().maxCoeff(); // 计算矩阵钟每行的最大值 返回的是一个行最大值组成的一个向量
VectorXf minVal = mat.rowwise().minCoeff(); // 同上
std::cout << "Maxima at positions " << endl;
// std::cout << maxIndex << std::endl;
std::cout << "maxVal : " << maxVal << endl;
std::cout << "minVal : " << minVal << endl;
VectorXf difference = maxVal - minVal; // 对应的行 maxVal[i]-minVal[i],返回的也是一个向量
std::cout << "difference : " << difference << endl;
Vector2f mm(-1,-2);
std::cout << "difference.norm() : " << difference.norm() << endl; // 计算模
std::cout << "mm.norm() : " << mm.norm() << endl;
// 计算每行的和 返回的是一个行向量
Vector2f source_mea=mat.rowwise().sum();
std::cout << "source_mea.norm() : " << source_mea<< endl;
cout << "矩阵的列数 " << mat.cols() << endl; // 4
// 计算没行的平均值
Vector2f mean=source_mea / 4;
std::cout << "mean : " << mean << endl;
MatrixXf vertices_source(2, 4);
vertices_source << -1, 2, 6, 19, //19+6+2-1= 26
3, 1, 7, -2; // 3+1+7-2=9
MatrixXf vertices_target(2, 4);
vertices_target << 0, 2, 6, 19, //19+6+2-1= 26
3, 1, 7, 2; // 3+1+7-2=9
//最大 最小
Vector2f source_scale = vertices_source.rowwise().maxCoeff() - vertices_source.rowwise().minCoeff();
Vector2f target_scale = vertices_target.rowwise().maxCoeff() - vertices_target.rowwise().minCoeff();
double scale = std::max(source_scale.norm(), target_scale.norm());
std::cout << "scale = " << scale << std::endl;
vertices_source /= scale;
vertices_target /= scale;
std::cout << "vertices_source : " << vertices_source << endl;
std::cout << "vertices_target : " << vertices_target << endl;
/// De-mean
Vector2f source_mean, target_mean;
source_mean = vertices_source.rowwise().sum() / double(vertices_source.cols());
target_mean = vertices_target.rowwise().sum() / double(vertices_target.cols());
std::cout << "source_mean : " << source_mean << endl;
std::cout << "target_mean : " << target_mean << endl;
vertices_source.colwise() += source_mean;
vertices_target.colwise() += target_mean;
std::cout << "vertices_source : " << vertices_source << endl;
std::cout << "vertices_target : " << vertices_target << endl;
std::cout << "aaa =========================================== : " << endl;
MatrixXf aaa(2, 4);
aaa << 1, 2, 3, 4, //
5, 6, 7, 8; //
Vector2f diff(10, 20);
aaa.colwise() += diff;
std::cout << "new_aaa : " << aaa << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
example:
#if 1
int main()
{
typedef double Scalar;
typedef Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 3, Eigen::Dynamic> Vertices;
typedef Eigen::Matrix<Scalar, 3, 1> VectorN;
//--- Model that will be rigidly transformed
Vertices vertices_source(3,4);
vertices_source << 1, 3, 5, 6,
2, 4, 12, 15,
4,16,17,56;
// 三行(xyz) 点数列的矩阵
std::cout << "vertices_source: " << vertices_source.rows() << " x " << vertices_source.cols() << std::endl;
//--- Model that source will be aligned to
Vertices vertices_target(3,4);
vertices_target << 1, 2, 3, 4,
5,6,7,8,
4, 12, 14, 16;
// 三行(xyz) 点数列的矩阵
std::cout << "vertices_target: " << vertices_target.rows() << " x " << vertices_target.cols() << std::endl;
// scaling 测量
Eigen::Vector3d source_scale, target_scale;
// 6 15 56 // 1 2 4
source_scale = vertices_source.rowwise().maxCoeff() - vertices_source.rowwise().minCoeff(); // 5 13 52
target_scale = vertices_target.rowwise().maxCoeff() - vertices_target.rowwise().minCoeff(); // 3 3 12
cout << "source_scale :" << source_scale << endl; // 5 13 52
cout << "target_scale : " << target_scale << endl; // 3 3 12
// vertices_source.rowwise().maxCoeff() 表示的是各行的最大值 xyz 中坐标的最大
// vertices_source.rowwise().minCoeff() 表示的是各行的最大值 xyz 中坐标的最小
// 计算模长 的差
std::cout << "source_scale.norm() " << source_scale.norm() << std::endl; //
double scale = std::max(source_scale.norm(), target_scale.norm());
// 分别计算出x y z 方向上的最大-最小
std::cout << "scale = " << scale << std::endl; //
vertices_source /= scale;
vertices_target /= scale;
std::cout << "new vertices_source " << vertices_source << std::endl;
std::cout << "new vertices_target " << vertices_target << std::endl;
/// De-mean
VectorN source_mean, target_mean;
source_mean = vertices_source.rowwise().sum() / double(vertices_source.cols());
target_mean = vertices_target.rowwise().sum() / double(vertices_target.cols());
std::cout << "new source_mean " << source_mean << std::endl;
std::cout << "new target_mean " << target_mean << std::endl;
vertices_source.colwise() -= source_mean;
vertices_target.colwise() -= target_mean;
std::cout << "new ---- vertices_source " << vertices_source << std::endl;
std::cout << "new ---- vertices_target " << vertices_target << std::endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#endif // ?
先更新到此,后续碰到再说。。。。。。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39354845/article/details/134851187
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!