Java并发(十八)----常见线程安全类及实例分析
2023-12-13 05:12:30
1、常见线程安全类
-
String
-
Integer
-
StringBuffer
-
Random
-
Vector
-
Hashtable
-
java.util.concurrent (JUC)包下的类
这里说它们是线程安全的是指,多个线程调用它们同一个实例的某个方法时,是线程安全的。
Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
?
new Thread(()->{
? ?table.put("key", "value1");
}).start();
?
new Thread(()->{
? ?table.put("key", "value2");
}).start();注意:
它们的每个方法是原子的
但它们多个方法的组合不是原子的。
1.1 线程安全类方法的组合
分析下面代码是否线程安全?
Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
// 线程1,线程2
if( table.get("key") == null) {
? ?table.put("key", value);
}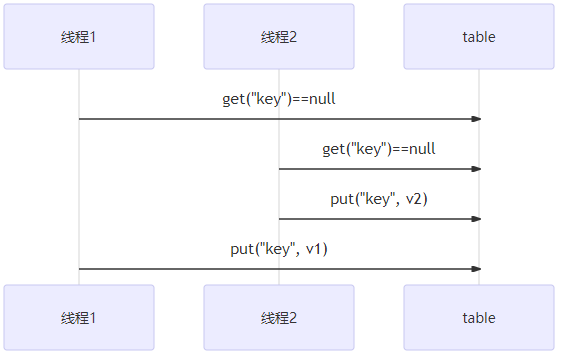
结论是线程不安全
1.2 不可变类线程安全性
String、Integer 等都是不可变类,因为其内部的状态不可以改变,因此它们的方法都是线程安全的
或许有疑问,String 有 replace,substring 等方法【可以】改变值啊,那么这些方法又是如何保证线程安全的呢?
原因为,原值并没有被改变,而是创建了一个新值,其内部的状态没有改变,因此它们的方法都是线程安全的。
例如下面的代码也是同理。
public class Immutable{
?private int value = 0;
?
?public Immutable(int value){
? ?this.value = value;
}
?
?public int getValue(){
? ?return this.value;
}
}如果想增加一个增加的方法呢?
public class Immutable{
?private int value = 0;
?
?public Immutable(int value){
? ?this.value = value;
}
?
?public int getValue(){
? ?return this.value;
}
?
?public Immutable add(int v){
? ?return new Immutable(this.value + v);
} ?
}2、线程安全实例分析
例1:
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
? ?// 是否安全? 不安全
? ?Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
? ?// 是否安全? 安全
? ?String S1 = "...";
? ?// 是否安全? 安全
? ?final String S2 = "...";
? ?// 是否安全? 不安全
? ?Date D1 = new Date();
? ?// 是否安全? 不安全 原因属于可变类型
? ?final Date D2 = new Date();
? ?
? ?public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
? ? ? ?// 使用上述变量
? }
}例2:
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
? ?// 是否安全? 不安全
? ?private UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
? ?
? ?public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
? ? ? ?userService.update(...);
? }
}
?
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
? ?// 记录调用次数
? ?private int count = 0;
? ?
? ?public void update() {
? ? ? ?// ...
? ? ? ?count++;
? }
}例3:
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect {
? ?// 是否安全? 不安全 修改为环绕通知即可解决
? ?private long start = 0L;
? ?
? ?@Before("execution(* *(..))")
? ?public void before() {
? ? ? ?start = System.nanoTime();
? }
? ?
? ?@After("execution(* *(..))")
? ?public void after() {
? ? ? ?long end = System.nanoTime();
? ? ? ?System.out.println("cost time:" + (end-start));
? }
}例4:
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
? ?// 是否安全 安全
? ?private UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
? ?
? ?public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
? ? ? ?userService.update(...);
? }
}
?
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
? ?// 是否安全 安全 没有可更改的属性
? ?private UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
? ?
? ?public void update() {
? ? ? ?userDao.update();
? }
}
?
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
? ?public void update() {
? ? ? ?String sql = "update user set password = ? where username = ?";
? ? ? ?// 是否安全 安全
? ? ? ?try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("","","")){
? ? ? ? ? ?// ...
? ? ? } catch (Exception e) {
? ? ? ? ? ?// ...
? ? ? }
? }
}例5:
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
? ?// 是否安全 安全
? ?private UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
? ?
? ?public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
? ? ? ?userService.update(...);
? }
}
?
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
? ?// 是否安全 安全
? ?private UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
? ?
? ?public void update() {
? ? ? ?userDao.update();
? }
}
?
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
? ?// 是否安全 ? 不安全
? ?private Connection conn = null;
? ?public void update() throws SQLException {
? ? ? ?String sql = "update user set password = ? where username = ?";
? ? ? ?conn = DriverManager.getConnection("","","");
? ? ? ?// ...
? ? ? ?conn.close();
? }
}例6:
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
? ?// 是否安全 安全
? ?private UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
? ?
? ?public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
? ? ? ?userService.update(...);
? }
}
?
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { ? ?
? ?public void update() {
? ? ? ?UserDao userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
? ? ? ?userDao.update();
? }
}
?
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
? ?// 是否安全 不安全
? ?private Connection = null;
? ?public void update() throws SQLException {
? ? ? ?String sql = "update user set password = ? where username = ?";
? ? ? ?conn = DriverManager.getConnection("","","");
? ? ? ?// ...
? ? ? ?conn.close();
? }
}例7:
public abstract class Test {
? ?
? ?public void bar() {
? ? ? ?// 是否安全 不安全 foo暴露出
? ? ? ?SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
? ? ? ?foo(sdf);
? }
? ?
? ?public abstract foo(SimpleDateFormat sdf);
? ?
? ?
? ?public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ?new Test().bar();
? }
}其中 foo 的行为是不确定的,可能导致不安全的发生,被称之为外星方法
public void foo(SimpleDateFormat sdf) {
? ?String dateStr = "1999-10-11 00:00:00";
? ?for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
? ? ? ?new Thread(() -> {
? ? ? ? ? ?try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?sdf.parse(dateStr);
? ? ? ? ? } catch (ParseException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?e.printStackTrace();
? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? }).start();
? }
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/FaithWh/article/details/134959268
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!