Vuex的学习-2
2023-12-20 22:23:06
Vuex的核心概念
- State
- Mutation
- Action
1.State
State提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都统一放在Store的State中进行存储。
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state : { count: 0 }
})
这是渲染的页面
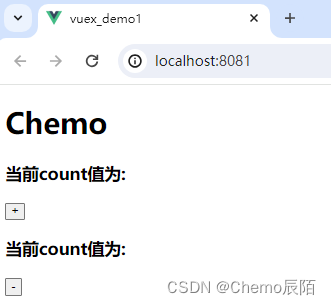
组件访问数据的第一种方式
?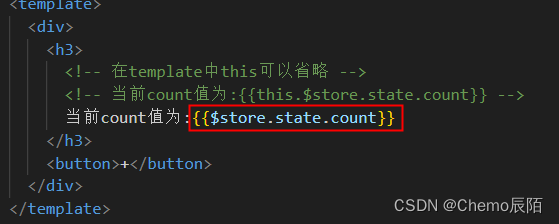

组件访问数据的第二种方式
// 1.从 vuex 中按需导入 mapState 函数
import { mapState } from 'vuex'通过刚才导入的 mapState 函数,将当前组件需要的全局数据,映射为当前组件的 computed 计算属性?
// 2.将全局数据,映射为当前组件的计算属性
computed:{
...mapState(['count'])
}?

2.Mutation
Mutation用来更改Store中的数据
- 只能通过mutation来更改Store数据,不可以直接操作Store中的数据
- 通过这种方式操作可以更好的集中监控所有数据的变化
触发mutations的第一种方式
A.-1
// 定义Mutation
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state:{
count:0
},
mutations:{
add(state){
//变更状态
state.count++
}
}
})
// 触发mutation
methods: {
btnAdd() {
//触发 mutation 的第一种方式
this.$store.commit('add')
}
}
 ?
?
?B.-n
// 定义Mutation
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state : {
count : 0
},
mutations : {
addN(state,step){
// 变更状态
state.count += step
}
}
})
// 触发 mutation
methods : {
handle(){
// 在调用 commit 函数
// 触发 mutationas 携带参数
this.$store.commit('addN',3)
}
} ?
?

触发mutations的第二种方式
// 1.从 vuex 中按需导入 mapMutations 函数
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'通过刚才导入的mapMutations函数,将需要的mutations函数,映射为当前组件的 methods 方法
// 2.将指定的mutations函数,映射为当前组件的methods函数
methods:{
...mapMutations(['add','addN'])
}A.-1?
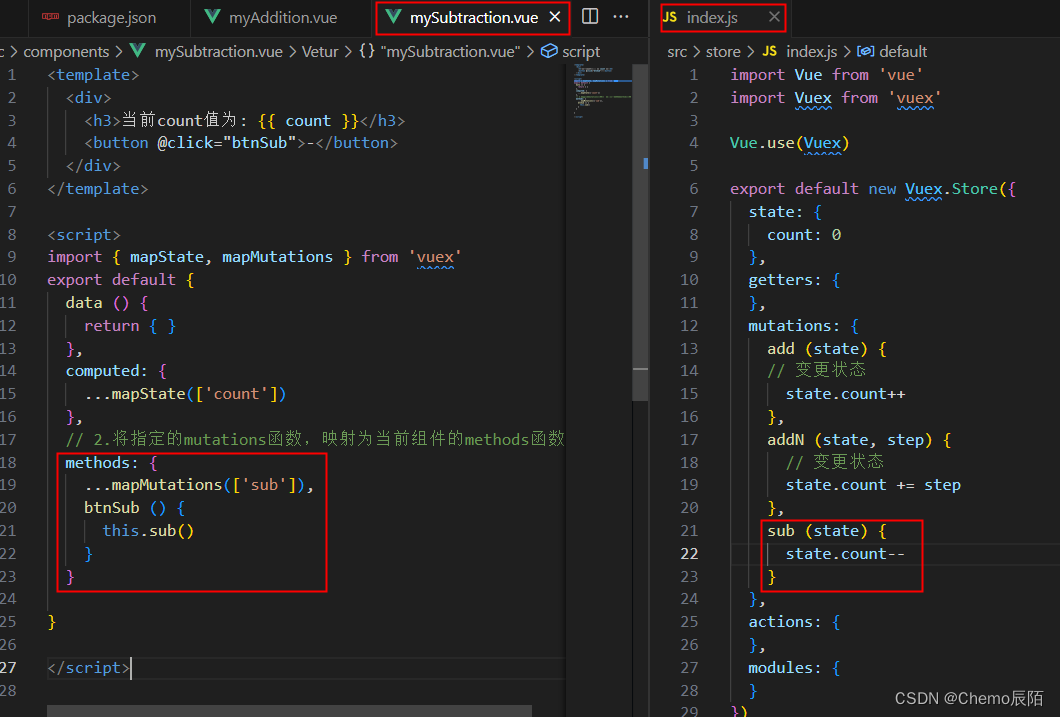

B.-n




3.Action
Action用于处理异步任务。
如果通过异步操作变更数据,必须通过Action,不能使用Mutation,但是在Action中还是要通过触发Mutation的方式简介变更数据。
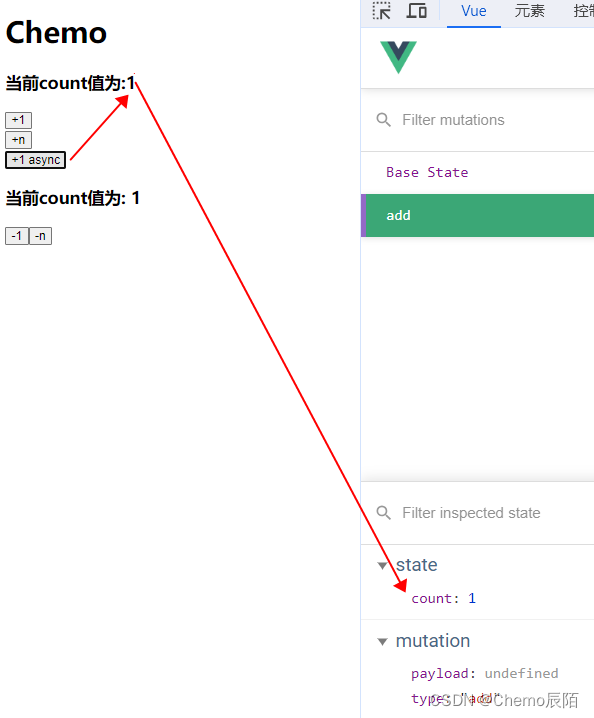
触发actions的第一种方式
A不带参数
// 定义 Action
const store = new Vuex.Store({
//...
mutations : {
add(state){
state.count++
}
},
actions :{
addAsync(context){
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('add')
},1000)
}
}
})
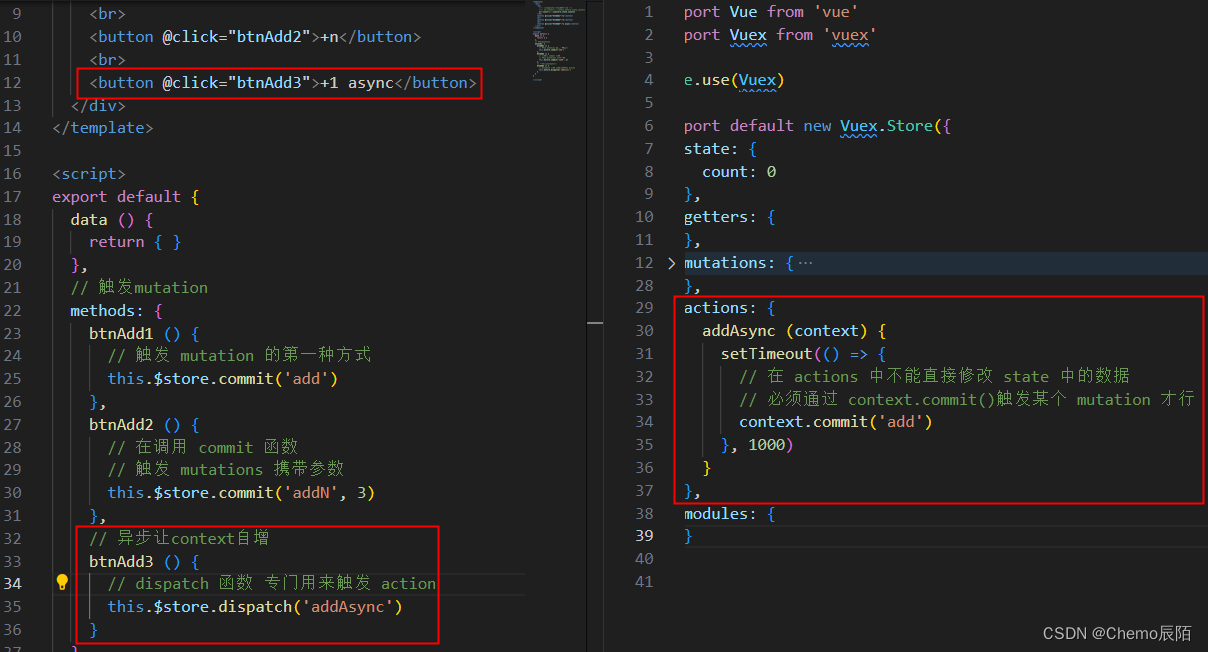
// 触发 Action
methods : {
btnAdd3 () {
//触发 actions的第一种方式
this.$store.dispatch('addAsync')
}
}
B带参数
// 定义 Action
const store = new Vuex.Store({
//...
mutations : {
addN(state, step){
state.count += step
}
},
actions :{
addNAsync(context, step){
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('addN', step)
},1000)
}
}
})
// 触发 Action
methods : {
btnAdd4 () {
// 在调用 dispatch 函数
// 触发 actions 时携带参数
this.$store.dispatch('addNAsync', 5)
}
}
 ?
?
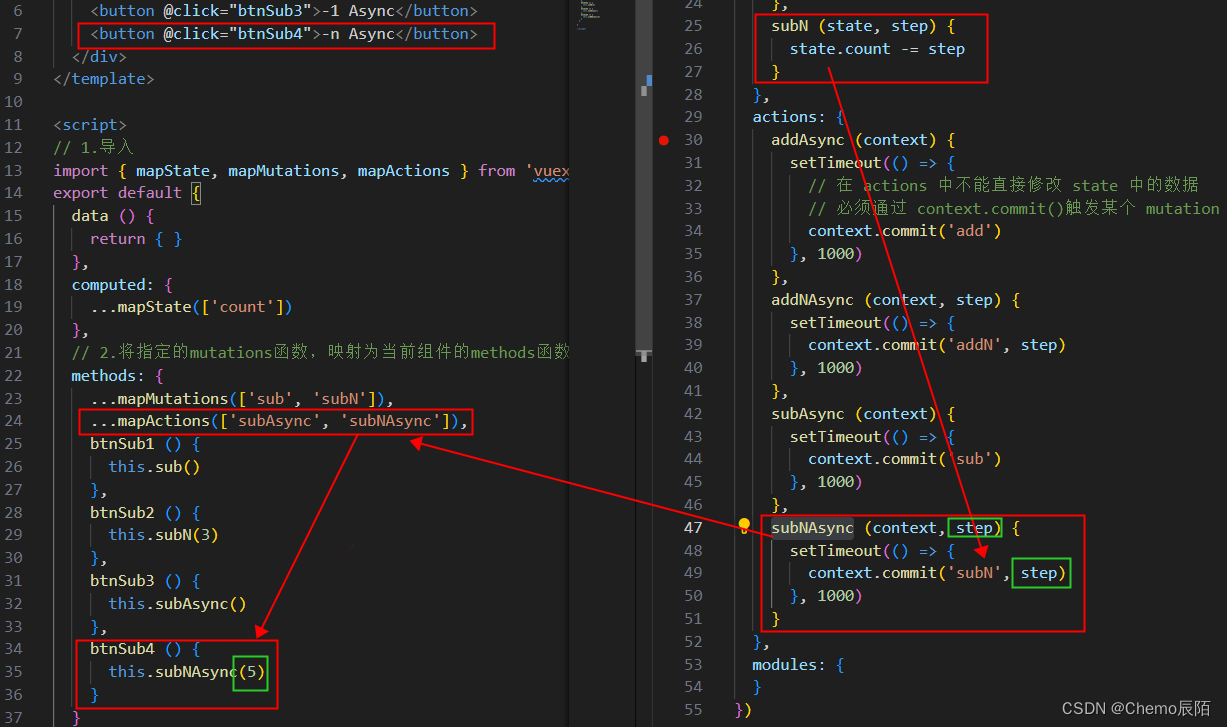
触发actions的第二种方式
// 1.从 vuex 中按需导入 mapActions 函数
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'通过刚才导入的 mapActions 函数,将需要的 actions 函数,映射为当前组建的 methods 方法
// 2.将指定的 actions 函数,映射为当前组件的 methods 函数
methods:{
...mapActions(['addAsync','addNAsync'])
}A.-1


B.-n

这就是大体步骤

4.Getter
Getter用于随Store中的数据进行加工处理形成新的数据
- Getter对Store中已有数据加工处理之后形成新的数据,类似vue的计算属性
- Store中数据发生变化,Getter的数据也会跟着变化
// 定义Getter
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state : {
count : 0
},
getters : {
showNum: state => {
return `当前数据是${state.count}`
}
}
})
// 触发 mutation
methods : {
handle(){
// 在调用 commit 函数
// 触发 mutationas 携带参数
this.$store.commit('addN',3)
}
}定义Getters?
 ?
?
使用getters的第一种方式
this.$store.getters.名称?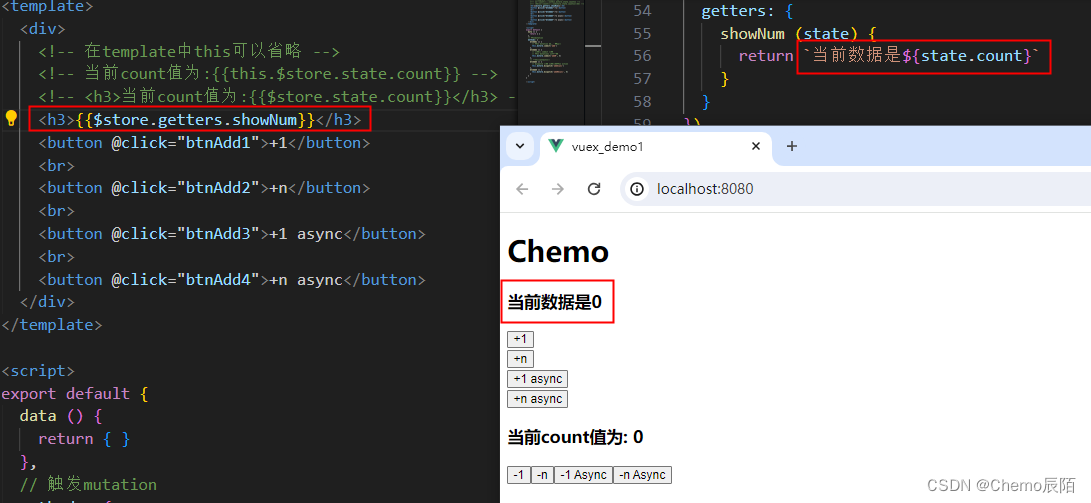
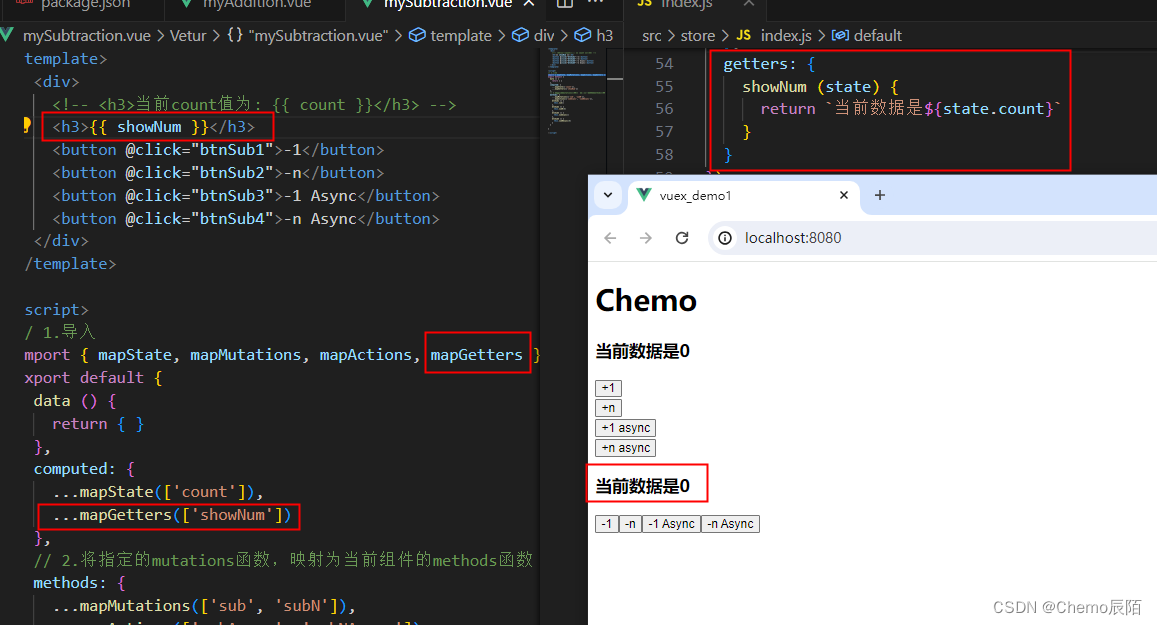
使用getters的第二种方式?
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapGetters(['showNum'])
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_53221528/article/details/135104678
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!