大数据CloudSim应用实践
CloudSimExampleA.java
1准备
1.1操作系统
本实验在Windows 7 或Windows 10系统运行均可。
1.2软件
cloudsim-3.0.3.zip;
commons-math3-3.2-bin.zip;
jdk-8u152-windows-x64.exe;
eclipse-jee-neon-3-win32-x86_64
所需资料链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1AE4UsmFW0rOny6BFCQiPMA?pwd=2023
2安装JDK
2.1安装JDK
双击运行jdk-8u152-windows-x64.exe。
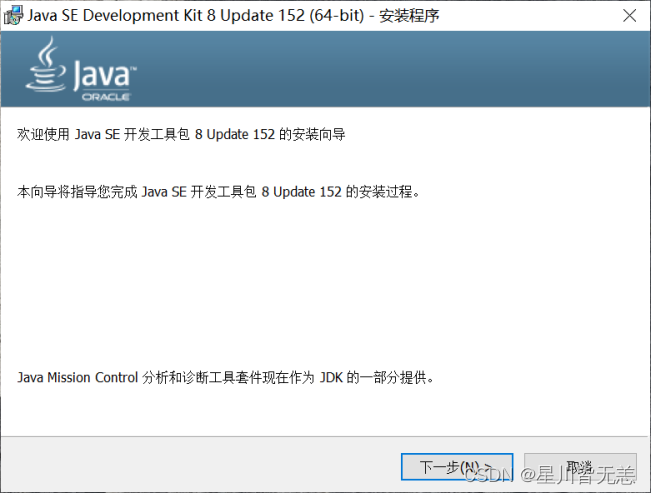
在上面对话框中选择默认目录或更改目录安装。

3配置Eclipse集成开发环境
3.1启动Eclipse
运行…\eclipse-jee-neon-3-win32-x86_64\eclipse目录下的eclipse.exe可执行文件。
注意:首次运行eclipse会提示选择WorkSpace,及工作目录,用于存放项目文件,根据自己情况选择一个文件夹即可。
3.2配置Java运行时环境JRE
在上一步打开的Eclipse集成开发环境窗口中,点击菜单“Window”“Preferences”菜单项:
打开“Preferences”对话框:
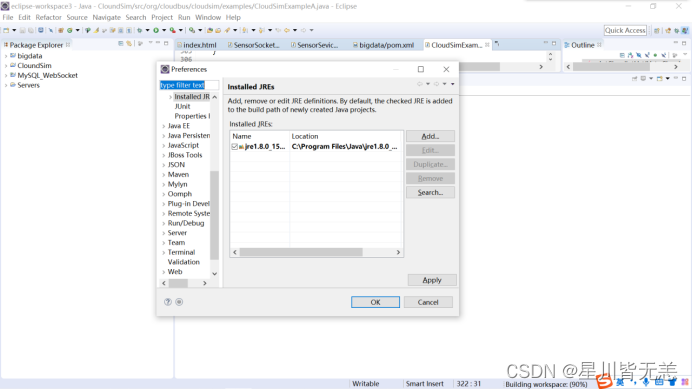
在“Preferences”窗口中点击“Java”左侧箭头,再点击其下方弹出的“Installed JREs”的左侧箭头(下面这幅图可能不一样,因为我当前这一步已经设置过,故“Installed JRE”中会有内容):
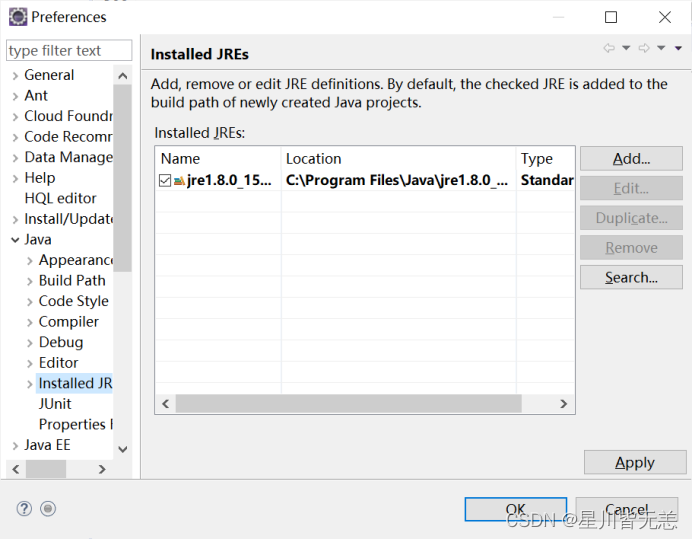
点击右侧窗口中的“Add”按钮,打开“Add JRE”窗口。
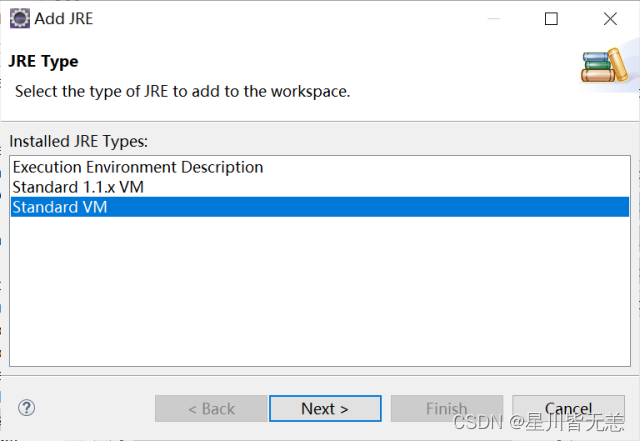
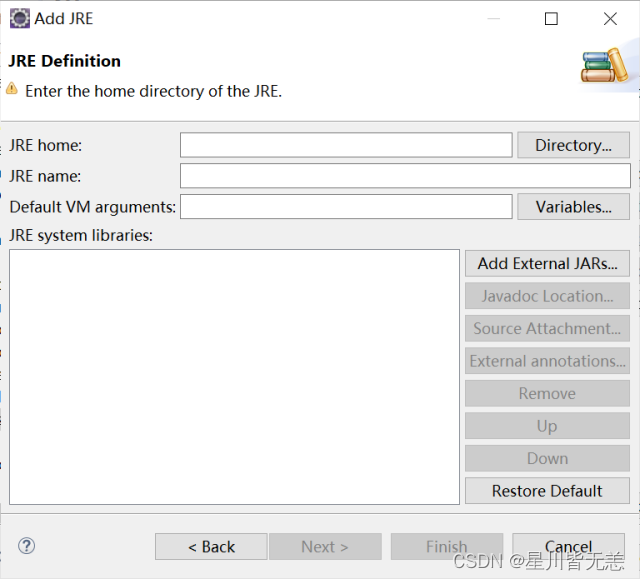
选择“Standard VM”项,点击下方“Next”按钮,在接下来的对话框中点击“Directory”按钮:
在弹出的“浏览文件夹”对话框中选择Java运行时环境所在的路径C:\Program Files\Java\jre1.8.0_152(视自己JDK具体安装路径而定):
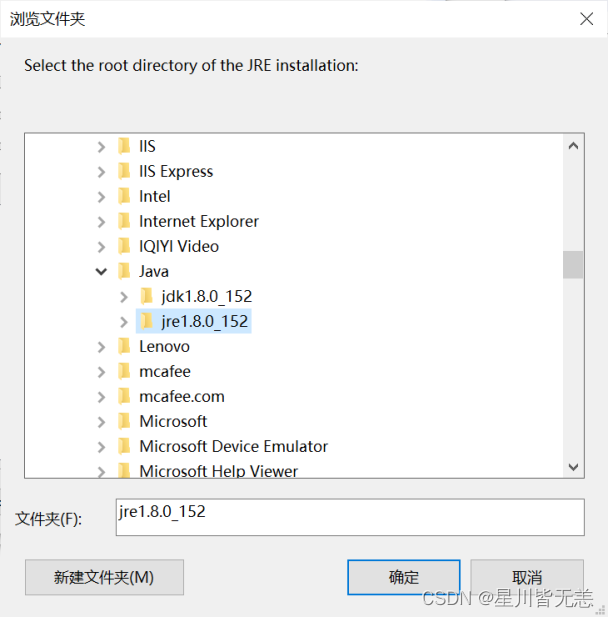
点击“确定”按钮返回。
4创建Java项目
4.1创建项目
在Eclipse集成开发窗口中,单击“File”“New”“Java Project”,新建Java项目,命名为“CloudSim”:
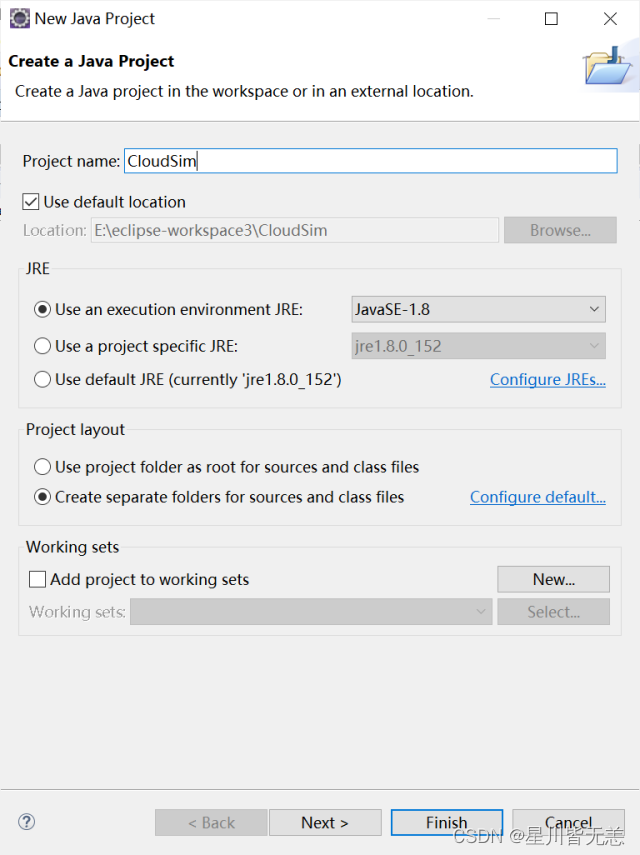
一直点击“Next”或“Finish”按钮即可。
4.2导入jar包
4.2.1导入CloudSim开发包
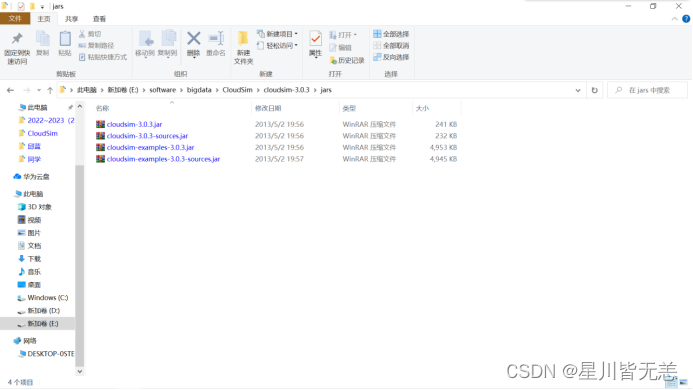
4.2.1.1.1解压CloudSim开发包
需要使用的CloudSim API在cloudsim-3.0.3.jar包中,该jar包可通过解压cloudsim-3.0.3.zip得到,位于解压后的…\cloudsim-3.0.3\jars文件夹下。
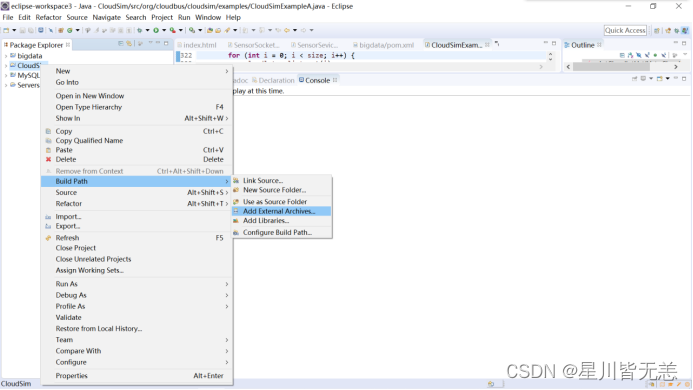
4.2.1.1.2导入CloudSim开发包
在Eclipse中,在左侧树状结构中,右键单击“CloudSim”项目,选择“Build Path”“Add External Archive”,导入cloudsim-3.0.3.jar。
4.2.2导入math库
4.2.2.1.1解压math库
因本项目中用到了math里面的类,需要引入commons-math3-3.2.jar这个库。此库通过解压commons-math3-3.2-bin.zip文件可以得到。
4.2.2.1.2导入math库
在Eclipse中,右键单击“CloudSim”项目,选择“Build Path”“Add External Archive”,导入commons-math3-3.2.jar。
4.3运行测试程序
4.3.1导入测试程序代码
CloudSim提供的实例程序放在CloudSim\cloudsim-3.0.3\examples\org\cloudbus\cloudsim\examples目录下。
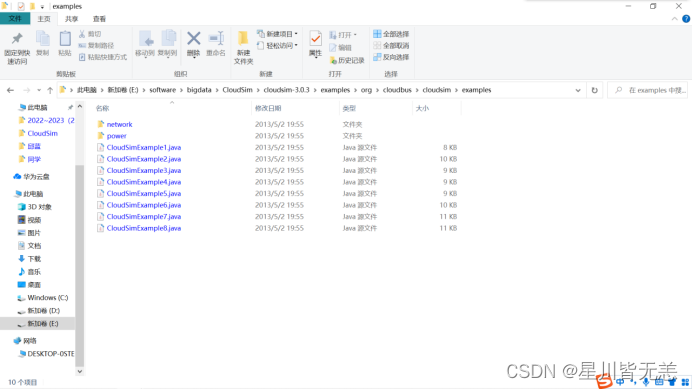
在以上examples文件夹中复制CloudSimExample6.java文件,在Eclipse中的“Package Explorer”树形结构中,展开“CloudSim” “src”,右键点击“src”文件夹,在弹出的上下文菜单中选择“Paste”菜单,将CloudSimExample6.java复制到工程中。
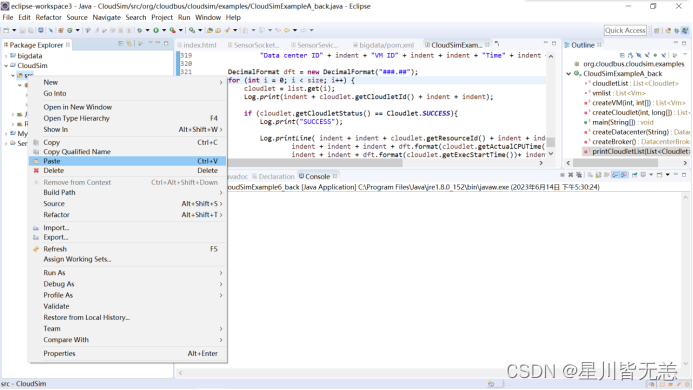
4.3.2修改错误
复制后CloudSimExample6.java文件显示效果及位置如下:
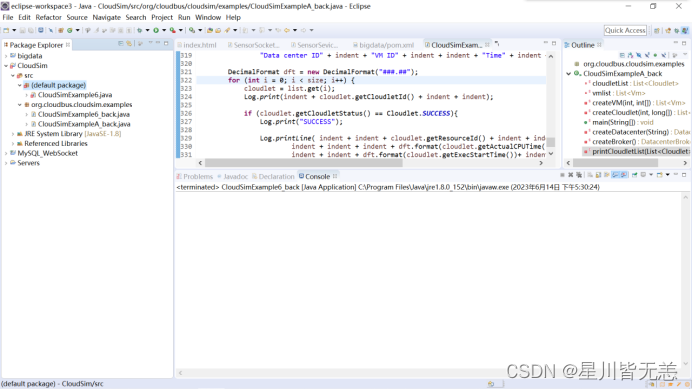
可以看出其位于“default package”默认包中。但注意上图中CloudSimExample6.java文件前面的图标左下角有个红色的“×”符号,意思是CloudSimExample6.java代码中有错误。接下来排除错误。
在Eclipse中双击CloudSimExample6.java文件,在右侧编辑窗口中打开它。
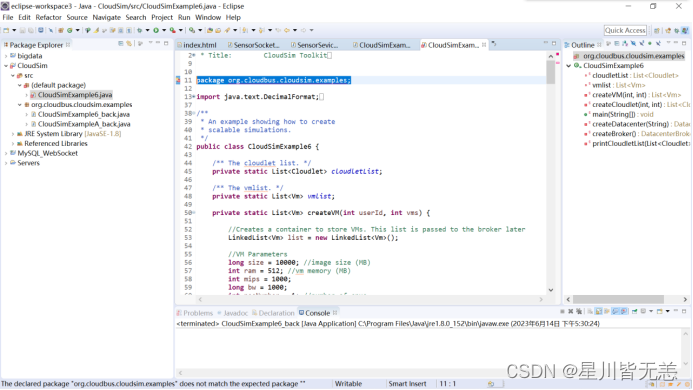
可以看到这条语句package org.cloudbus.cloudsim.examples;中有红色波浪下划线,表明有语法问题。鼠标放到该语句上,显示:
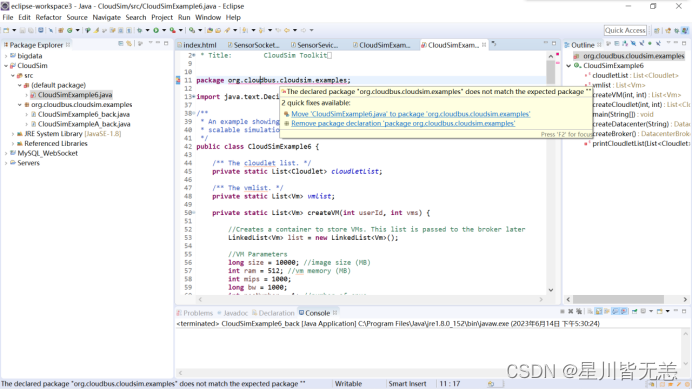
点击2行蓝色文字中的第一行,“Move ‘CloudSimExample6.java to package org.cloudbus.cloudsim.examples’”,表示将CloudSimExample6.java文件放到Eclipse窗口左面的树形结构的org.cloudbus.cloudsim.examples包中。这样代码中原先带红色波浪线的语句就与实际的包(代码的存放位置)相符,其错误得到了修改。修改之后的效果如下:
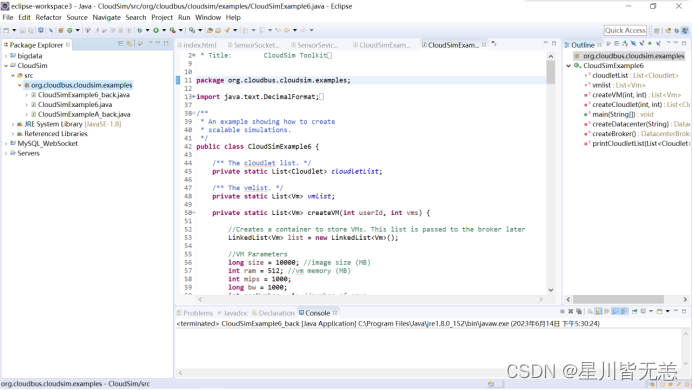
包的存放文件夹与包的对应关系(此图仅为帮助理解):
4.3.3运行
保证右侧编辑区当前活动(当前正在编辑状态)的窗口为CloudSimExample6.java。
点击工具栏上的绿色三角形按钮Run AsJava Application Alt+Shift+X,J,运行程序,如图:
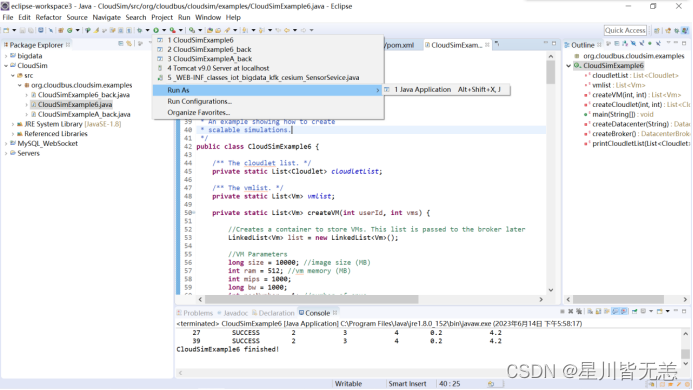
5数据中心仿真实例
5.1导入实例代码
1.将我随本Word文档打包的CloudSimExampleA.java代码导入项目,具体步骤同4.3.1,不同的是由原来导入CloudSimExample6.java文件,改为现在导入CloudSimExampleA.java文件。
2.遵照4.3.2步骤将CloudSimExampleA放到org.cloudbus.cloudsim.examples包中,如下图。
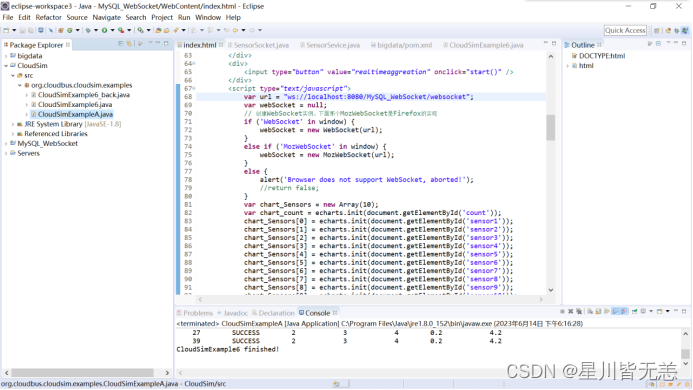
5.2运行
附CloudSimExampleA.java代码:
/*
* Title: CloudSim Toolkit
* Description: CloudSim (Cloud Simulation) Toolkit for Modeling and Simulation
* of Clouds
* Licence: GPL - http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/gpl.html
*
* Copyright (c) 2009, The University of Melbourne, Australia
*/
package org.cloudbus.cloudsim.examples;//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.Cloudlet;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.CloudletSchedulerTimeShared;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.Datacenter;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.DatacenterBroker;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.DatacenterCharacteristics;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.Host;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.Log;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.Pe;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.Storage;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.UtilizationModel;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.UtilizationModelFull;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.Vm;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.VmAllocationPolicySimple;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.VmSchedulerTimeShared;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.core.CloudSim;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.provisioners.BwProvisionerSimple;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.provisioners.PeProvisionerSimple;
import org.cloudbus.cloudsim.provisioners.RamProvisionerSimple;
/**
* An example showing how to create
* scalable simulations.
*/
//public class CloudSimExample6 {//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
public class CloudSimExampleA {//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
/** The cloudlet list. */
private static List<Cloudlet> cloudletList;
/** The vmlist. */
private static List<Vm> vmlist;
//private static List<Vm> createVM(int userId, int vms) {//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
private static List<Vm> createVM(int userId, int mips[]) {//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
//Creates a container to store VMs. This list is passed to the broker later
LinkedList<Vm> list = new LinkedList<Vm>();
//VM Parameters
long size = 10000; //image size (MB)
int ram = 512; //vm memory (MB)
//int mips = 1000;//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
long bw = 1000;
int pesNumber = 1; //number of cpus
String vmm = "Xen"; //VMM name
//create VMs
//Vm[] vm = new Vm[vms];//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
Vm[] vm = new Vm[mips.length];//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
for(int i=0;i<mips.length;i++){
//vm[i] = new Vm(i, userId, mips, pesNumber, ram, bw, size, vmm,//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
//new CloudletSchedulerTimeShared());//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
vm[i] = new Vm(i, userId, mips[i], pesNumber, ram, bw, size, vmm,
new CloudletSchedulerTimeShared());//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
//for creating a VM with a space shared scheduling policy for cloudlets:
//vm[i] = Vm(i, userId, mips, pesNumber, ram, bw, size, priority, vmm, new CloudletSchedulerSpaceShared());
list.add(vm[i]);
}
return list;
}
//private static List<Cloudlet> createCloudlet(int userId, int cloudlets){//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
private static List<Cloudlet> createCloudlet(int userId, long cloudlets[]){//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
// Creates a container to store Cloudlets
LinkedList<Cloudlet> list = new LinkedList<Cloudlet>();
//cloudlet parameters
//long length = 1000;//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
long fileSize = 300;
long outputSize = 300;
int pesNumber = 1;
UtilizationModel utilizationModel = new UtilizationModelFull();
//Cloudlet[] cloudlet = new Cloudlet[cloudlets];//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
Cloudlet[] cloudlet = new Cloudlet[cloudlets.length];//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
//for(int i=0;i<cloudlets;i++){//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
for(int i=0;i<cloudlets.length;i++){
/*cloudlet[i] = new Cloudlet(i, length, pesNumber, fileSize, outputSize,
utilizationModel, utilizationModel, utilizationModel);*///qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
cloudlet[i] = new Cloudlet(i, cloudlets[i], pesNumber, fileSize,
outputSize, utilizationModel, utilizationModel, utilizationModel);//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
// setting the owner of these Cloudlets
cloudlet[i].setUserId(userId);
list.add(cloudlet[i]);
}
return list;
}
// STATIC METHODS ///
/**
* Creates main() to run this example
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Log.printLine("Starting CloudSimExample6...");//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
Log.printLine("Starting CloudSimExampleA...");//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
try {
// First step: Initialize the CloudSim package. It should be called
// before creating any entities.
int num_user = 1; // number of grid users
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
boolean trace_flag = false; // mean trace events
// Initialize the CloudSim library
CloudSim.init(num_user, calendar, trace_flag);
// Second step: Create Datacenters
//Datacenters are the resource providers in CloudSim. We need at list one of them to run a CloudSim simulation
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
Datacenter datacenter0 = createDatacenter("Datacenter_0");
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
Datacenter datacenter1 = createDatacenter("Datacenter_1");
//Third step: Create Broker
DatacenterBroker broker = createBroker();
int brokerId = broker.getId();
//Fourth step: Create VMs and Cloudlets and send them to broker
/*vmlist = createVM(brokerId,20); //creating 20 vms
cloudletList = createCloudlet(brokerId,40); // creating 40 cloudlets*/
int mips[] = {278,289,132,209,286,333,212,423};//虚拟机的CPU性能(mips)//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
/*所需的指令数*/
long cloudlets[] = new long[] {19365, 49809, 30218, 44157, 16754, 18336,
20045, 31493, 30727, 31017, 59008, 32000, 46790, 77779, 93467,
67853};//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
//vmlist = createVM(brokerId,20); //creating 20 vms//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
vmlist = createVM(brokerId, mips); //creating 20 vms//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
//cloudletList = createCloudlet(brokerId,40); // creating 40 cloudlets//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
cloudletList = createCloudlet(brokerId, cloudlets); // creating 40 cloudlets//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
broker.submitVmList(vmlist);
broker.submitCloudletList(cloudletList);
// Fifth step: Starts the simulation
CloudSim.startSimulation();
// Final step: Print results when simulation is over
List<Cloudlet> newList = broker.getCloudletReceivedList();
CloudSim.stopSimulation();
printCloudletList(newList);
//Log.printLine("CloudSimExample6 finished!");//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
Log.printLine("CloudSimExampleA finished!");//qiuzhuli, 2023-06-11
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
Log.printLine("The simulation has been terminated due to an unexpected error");
}
}
private static Datacenter createDatacenter(String name){
// Here are the steps needed to create a PowerDatacenter:
// 1. We need to create a list to store one or more
// Machines
List<Host> hostList = new ArrayList<Host>();
// 2. A Machine contains one or more PEs or CPUs/Cores. Therefore, should
// create a list to store these PEs before creating
// a Machine.
List<Pe> peList1 = new ArrayList<Pe>();
int mips = 1000;
// 3. Create PEs and add these into the list.
//for a quad-core machine, a list of 4 PEs is required:
peList1.add(new Pe(0, new PeProvisionerSimple(mips))); // need to store Pe id and MIPS Rating
peList1.add(new Pe(1, new PeProvisionerSimple(mips)));
peList1.add(new Pe(2, new PeProvisionerSimple(mips)));
peList1.add(new Pe(3, new PeProvisionerSimple(mips)));
//Another list, for a dual-core machine
List<Pe> peList2 = new ArrayList<Pe>();
peList2.add(new Pe(0, new PeProvisionerSimple(mips)));
peList2.add(new Pe(1, new PeProvisionerSimple(mips)));
//4. Create Hosts with its id and list of PEs and add them to the list of machines
int hostId=0;
int ram = 2048; //host memory (MB)
long storage = 1000000; //host storage
int bw = 10000;
hostList.add(
new Host(
hostId,
new RamProvisionerSimple(ram),
new BwProvisionerSimple(bw),
storage,
peList1,
new VmSchedulerTimeShared(peList1)
)
); // This is our first machine
hostId++;
hostList.add(
new Host(
hostId,
new RamProvisionerSimple(ram),
new BwProvisionerSimple(bw),
storage,
peList2,
new VmSchedulerTimeShared(peList2)
)
); // Second machine
//To create a host with a space-shared allocation policy for PEs to VMs:
//hostList.add(
// new Host(
// hostId,
// new CpuProvisionerSimple(peList1),
// new RamProvisionerSimple(ram),
// new BwProvisionerSimple(bw),
// storage,
// new VmSchedulerSpaceShared(peList1)
// )
// );
//To create a host with a oportunistic space-shared allocation policy for PEs to VMs:
//hostList.add(
// new Host(
// hostId,
// new CpuProvisionerSimple(peList1),
// new RamProvisionerSimple(ram),
// new BwProvisionerSimple(bw),
// storage,
// new VmSchedulerOportunisticSpaceShared(peList1)
// )
// );
// 5. Create a DatacenterCharacteristics object that stores the
// properties of a data center: architecture, OS, list of
// Machines, allocation policy: time- or space-shared, time zone
// and its price (G$/Pe time unit).
String arch = "x86"; // system architecture
String os = "Linux"; // operating system
String vmm = "Xen";
double time_zone = 10.0; // time zone this resource located
double cost = 3.0; // the cost of using processing in this resource
double costPerMem = 0.05; // the cost of using memory in this resource
double costPerStorage = 0.1; // the cost of using storage in this resource
double costPerBw = 0.1; // the cost of using bw in this resource
LinkedList<Storage> storageList = new LinkedList<Storage>(); //we are not adding SAN devices by now
DatacenterCharacteristics characteristics = new DatacenterCharacteristics(
arch, os, vmm, hostList, time_zone, cost, costPerMem, costPerStorage, costPerBw);
// 6. Finally, we need to create a PowerDatacenter object.
Datacenter datacenter = null;
try {
datacenter = new Datacenter(name, characteristics, new VmAllocationPolicySimple(hostList), storageList, 0);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return datacenter;
}
//We strongly encourage users to develop their own broker policies, to submit vms and cloudlets according
//to the specific rules of the simulated scenario
private static DatacenterBroker createBroker(){
DatacenterBroker broker = null;
try {
broker = new DatacenterBroker("Broker");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
return broker;
}
/**
* Prints the Cloudlet objects
* @param list list of Cloudlets
*/
private static void printCloudletList(List<Cloudlet> list) {
int size = list.size();
Cloudlet cloudlet;
String indent = " ";
Log.printLine();
Log.printLine("========== OUTPUT ==========");
Log.printLine("Cloudlet ID" + indent + "STATUS" + indent +
"Data center ID" + indent + "VM ID" + indent + indent + "Time" + indent + "Start Time" + indent + "Finish Time");
DecimalFormat dft = new DecimalFormat("###.##");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cloudlet = list.get(i);
Log.print(indent + cloudlet.getCloudletId() + indent + indent);
if (cloudlet.getCloudletStatus() == Cloudlet.SUCCESS){
Log.print("SUCCESS");
Log.printLine( indent + indent + cloudlet.getResourceId() + indent + indent + indent + cloudlet.getVmId() +
indent + indent + indent + dft.format(cloudlet.getActualCPUTime()) +
indent + indent + dft.format(cloudlet.getExecStartTime())+ indent + indent + indent + dft.format(cloudlet.getFinishTime()));
}
}
}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!