4.vue学习笔记(数组变化的侦测+计算属性+Class绑定)
2024-01-03 16:41:20
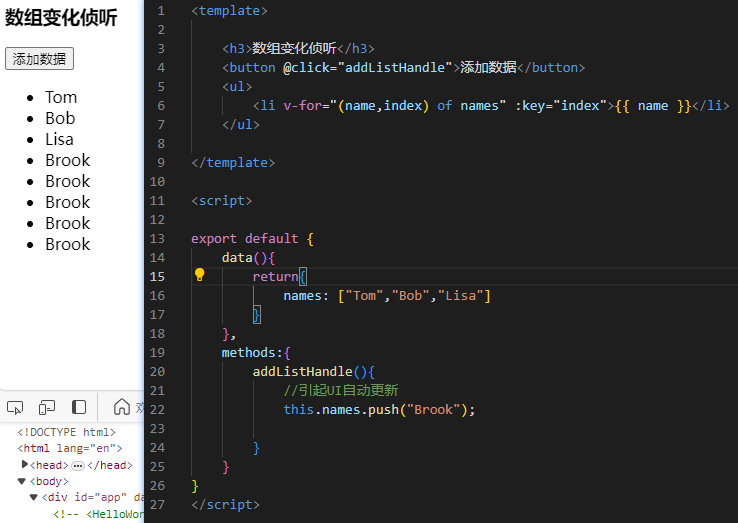
1.数组变化的侦测
1.1.变更方法
vue能够侦听响应式数组的变更方法,并在它们被调用时出发相关的更新。这些变更方法包括:
push()
pop()
shift()
unshift()
splice()
sort()
reverse()
1.2.替换一个数组
变更方法,就是会对调用它们的原数组进行变更。相对的,也有一些不可变的方法,例如:
filter() concat() slice()
这些不会更改原数组,而总是返回一个新数组,当遇到的是非变更方法时,我们需要将旧的数组替换为新的
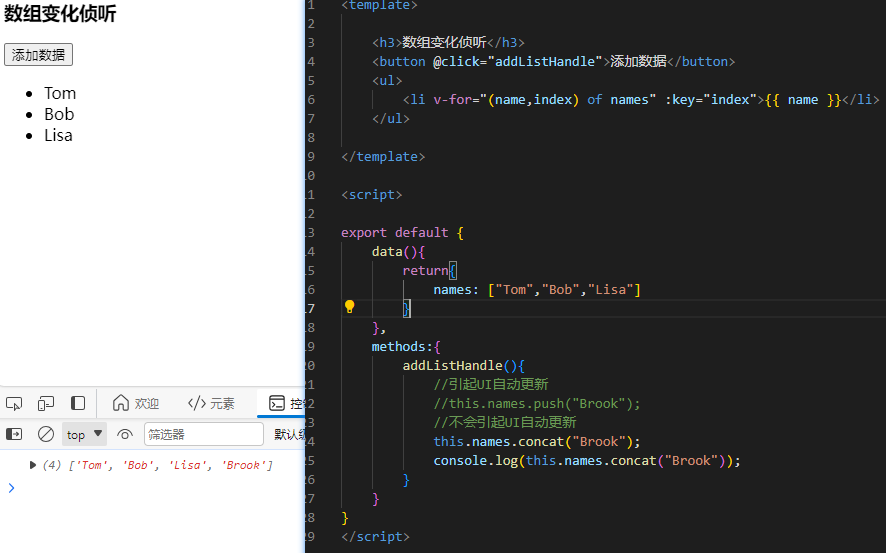
//重新赋值后产生变换
this.names = this.names.concat("Brook");
<template>
<h3>数组变化侦听</h3>
<button @click="addListHandle">添加数据</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(name,index) of names" :key="index">{{ name }}</li>
</ul>
<button @click="concatHandle">合并数组</button>
<h3>数组1</h3>
<p v-for="(num,index) of num1" :key="index">{{ num }}</p>
<h3>数组2</h3>
<p v-for="(num,index) of num2" :key="index">{{ num }}</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
names: ["Tom","Bob","Lisa"],
num1: [1,2,3,4,5],
num2: [6,7,8,9,10]
}
},
methods:{
addListHandle(){
//引起UI自动更新
//this.names.push("Brook");
//不会引起UI自动更新
// this.names.concat("Brook");
// console.log(this.names.concat("Brook"));
//重新赋值后产生变换
this.names = this.names.concat("Brook");
},
concatHandle(){
this.num1 = this.num1.concat(this.num2);
}
}
}
</script>
2.计算属性
模板中的表达式虽然方便,但也只能用来做简单的操作,如果在模板中写太多的逻辑,会让模板变得臃肿,难以维护。
因此我们推荐使用计算属性来描述依赖响应式状态的复杂逻辑
<template>
<h3>{{ person.name }}</h3>
<p>{{ person.content.length > 0 ? "yes" : "no" }}</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return {
person:{
name: "张三",
content: ["软件工程","Java","互联网与应用技术"]
}
}
}
}
</script>
改造后
<template>
<h3>{{ person.name }}</h3>
<p>{{ personContent }}</p>
<p>{{ personContent1() }}</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return {
person:{
name: "张三",
content: ["软件工程","Java","互联网与应用技术"]
}
}
},
//计算属性
computed:{
personContent(){
return this.person.content.length > 0 ? "yes" : "no"
}
},
//放函数或者方法
methods:{
personContent1(){
return this.person.content.length > 0 ? "yes" : "no"
}
}
}
</script>
计算属性缓存vs方法
以上代码可以看出,计算属性和方法都能实现,那么为什么要使用计算属性:
计算属性:计算属性值会基于其响应式依赖被缓存。一个计算属性仅会在其响应式依赖更新时才会重新计算
(只要代码不变,只执行一次,多次调用的值也只执行一次)
方法:方法调用总是会在重渲染发生时再次执行函数
(方法调用几次,执行几次)
3.Class绑定
数据绑定的一个常见需求场景是操纵元素的 CSS class列表,因为class是attribute,我们可以和其他attribute一样使用v-bind将它们和动态字符串绑定。
但是,在处理比较复杂的绑定时,通过拼接生成字符串是麻烦且容易出错的。
因此,Vue专门为class的v-bind用法提供了特殊的功能增强。除了字符串外,表达式的值也可以是对象或数组
<template>
<h3>Class样式</h3>
<p :class="myClass">Class样式绑定</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
myClass: "Demo"
}
}
}
</script>
3.1.绑定对象
<template>
<h3>Class样式</h3>
<p :class="{ 'active':isActive,'text-danger':hasError }">Class样式绑定</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
isActive: true,
hasError: true
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.active{
font-size: 30px;
}
.text-danger{
color:red;
}
</style>
3.2.多个对象的绑定形式
<template>
<h3>Class样式</h3>
<p :class="ClassObject">Class样式绑定</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
ClassObject:{
active: true,
'text-danger': true
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.active{
font-size: 30px;
}
.text-danger{
color:red;
}
</style>
3.3.绑定数组
<template>
<h3>Class样式</h3>
<p :class="[arrActive,arrTextDanger]">Class样式绑定3</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
arrActive: 'active',
arrTextDanger: 'text-danger'
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.active{
font-size: 30px;
}
.text-danger{
color:red;
}
</style>
如果想在数组中有条件地渲染某个class,也可以使用三元运算符
<template>
<h3>Class样式</h3>
<p :class="[isActive ? 'active' : '']">Class样式绑定4</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
isActive: true
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.active{
font-size: 30px;
}
.text-danger{
color:red;
}
</style>
3.4.数组与对象
数组和对象嵌套过程中,只能是数组嵌套对象。[{},{}]
<template>
<h3>Class样式</h3>
<p :class="[{'active':isActive},arrTextDanger]">Class样式绑定5</p>
<p :class="[isActive ? 'active' : '',{'text-danger':hasError}]">Class样式绑定6</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
isActive: true,
hasError: true,
arrActive: 'active',
arrTextDanger: 'text-danger'
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.active{
font-size: 30px;
}
.text-danger{
color:red;
}
</style>
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46055386/article/details/135362990
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!