双因子认证(Two-factor authentication)
一、简介
简言之,双因素身份验证(也称为“两步验证”)是指身份验证涉及两个阶段——通常是除了常规密码)之外的某种一次性密码(OTP:One-Time Password)。网上银行已经使用这种方法很长一段时间了,最近这种方法也在全网流行起来。还有其他可用的方法,但基于时间的一次性密码(TOTP)非常常用。有几个移动应用程序支持该标准,Google Authenticator就是其中之一(Android、iOS)
摘抄自:https://vaadin.com/blog/two-factor-authentication-with-google-authenticator
下图就是一个使用场景。( MFA(Multi-Factor Authentication)
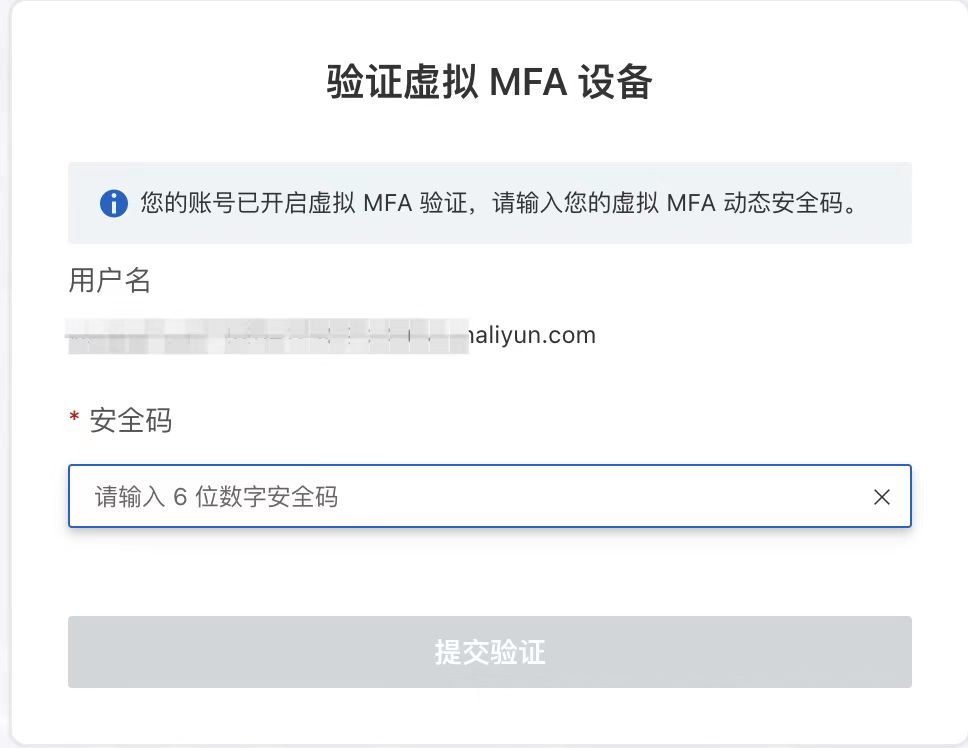

二、TOTP
1、什么是TOTP
TOTP:全称是"基于时间的一次性密码"(Time-based One-time Password)。它是公认的可靠解决方案,已经写入国际标准RFC6238。
2、TOTP的简单原理
TOTP基于具有时间戳计数器的OTP(一次性密码),其算法公式为TOTP=HMAC-SHA-1(K, (T - T0)/X),其中K为共享密钥,T为当前时间戳,T0为开始的时间戳,X为时间步长(或者叫时间窗口)。
- **密钥生成:**在为帐户设置TOTP时,将生成一个唯一的密钥。该密钥在用户设备和认证服务器之间共享。
- **时间同步:**用户设备和认证服务器需要同步到相同的时间源。TOTP算法依赖于当前时间来生成一次性密码。
- **OTP生成:**TOTP算法将密钥和当前时间结合起来,应用Hash函数生成一次性密码。此密码通常包含6-8位数字,并具有有限的有效期,例如30或60秒。
- **OTP验证:**当用户尝试登录时,输入常规密码以及由TOTP应用程序或设备生成的一次性密码。然后,认证服务器根据共享密钥和当前时间独立生成预期的OTP。如果用户输入的OTP与服务器生成的OTP匹配,则授权访问。
3、Java实现
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base32;
import javax.crypto.Mac;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.time.Instant;
public class TestTOTP {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//生成Code
int code = generalCode();
//正确的情况
verifyCode(code);
//错误的情况
verifyCode(666666);
}
/**
* 基于TOTP生成Code
*/
public static int generalCode() throws Exception {
String base32Key = "123456";
long timestamp = Instant.now().getEpochSecond() / 60; // 每30秒变化一次验证码
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);
buffer.putLong(timestamp);
byte[] timeBytes = buffer.array();
Base32 base32 = new Base32();
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(base32.decode(base32Key), "HmacSHA1");
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA1");
mac.init(secretKeySpec);
byte[] hmacBytes = mac.doFinal(timeBytes);
int offset = hmacBytes[hmacBytes.length - 1] & 0xF;
int otp = ((hmacBytes[offset] & 0x7F) << 24) |
((hmacBytes[offset + 1] & 0xFF) << 16) |
((hmacBytes[offset + 2] & 0xFF) << 8) |
(hmacBytes[offset + 3] & 0xFF);
otp %= 1000000; // 生成6位验证码
System.out.println("TOTP: " + otp);
return otp;
}
/**
* 校验Code是否正确
*/
public static void verifyCode(int userOTP) throws Exception {
String base32Key = "123456";
long timestamp = Instant.now().getEpochSecond() / 60; // 每30秒变化一次验证码
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);
buffer.putLong(timestamp);
byte[] timeBytes = buffer.array();
Base32 base32 = new Base32();
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(base32.decode(base32Key), "HmacSHA1");
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA1");
mac.init(secretKeySpec);
byte[] hmacBytes = mac.doFinal(timeBytes);
int offset = hmacBytes[hmacBytes.length - 1] & 0xF;
int otp = ((hmacBytes[offset] & 0x7F) << 24) |
((hmacBytes[offset + 1] & 0xFF) << 16) |
((hmacBytes[offset + 2] & 0xFF) << 8) |
(hmacBytes[offset + 3] & 0xFF);
otp %= 1000000; // 生成6位验证码
if (otp == userOTP) {
System.out.println("Verification successful!");
} else {
System.out.println("Verification fail!");
}
}
三、Google双因子认证
1、流程
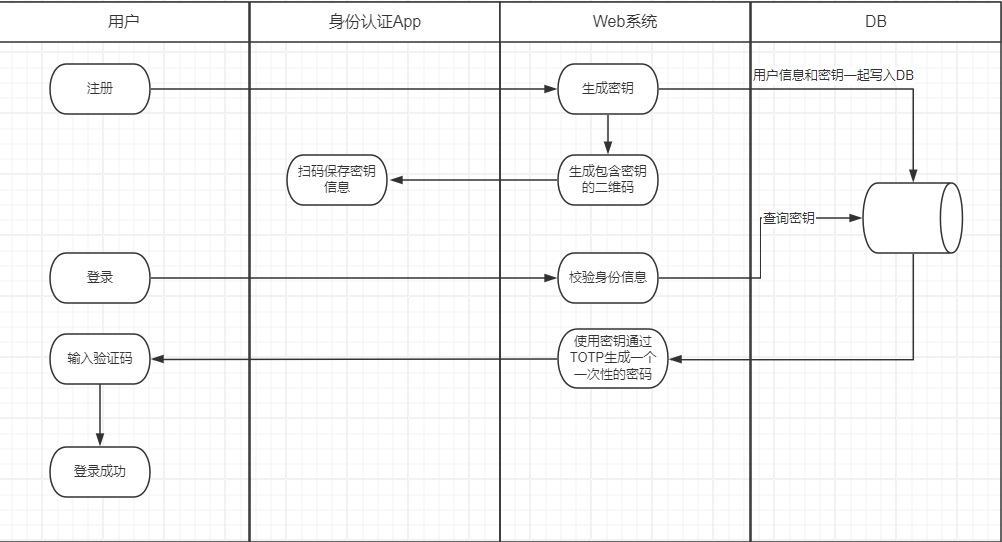
1、用户注册成功时,由后台系统生成随机的密钥(每个用户的密钥不同),注意这里的密钥并不是用于登录,而是之后用于生成一次性动态的密码。
2、将密钥保存到用户信息中,同时将含有密钥的信息发送给用户,可以通过扫描二维码的形式。
3、当用户登录时,第一步校验用户的账号密码是否正确,如果能够正确登录则获取数据库中用户的密钥,与当前时间生成一个一次性的密码。
4、身份认证APP也使用同样的密钥去尝试生成一个动态密码,由服务端来判断这两个密码是否一致,如果一致则表示登录成功,否则登录失败,触发其他的逻辑。
2、Java实现
下面是一个Java实现的版本
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base32;
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64;
import javax.crypto.Mac;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.security.InvalidKeyException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
/**
* Java Server side class for Google Authenticator's TOTP generator
* Thanks to Enrico's blog for the sample code:
*
* @see <a href="http://thegreyblog.blogspot.com/2011/12/google-authenticator-using-it-in-your.html">...</a>
* @see http://code.google.com/p/google-authenticator
* @see http://tools.ietf.org/id/draft-mraihi-totp-timebased-06.txt
*/
public class GoogleAuthenticator {
// 生成的key长度( Generate secret key length)
private static final int SECRET_SIZE = 10;
private static final String SEED = "g8GjEvTbW5oVSV7avL47357438reyhreyuryetredLDVKs2m0QN7vxRs2im5MDaNCWGmcD2rvcZx";
// Java实现随机数算法
private static final String RANDOM_NUMBER_ALGORITHM = "SHA1PRNG";
// 最多可偏移的时间
private int window_size = 1; // default 3 - max 17
/**
* set the windows size. This is an integer value representing the number of
* 30 second windows we allow The bigger the window, the more tolerant of
* clock skew we are.
*
* @param s window size - must be >=1 and <=17. Other values are ignored
*/
public void setWindowSize(int s) {
if (s >= 1 && s <= 17)
window_size = s;
}
/**
* Generate a random secret key. This must be saved by the server and
* associated with the users account to verify the code displayed by Google
* Authenticator. The user must register this secret on their device.
* 生成一个随机秘钥
*
* @return secret key
*/
public String generateSecretKey() {
SecureRandom sr;
try {
sr = SecureRandom.getInstance(RANDOM_NUMBER_ALGORITHM);
sr.setSeed(Base64.decodeBase64(SEED));
byte[] buffer = sr.generateSeed(SECRET_SIZE);
Base32 codec = new Base32();
byte[] bEncodedKey = codec.encode(buffer);
return new String(bEncodedKey);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
// should never occur... configuration error
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 生成绑定二维码(字符串)
*
* @param account 账户信息(展示在Google Authenticator App中的)
* @param secretKey 密钥
* @param title 标题 (展示在Google Authenticator App中的)
* @return
*/
public String spawnScanQRString(String account, String secretKey, String title) {
return "otpauth://totp/" + title + ":" + account + "?secret=" + secretKey + "&issuer=" + title;
}
/**
* Return a URL that generates and displays a QR barcode. The user scans
* this bar code with the Google Authenticator application on their
* smartphone to register the auth code. They can also manually enter the
* secret if desired
*
* @param user user id (e.g. fflinstone)
* @param host host or system that the code is for (e.g. myapp.com)
* @param secret the secret that was previously generated for this user
* @return the URL for the QR code to scan
*/
public String getQRBarcodeURL(String user, String host, String secret) {
String format = "http://www.google.com/chart?chs=200x200&chld=M%%7C0&cht=qr&chl=otpauth://totp/%s@%s?secret=%s";
return String.format(format, user, host, secret);
}
/**
* 生成一个google身份验证器,识别的字符串,只需要把 该方法返回值生成二维码扫描 就可以了。
*
* @param user 账号
* @param secret 密钥
* @return
*/
public String getQRBarcode(String user, String secret) {
String format = "otpauth://totp/%s?secret=%s";
return String.format(format, user, secret);
}
/**
* Check the code entered by the user to see if it is valid 验证code是否合法
*
* @param secret The users secret.
* @param code The code displayed on the users device
* @param t The time in msec (System.currentTimeMillis() for example)
* @return
*/
public boolean checkCode(String secret, long code, long timeMsec) {
Base32 codec = new Base32();
byte[] decodedKey = codec.decode(secret);
// convert unix msec time into a 30 second "window"
// this is per the TOTP spec (see the RFC for details)
long t = (timeMsec / 1000L) / 30L;
// Window is used to check codes generated in the near past.
// You can use this value to tune how far you're willing to go.
for (int i = -window_size; i <= window_size; ++i) {
long hash;
try {
hash = verifyCode(decodedKey, t + i);
} catch (Exception e) {
// Yes, this is bad form - but
// the exceptions thrown would be rare and a static
// configuration problem
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
// return false;
}
if (hash == code) {
return true;
}
}
// The validation code is invalid.
return false;
}
private int verifyCode(byte[] key, long t) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeyException {
byte[] data = new byte[8];
long value = t;
for (int i = 8; i-- > 0; value >>>= 8) {
data[i] = (byte) value;
}
SecretKeySpec signKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "HmacSHA1");
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA1");
mac.init(signKey);
byte[] hash = mac.doFinal(data);
int offset = hash[20 - 1] & 0xF;
// We're using a long because Java hasn't got unsigned int.
long truncatedHash = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
truncatedHash <<= 8;
// We are dealing with signed bytes:
// we just keep the first byte.
truncatedHash |= (hash[offset + i] & 0xFF);
}
truncatedHash &= 0x7FFFFFFF;
truncatedHash %= 1000000;
return (int) truncatedHash;
}
}
3、测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
GoogleAuthenticator authenticator = new GoogleAuthenticator();
//设置时间窗口
authenticator.setWindowSize(3);
//生成密钥
String secretKey = authenticator.generateSecretKey();
log.info("secretKey:{}",secretKey);
//生成绑定的二维码
String qrCode = authenticator.spawnScanQRString("zcy.artisan", secretKey, "hardy");
log.info("qrCode:{}",qrCode);
}
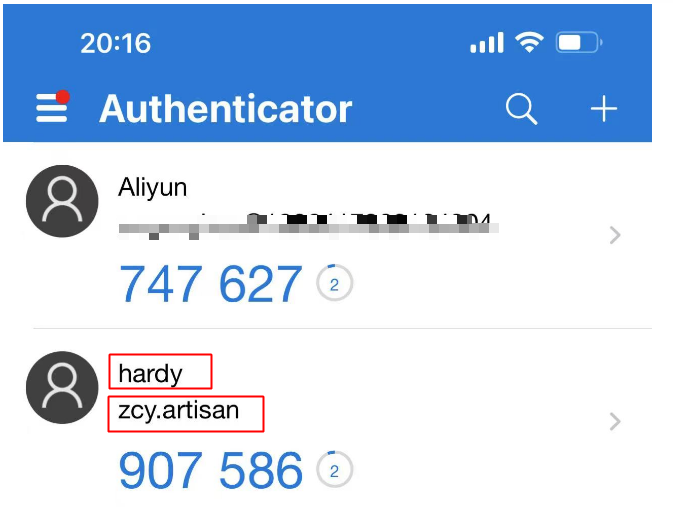
我们使用刚才编写的工具类去绑定一个我们自己的双因子认证,将qrCode生成二维码并使用Authenticator App去绑定效果如下。
四、结束语
至此已经简单的介绍了双因子认证是的实现原理,希望对你有所帮助
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!