nuc980开发板使用Agile Modbus软件包-基于 rs485 通讯
2023-12-26 19:58:35
一、nuc980开发板电路
打开 nuc980-eth2p 开发板原理图,如下:
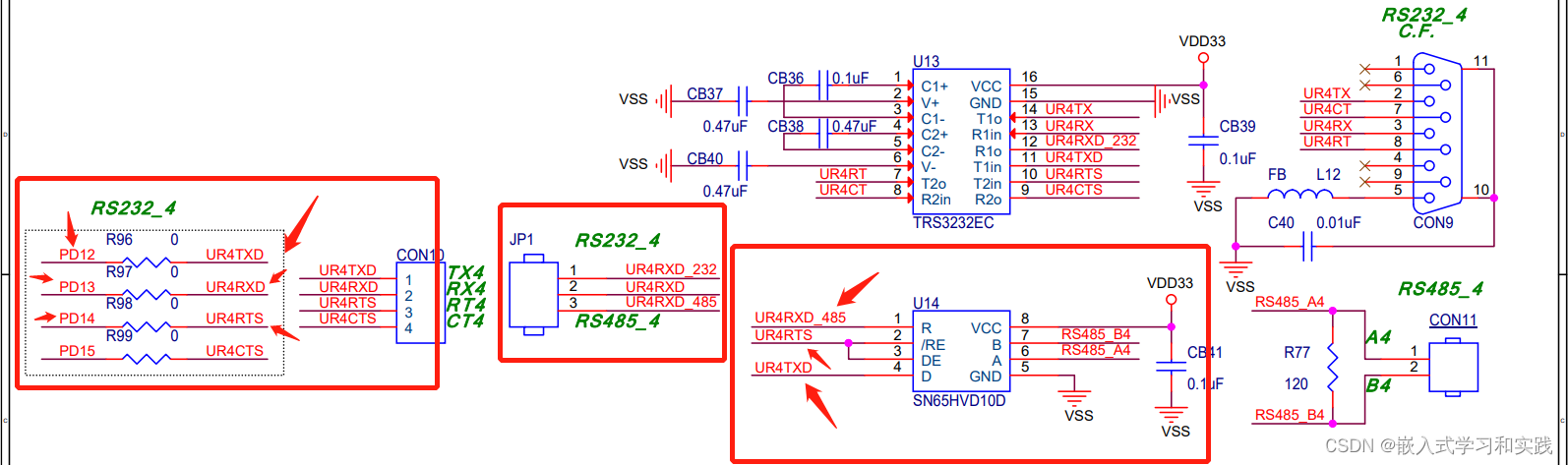
将JP1跳线帽连接到rs485。使用rs485转usb连接到电脑即可。
除了收发引脚,多了一个控制引脚。
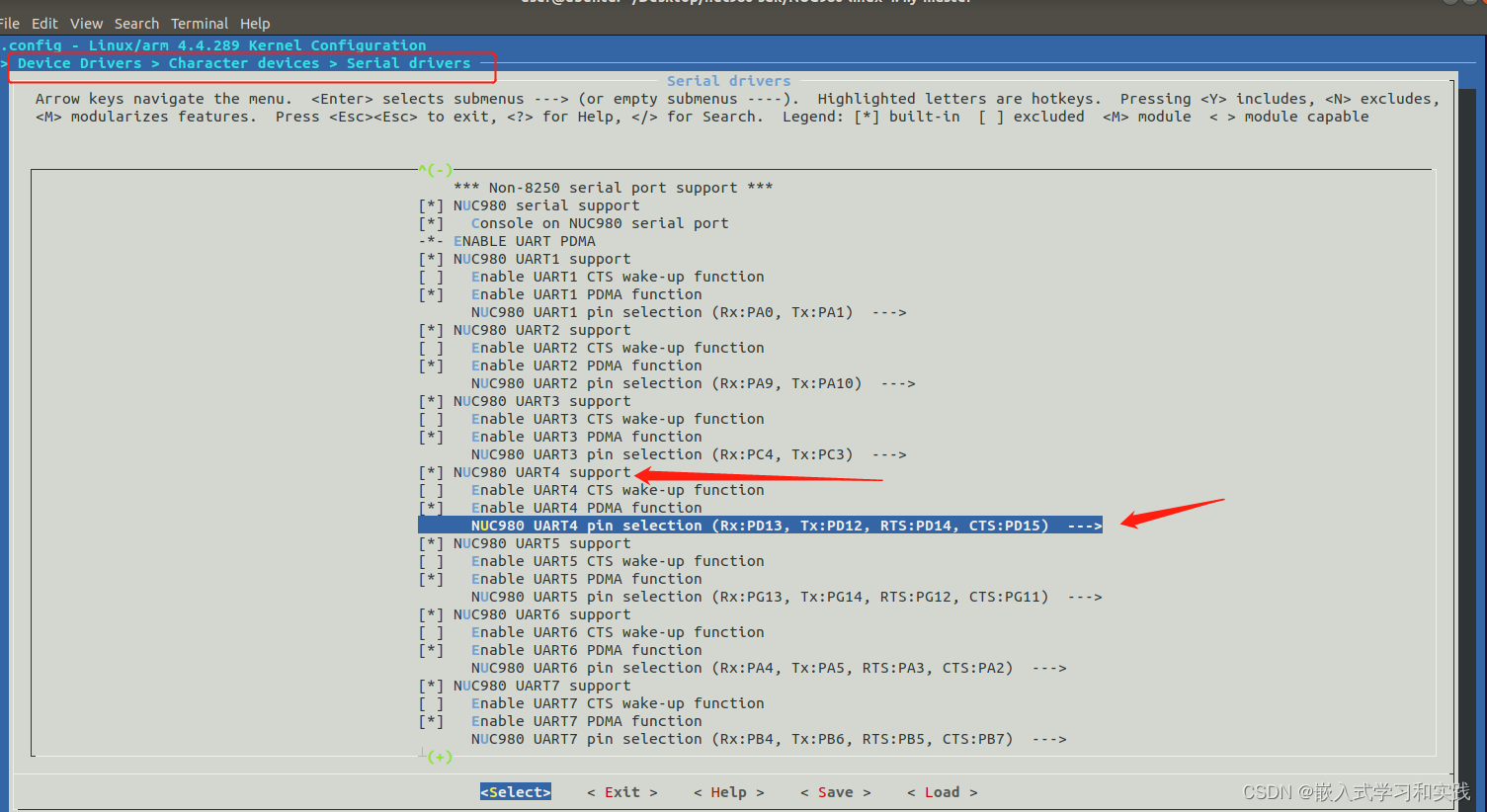
linux内核使能串口4
二、Agile Modbus软件包
1、软件包的获取
下载网址
选择最新版即可。
2、软件包的demo
打开下载的文件,文件工程的结构如下,包含doc、examples、inc、src等文件。
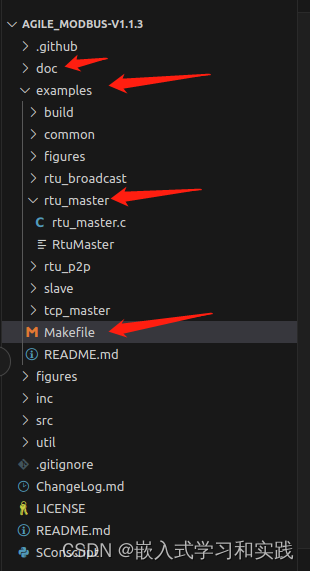
因为我们是 rtu-master,所以打开官方自带的 rtu_master 文件夹。查看串口初始化部分。
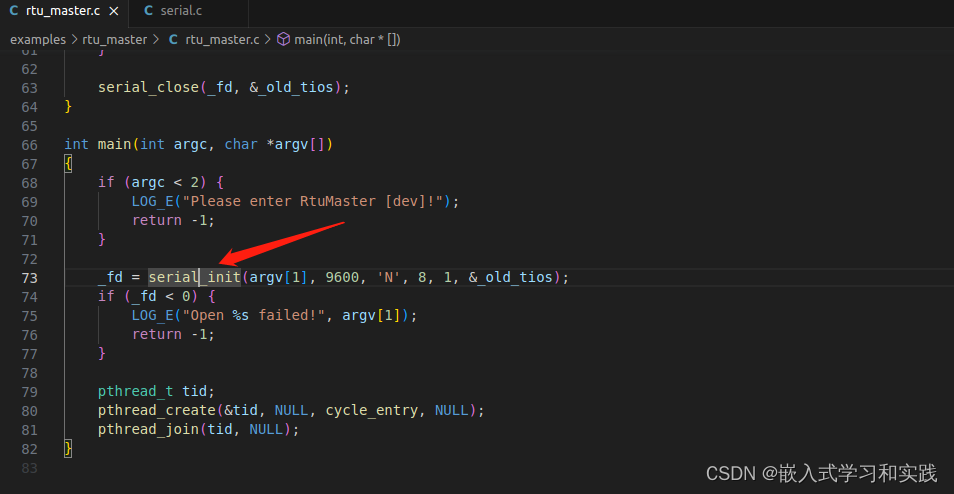
int serial_init(const char *device,
int baud, char parity, int data_bit,
int stop_bit, struct termios *old_tios)
{
struct termios tios;
speed_t speed;
int flags;
/* The O_NOCTTY flag tells UNIX that this program doesn't want
to be the "controlling terminal" for that port. If you
don't specify this then any input (such as keyboard abort
signals and so forth) will affect your process
Timeouts are ignored in canonical input mode or when the
NDELAY option is set on the file via open or fcntl */
flags = O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY | O_EXCL;
#ifdef O_CLOEXEC
flags |= O_CLOEXEC;
#endif
int s = open(device, flags);
if (s == -1) {
LOG_E("ERROR Can't open the device %s (%s)", device, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
flags = fcntl(s, F_GETFL, 0);
flags |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(s, F_SETFL, flags);
flags = fcntl(s, F_GETFD);
flags |= FD_CLOEXEC;
fcntl(s, F_SETFD, flags);
/* Save */
tcgetattr(s, old_tios);
memset(&tios, 0, sizeof(struct termios));
/* C_ISPEED Input baud (new interface)
C_OSPEED Output baud (new interface)
*/
switch (baud) {
case 110:
speed = B110;
break;
case 300:
speed = B300;
break;
case 600:
speed = B600;
break;
case 1200:
speed = B1200;
break;
case 2400:
speed = B2400;
break;
case 4800:
speed = B4800;
break;
case 9600:
speed = B9600;
break;
case 19200:
speed = B19200;
break;
case 38400:
speed = B38400;
break;
#ifdef B57600
case 57600:
speed = B57600;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B115200
case 115200:
speed = B115200;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B230400
case 230400:
speed = B230400;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B460800
case 460800:
speed = B460800;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B500000
case 500000:
speed = B500000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B576000
case 576000:
speed = B576000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B921600
case 921600:
speed = B921600;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B1000000
case 1000000:
speed = B1000000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B1152000
case 1152000:
speed = B1152000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B1500000
case 1500000:
speed = B1500000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B2500000
case 2500000:
speed = B2500000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B3000000
case 3000000:
speed = B3000000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B3500000
case 3500000:
speed = B3500000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B4000000
case 4000000:
speed = B4000000;
break;
#endif
default:
speed = B9600;
LOG_W("WARNING Unknown baud rate %d for %s (B9600 used)", baud, device);
}
/* Set the baud rate */
if ((cfsetispeed(&tios, speed) < 0) ||
(cfsetospeed(&tios, speed) < 0)) {
close(s);
s = -1;
return -1;
}
/* C_CFLAG Control options
CLOCAL Local line - do not change "owner" of port
CREAD Enable receiver
*/
tios.c_cflag |= (CREAD | CLOCAL);
/* CSIZE, HUPCL, CRTSCTS (hardware flow control) */
/* Set data bits (5, 6, 7, 8 bits)
CSIZE Bit mask for data bits
*/
tios.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
switch (data_bit) {
case 5:
tios.c_cflag |= CS5;
break;
case 6:
tios.c_cflag |= CS6;
break;
case 7:
tios.c_cflag |= CS7;
break;
case 8:
default:
tios.c_cflag |= CS8;
break;
}
/* Stop bit (1 or 2) */
if (stop_bit == 1)
tios.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
else /* 2 */
tios.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;
/* PARENB Enable parity bit
PARODD Use odd parity instead of even */
if (parity == 'N') {
/* None */
tios.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
} else if (parity == 'E') {
/* Even */
tios.c_cflag |= PARENB;
tios.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;
} else {
/* Odd */
tios.c_cflag |= PARENB;
tios.c_cflag |= PARODD;
}
/* Read the man page of termios if you need more information. */
/* This field isn't used on POSIX systems
tios.c_line = 0;
*/
/* C_LFLAG Line options
ISIG Enable SIGINTR, SIGSUSP, SIGDSUSP, and SIGQUIT signals
ICANON Enable canonical input (else raw)
XCASE Map uppercase \lowercase (obsolete)
ECHO Enable echoing of input characters
ECHOE Echo erase character as BS-SP-BS
ECHOK Echo NL after kill character
ECHONL Echo NL
NOFLSH Disable flushing of input buffers after
interrupt or quit characters
IEXTEN Enable extended functions
ECHOCTL Echo control characters as ^char and delete as ~?
ECHOPRT Echo erased character as character erased
ECHOKE BS-SP-BS entire line on line kill
FLUSHO Output being flushed
PENDIN Retype pending input at next read or input char
TOSTOP Send SIGTTOU for background output
Canonical input is line-oriented. Input characters are put
into a buffer which can be edited interactively by the user
until a CR (carriage return) or LF (line feed) character is
received.
Raw input is unprocessed. Input characters are passed
through exactly as they are received, when they are
received. Generally you'll deselect the ICANON, ECHO,
ECHOE, and ISIG options when using raw input
*/
/* Raw input */
tios.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG);
/* C_IFLAG Input options
Constant Description
INPCK Enable parity check
IGNPAR Ignore parity errors
PARMRK Mark parity errors
ISTRIP Strip parity bits
IXON Enable software flow control (outgoing)
IXOFF Enable software flow control (incoming)
IXANY Allow any character to start flow again
IGNBRK Ignore break condition
BRKINT Send a SIGINT when a break condition is detected
INLCR Map NL to CR
IGNCR Ignore CR
ICRNL Map CR to NL
IUCLC Map uppercase to lowercase
IMAXBEL Echo BEL on input line too long
*/
if (parity == 'N') {
/* None */
tios.c_iflag &= ~INPCK;
} else {
tios.c_iflag |= INPCK;
}
/* Software flow control is disabled */
tios.c_iflag &= ~(IXON | IXOFF | IXANY);
/* C_OFLAG Output options
OPOST Postprocess output (not set = raw output)
ONLCR Map NL to CR-NL
ONCLR ant others needs OPOST to be enabled
*/
/* Raw ouput */
tios.c_oflag &= ~OPOST;
/* C_CC Control characters
VMIN Minimum number of characters to read
VTIME Time to wait for data (tenths of seconds)
UNIX serial interface drivers provide the ability to
specify character and packet timeouts. Two elements of the
c_cc array are used for timeouts: VMIN and VTIME. Timeouts
are ignored in canonical input mode or when the NDELAY
option is set on the file via open or fcntl.
VMIN specifies the minimum number of characters to read. If
it is set to 0, then the VTIME value specifies the time to
wait for every character read. Note that this does not mean
that a read call for N bytes will wait for N characters to
come in. Rather, the timeout will apply to the first
character and the read call will return the number of
characters immediately available (up to the number you
request).
If VMIN is non-zero, VTIME specifies the time to wait for
the first character read. If a character is read within the
time given, any read will block (wait) until all VMIN
characters are read. That is, once the first character is
read, the serial interface driver expects to receive an
entire packet of characters (VMIN bytes total). If no
character is read within the time allowed, then the call to
read returns 0. This method allows you to tell the serial
driver you need exactly N bytes and any read call will
return 0 or N bytes. However, the timeout only applies to
the first character read, so if for some reason the driver
misses one character inside the N byte packet then the read
call could block forever waiting for additional input
characters.
VTIME specifies the amount of time to wait for incoming
characters in tenths of seconds. If VTIME is set to 0 (the
default), reads will block (wait) indefinitely unless the
NDELAY option is set on the port with open or fcntl.
*/
/* Unused because we use open with the NDELAY option */
tios.c_cc[VMIN] = 0;
tios.c_cc[VTIME] = 0;
if (tcsetattr(s, TCSANOW, &tios) < 0) {
close(s);
s = -1;
return -1;
}
return s;
}
修改Makefile文件
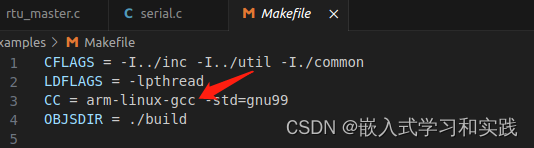
将 gcc 改为 arm-linux-gcc
CC = arm-linux-gcc -std=gnu99
此时编译并下载到开发板,肯定不能正常通信,还需要对 serial.c 文件进行适当的修改。
三、修改思路
思路:通过对控制引脚的控制,来控制数据的接收和发送。
方法1
不修改串口的初始化,通过配置控制引脚的输出高低电平来操作数据的收发。
方法2
修改串口的初始化,配置为rs485模式,配置 RTS的引脚即可。
文章主要介绍方法2。
rs485收发测试可参考linux 串口测试指令和测试程序
四、串口配置修改
添加头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <linux/serial.h>
初始化添加代码
int portfd;
#if (__GNUC__ == 4 && __GNUC_MINOR__ == 3)
struct my_serial_rs485 rs485conf;
struct my_serial_rs485 rs485conf_bak;
#else
struct serial_rs485 rs485conf;
#endif
portfd=s;
if (ioctl (portfd, TIOCGRS485, &rs485conf) < 0)
{
/* Error handling.*/
printf("ioctl TIOCGRS485 error.\n");
}
/* Enable RS485 mode: */
rs485conf.flags |= SER_RS485_ENABLED;
/* Set logical level for RTS pin equal to 1 when sending: */
rs485conf.flags |= SER_RS485_RTS_ON_SEND;
/* set logical level for RTS pin equal to 0 after sending: */
rs485conf.flags &= ~(SER_RS485_RTS_AFTER_SEND);
/* Set rts delay after send, if needed: */
rs485conf.delay_rts_after_send = 0x80;
if (ioctl (portfd, TIOCSRS485, &rs485conf) < 0)
{
/* Error handling.*/
printf("ioctl TIOCSRS485 error.\n");
}
else
{
printf("rs485conf.flags 0x%x.\n", rs485conf.flags);
printf("rs485conf.delay_rts_before_send 0x%x.\n", rs485conf.delay_rts_before_send);
printf("rs485conf.delay_rts_after_send 0x%x.\n", rs485conf.delay_rts_after_send);
}
serial.c 整体代码
#include "serial.h"
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <linux/serial.h>
#define DBG_ENABLE
#define DBG_COLOR
#define DBG_SECTION_NAME "serial"
#define DBG_LEVEL DBG_LOG
#include "dbg_log.h"
int serial_init(const char *device,
int baud, char parity, int data_bit,
int stop_bit, struct termios *old_tios)
{
struct termios tios;
speed_t speed;
int flags;
/* The O_NOCTTY flag tells UNIX that this program doesn't want
to be the "controlling terminal" for that port. If you
don't specify this then any input (such as keyboard abort
signals and so forth) will affect your process
Timeouts are ignored in canonical input mode or when the
NDELAY option is set on the file via open or fcntl */
flags = O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY | O_EXCL;
#ifdef O_CLOEXEC
flags |= O_CLOEXEC;
#endif
int s = open(device, flags);
if (s == -1) {
LOG_E("ERROR Can't open the device %s (%s)", device, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
flags = fcntl(s, F_GETFL, 0);
flags |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(s, F_SETFL, flags);
flags = fcntl(s, F_GETFD);
flags |= FD_CLOEXEC;
fcntl(s, F_SETFD, flags);
/* Save */
tcgetattr(s, old_tios);
memset(&tios, 0, sizeof(struct termios));
/* C_ISPEED Input baud (new interface)
C_OSPEED Output baud (new interface)
*/
switch (baud) {
case 110:
speed = B110;
break;
case 300:
speed = B300;
break;
case 600:
speed = B600;
break;
case 1200:
speed = B1200;
break;
case 2400:
speed = B2400;
break;
case 4800:
speed = B4800;
break;
case 9600:
speed = B9600;
break;
case 19200:
speed = B19200;
break;
case 38400:
speed = B38400;
break;
#ifdef B57600
case 57600:
speed = B57600;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B115200
case 115200:
speed = B115200;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B230400
case 230400:
speed = B230400;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B460800
case 460800:
speed = B460800;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B500000
case 500000:
speed = B500000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B576000
case 576000:
speed = B576000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B921600
case 921600:
speed = B921600;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B1000000
case 1000000:
speed = B1000000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B1152000
case 1152000:
speed = B1152000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B1500000
case 1500000:
speed = B1500000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B2500000
case 2500000:
speed = B2500000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B3000000
case 3000000:
speed = B3000000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B3500000
case 3500000:
speed = B3500000;
break;
#endif
#ifdef B4000000
case 4000000:
speed = B4000000;
break;
#endif
default:
speed = B9600;
LOG_W("WARNING Unknown baud rate %d for %s (B9600 used)", baud, device);
}
/* Set the baud rate */
if ((cfsetispeed(&tios, speed) < 0) ||
(cfsetospeed(&tios, speed) < 0)) {
close(s);
s = -1;
return -1;
}
/* C_CFLAG Control options
CLOCAL Local line - do not change "owner" of port
CREAD Enable receiver
*/
tios.c_cflag |= (CREAD | CLOCAL);
/* CSIZE, HUPCL, CRTSCTS (hardware flow control) */
/* Set data bits (5, 6, 7, 8 bits)
CSIZE Bit mask for data bits
*/
tios.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
switch (data_bit) {
case 5:
tios.c_cflag |= CS5;
break;
case 6:
tios.c_cflag |= CS6;
break;
case 7:
tios.c_cflag |= CS7;
break;
case 8:
default:
tios.c_cflag |= CS8;
break;
}
/* Stop bit (1 or 2) */
if (stop_bit == 1)
tios.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
else /* 2 */
tios.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;
/* PARENB Enable parity bit
PARODD Use odd parity instead of even */
if (parity == 'N') {
/* None */
tios.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
} else if (parity == 'E') {
/* Even */
tios.c_cflag |= PARENB;
tios.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;
} else {
/* Odd */
tios.c_cflag |= PARENB;
tios.c_cflag |= PARODD;
}
/* Read the man page of termios if you need more information. */
/* This field isn't used on POSIX systems
tios.c_line = 0;
*/
/* C_LFLAG Line options
ISIG Enable SIGINTR, SIGSUSP, SIGDSUSP, and SIGQUIT signals
ICANON Enable canonical input (else raw)
XCASE Map uppercase \lowercase (obsolete)
ECHO Enable echoing of input characters
ECHOE Echo erase character as BS-SP-BS
ECHOK Echo NL after kill character
ECHONL Echo NL
NOFLSH Disable flushing of input buffers after
interrupt or quit characters
IEXTEN Enable extended functions
ECHOCTL Echo control characters as ^char and delete as ~?
ECHOPRT Echo erased character as character erased
ECHOKE BS-SP-BS entire line on line kill
FLUSHO Output being flushed
PENDIN Retype pending input at next read or input char
TOSTOP Send SIGTTOU for background output
Canonical input is line-oriented. Input characters are put
into a buffer which can be edited interactively by the user
until a CR (carriage return) or LF (line feed) character is
received.
Raw input is unprocessed. Input characters are passed
through exactly as they are received, when they are
received. Generally you'll deselect the ICANON, ECHO,
ECHOE, and ISIG options when using raw input
*/
/* Raw input */
tios.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG);
/* C_IFLAG Input options
Constant Description
INPCK Enable parity check
IGNPAR Ignore parity errors
PARMRK Mark parity errors
ISTRIP Strip parity bits
IXON Enable software flow control (outgoing)
IXOFF Enable software flow control (incoming)
IXANY Allow any character to start flow again
IGNBRK Ignore break condition
BRKINT Send a SIGINT when a break condition is detected
INLCR Map NL to CR
IGNCR Ignore CR
ICRNL Map CR to NL
IUCLC Map uppercase to lowercase
IMAXBEL Echo BEL on input line too long
*/
if (parity == 'N') {
/* None */
tios.c_iflag &= ~INPCK;
} else {
tios.c_iflag |= INPCK;
}
/* Software flow control is disabled */
tios.c_iflag &= ~(IXON | IXOFF | IXANY);
/* C_OFLAG Output options
OPOST Postprocess output (not set = raw output)
ONLCR Map NL to CR-NL
ONCLR ant others needs OPOST to be enabled
*/
/* Raw ouput */
tios.c_oflag &= ~OPOST;
/* C_CC Control characters
VMIN Minimum number of characters to read
VTIME Time to wait for data (tenths of seconds)
UNIX serial interface drivers provide the ability to
specify character and packet timeouts. Two elements of the
c_cc array are used for timeouts: VMIN and VTIME. Timeouts
are ignored in canonical input mode or when the NDELAY
option is set on the file via open or fcntl.
VMIN specifies the minimum number of characters to read. If
it is set to 0, then the VTIME value specifies the time to
wait for every character read. Note that this does not mean
that a read call for N bytes will wait for N characters to
come in. Rather, the timeout will apply to the first
character and the read call will return the number of
characters immediately available (up to the number you
request).
If VMIN is non-zero, VTIME specifies the time to wait for
the first character read. If a character is read within the
time given, any read will block (wait) until all VMIN
characters are read. That is, once the first character is
read, the serial interface driver expects to receive an
entire packet of characters (VMIN bytes total). If no
character is read within the time allowed, then the call to
read returns 0. This method allows you to tell the serial
driver you need exactly N bytes and any read call will
return 0 or N bytes. However, the timeout only applies to
the first character read, so if for some reason the driver
misses one character inside the N byte packet then the read
call could block forever waiting for additional input
characters.
VTIME specifies the amount of time to wait for incoming
characters in tenths of seconds. If VTIME is set to 0 (the
default), reads will block (wait) indefinitely unless the
NDELAY option is set on the port with open or fcntl.
*/
/* Unused because we use open with the NDELAY option */
tios.c_cc[VMIN] = 0;
tios.c_cc[VTIME] = 0;
if (tcsetattr(s, TCSANOW, &tios) < 0) {
close(s);
s = -1;
return -1;
}
/***************************/
int portfd;
#if (__GNUC__ == 4 && __GNUC_MINOR__ == 3)
struct my_serial_rs485 rs485conf;
struct my_serial_rs485 rs485conf_bak;
#else
struct serial_rs485 rs485conf;
//struct serial_rs485 rs485conf_bak;
#endif
//struct termios newtios,oldtios; /*termianal settings */
portfd=s;
/*get serial port parnms,save away */
// tcgetattr(portfd,&newtios);
// memcpy(&oldtios,&newtios,sizeof newtios);
// /* configure new values */
// cfmakeraw(&newtios); /*see man page */
// newtios.c_iflag |=IGNPAR; /*ignore parity on input */
// newtios.c_oflag &= ~(OPOST | ONLCR | OLCUC | OCRNL | ONOCR | ONLRET | OFILL);
// newtios.c_cflag = CS8 | CLOCAL | CREAD;
// newtios.c_cc[VMIN]=1; /* block until 1 char received */
// newtios.c_cc[VTIME]=0; /*no inter-character timer */
/* 115200 bps */
// cfsetospeed(&newtios,B9600);
// cfsetispeed(&newtios,B9600);
// /* register cleanup stuff */
// atexit(reset_tty_atexit);
// memset(&sa,0,sizeof sa);
// sa.sa_handler = reset_tty_handler;
// sigaction(SIGHUP,&sa,NULL);
// sigaction(SIGINT,&sa,NULL);
// sigaction(SIGPIPE,&sa,NULL);
// sigaction(SIGTERM,&sa,NULL);
// /*apply modified termios */
// saved_portfd=portfd;
// tcflush(portfd,TCIFLUSH);
// tcsetattr(portfd,TCSADRAIN,&newtios);
if (ioctl (portfd, TIOCGRS485, &rs485conf) < 0)
{
/* Error handling.*/
printf("ioctl TIOCGRS485 error.\n");
}
/* Enable RS485 mode: */
rs485conf.flags |= SER_RS485_ENABLED;
/* Set logical level for RTS pin equal to 1 when sending: */
rs485conf.flags |= SER_RS485_RTS_ON_SEND;
//rs485conf.flags |= SER_RS485_RTS_AFTER_SEND;
/* set logical level for RTS pin equal to 0 after sending: */
rs485conf.flags &= ~(SER_RS485_RTS_AFTER_SEND);
//rs485conf.flags &= ~(SER_RS485_RTS_ON_SEND);
/* Set rts delay after send, if needed: */
rs485conf.delay_rts_after_send = 0x80;
if (ioctl (portfd, TIOCSRS485, &rs485conf) < 0)
{
/* Error handling.*/
printf("ioctl TIOCSRS485 error.\n");
}
else
{
printf("rs485conf.flags 0x%x.\n", rs485conf.flags);
printf("rs485conf.delay_rts_before_send 0x%x.\n", rs485conf.delay_rts_before_send);
printf("rs485conf.delay_rts_after_send 0x%x.\n", rs485conf.delay_rts_after_send);
}
/****************************/
return s;
}
void serial_close(int s, struct termios *old_tios)
{
if (s != -1) {
tcsetattr(s, TCSANOW, old_tios);
close(s);
}
}
int serial_send(int s, const uint8_t *buf, int length)
{
return write(s, buf, length);
}
int serial_receive(int s, uint8_t *buf, int bufsz, int timeout)
{
int len = 0;
int rc = 0;
fd_set rset;
struct timeval tv;
while (bufsz > 0) {
FD_ZERO(&rset);
FD_SET(s, &rset);
tv.tv_sec = timeout / 1000;
tv.tv_usec = (timeout % 1000) * 1000;
rc = select(s + 1, &rset, NULL, NULL, &tv);
if (rc == -1) {
if (errno == EINTR)
continue;
}
if (rc <= 0) {
break;
}
rc = read(s, buf + len, bufsz);
if (rc <= 0) {
break;
}
len += rc;
bufsz -= rc;
timeout = 20;
}
if (rc >= 0) {
rc = len;
}
return rc;
}
int serial_flush(int s)
{
if (s != -1) {
tcflush(s, TCIOFLUSH);
}
return 0;
}
五、编译验证
将修改后的代码进行交叉编译,并下载到开发板。
打开测试软件,启动程序。
软件通信日志部分:
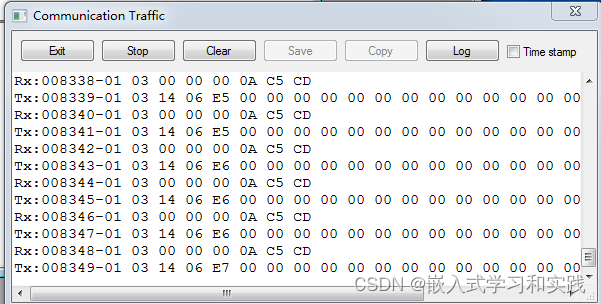
开发板串口打印信息:
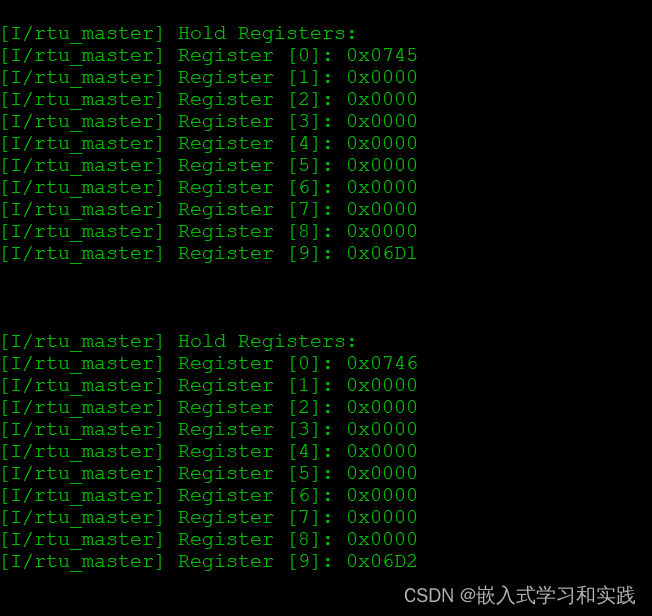
程序能能够通过rs485正常获取到modbus数据。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46158019/article/details/135217703
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!