生信算法2 - DNA测序算法实践之序列统计
2023-12-13 16:36:55
生信序列基本操作算法
建议在Jupyter实践,python版本3.9
1. 读取fastq序列
# fastq序列获取
!wget http://d28rh4a8wq0iu5.cloudfront.net/ads1/data/SRR835775_1.first1000.fastq
def readFastq(filename):
# 序列列表
sequences = []
# 质量值列表
qualities = []
with open(filename) as fh:
# 根据fastq文件格式获取内容
while True:
# 跳过行
fh.readline()
# 读取序列,并去除末尾换行符\n
seq = fh.readline().rstrip()
# 跳过行
fh.readline()
# 碱基质量
qual = fh.readline().rstrip()
if len(seq) == 0:
break
sequences.append(seq)
qualities.append(qual)
return sequences, qualities
seqs, quals = readFastq('SRR835775_1.first1000.fastq')
print(seqs)
print(quals)

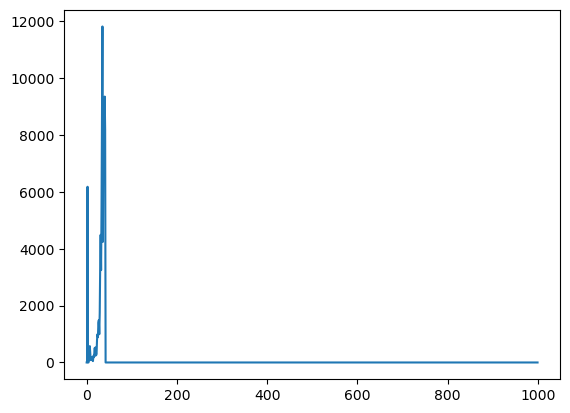
2. 获取fastq数据测序碱基质量直方图
# 质量值转换
def phred33ToQ(qual):
return ord(qual) - 33
# 获取碱基质量值数据
def createHist(qualities: list):
hist = [0]* len(qualities)
for read in qualities:
for phred in read:
q = phred33ToQ(phred)
hist[q] += 1
return hist
hist_data = createHist(quals)
print(hist_data)
# matplotlib绘图
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(range(len(hist_data)), hist_data)
plt.show()
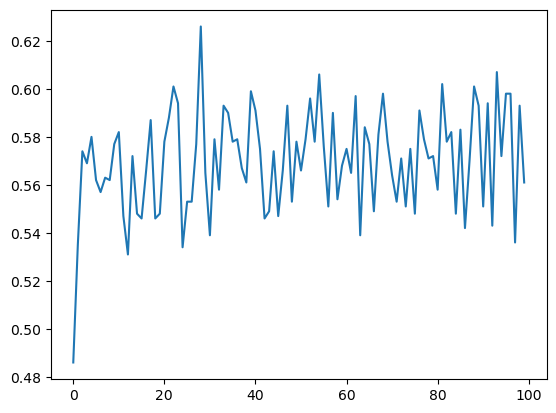
3. 计算fastq序列的平均GC含量
# 获取fastq序列的平均GC含量
def getGCByPosition(reads):
gc = [0] * 100
totals = [0] * 100
for read in reads:
# 遍历单个reads
for i in range(len(read)):
if read[i] == 'C' or read[i] == 'G':
gc[i] += 1
# 总reads数加1
totals[i] += 1
# 获取GC含量平均值
for i in range(len(gc)):
if totals[i] > 0:
gc[i] /= float(totals[i])
return gc
gc = getGCByPosition(seqs)
# 绘图
plt.plot(range(len(gc)), gc)
plt.show()
4. 计算fastq序列的ATCGN碱基数量
import collections
count = collections.Counter()
for seq in seqs:
count.update(seq)
count
# Counter({'G': 28742, 'C': 28272, 'T': 21836, 'A': 21132, 'N': 18})
5. 读取基因组fasta文件
!wget http://d28rh4a8wq0iu5.cloudfront.net/ads1/data/phix.fa
def readGenome(file_path):
genome = ''
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
# 遍历fasta文件每行
for line in f:
# 忽略>行
if not line[0] == '>':
genome += line.rstrip()
return genome
genome = readGenome('phix.fa')
genome

5. 获取短重复序列的序列位置算法
# 获取短重复序列的序列位置
def getRepeatSequencePosition(repeatSeq, seq):
occurrences = []
for i in range(len(seq) - len(repeatSeq) + 1):
match = True
for j in range(len(repeatSeq)):
print(seq[i+j], '\t', repeatSeq[j])
if seq[i+j] != repeatSeq[j]:
match = False
break
if match:
occurrences.append(f"{i}:{i+j}")
return occurrences
repeatSeq = 'AG'
seq = 'AGCTTAGATAGCAGG'
getRepeatSequencePosition(repeatSeq, seq)
# ['0:1', '5:6', '9:10', '12:13']
6. 基于基因组序列随机生成reads算法
import random
# 根据给定基因组fasta文件随机生成reads序列
def generateReads(genome, numReads, readLength):
reads = []
for _ in range(numReads):
start = random.randint(0, len(genome)-readLength) - 1
reads.append(genome[start : start+readLength])
return reads
# 生成50个长度为100bp的reads序列
reads = generateReads(genome, 50, 100)
reads

生信算法文章
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/LittleComputerRobot/article/details/134970714
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!