【二叉树的顺序结构及实现二-堆】
2024-01-03 10:53:34
一、Heap.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// 堆结构体
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef struct Heap
{
HPDataType* a;
int size;
int capacity;
}HP;
//向上调整算法
void AdjustUp(int* a, int child);
//向下调整算法
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent);
//交换函数
void Swap(HPDataType* px, HPDataType* py);
// 堆的初始化
void HeapInit(HP* hp);
// 堆的销毁
void HeapDestroy(HP* hp);
// 堆的插入
void HeapPush(HP* hp, HPDataType x);
// 堆的删除
void HeapPop(HP* hp);
//取堆顶的数据
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* hp);
//堆的打印
void HeapPrint(HP* hp);
// 堆的判空
bool HeapEmpty(HP* hp);
// 堆的数据个数
int HeapSize(HP* hp);
二、Heap.c
#include "Heap.h"
void Swap(HPDataType* px, HPDataType* py)
{
HPDataType tmp = *px;
*px = *py;
*py = tmp;
}
void HeapInit(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
hp->a = NULL;
hp->size = hp->capacity = 0;
}
void HeapDestroy(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
free(hp->a);
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
}
void AdjustUp(int* a, int child)
{
assert(a);
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
//while (parent >= 0)
while (child > 0)
{
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void HeapPrint(HP* hp)
{
for (int i = 0; i < hp->size; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", hp->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void HeapPush(HP* hp, HPDataType x)
{
assert(hp);
if (hp->size == hp->capacity)
{
size_t newCapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2;
HPDataType* tmp = realloc(hp->a, sizeof(HPDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
hp->a = tmp;
hp->capacity = newCapacity;
}
hp->a[hp->size] = x;
hp->size++;
AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size - 1);
}
bool HeapEmpty(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->size == 0;
}
int HeapSize(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
return hp->size;
}
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
assert(!HeapEmpty(hp));
return hp->a[0];
}
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < n)
{
// 选出左右孩子中小的那一个
if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] < a[child])
{
++child;
}
// 如果小的孩子小于父亲,则交换,并继续向下调整
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 删除堆顶的数据
void HeapPop(HP* hp)
{
assert(hp);
assert(!HeapEmpty(hp));
Swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size - 1]);
hp->size--;
AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0);
}
三、Test.c
#include "Heap.h"
// 在N个数找出最大的前K个 or 在N个数找出最小的前K个
void PrintTopK(int* a, int n, int k)
{
HP hp;
HeapInit(&hp);
// 创建一个K个数的小堆
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
}
// 剩下的N-K个数跟堆顶的数据比较,比他大,就替换他进堆
for (int i = k; i < n; ++i)
{
if (a[i] > HeapTop(&hp))
{
HeapPop(&hp);
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
//hp.a[0] = a[i];
//AdjustDown(hp.a, hp.size, 0);
}
}
HeapPrint(&hp);
HeapDestroy(&hp);
}
void TestTopk()
{
int n = 1000000;
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
srand(time(0));
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
a[i] = rand() % 1000000;
}
// 再去设置10个比100w大的数
a[5] = 1000000 + 1;
a[1231] = 1000000 + 2;
a[5355] = 1000000 + 3;
a[51] = 1000000 + 4;
a[15] = 1000000 + 5;
a[2335] = 1000000 + 6;
a[9999] = 1000000 + 7;
a[76] = 1000000 + 8;
a[423] = 1000000 + 9;
a[3144] = 1000000 + 10;
PrintTopK(a, n, 10);
}
void TestHeap()
{
int a[] = { 49,25,34,18,37,19,65,15,27,28 };
HP hp;
HeapInit(&hp);
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); ++i)
{
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
}
HeapPrint(&hp);
HeapPop(&hp);
HeapPrint(&hp);
HeapPop(&hp);
HeapPrint(&hp);
HeapPop(&hp);
HeapPrint(&hp);
HeapPop(&hp);
HeapPrint(&hp);
HeapDestroy(&hp);
}
int main()
{
printf("TestTopk():\n");
TestTopk();
printf("TestHeap():\n");
TestHeap();
return 0;
}
//升序 空间复杂度是O(N)
void HeapSort1(int* a, int n)
{
HP hp;
HeapInit(&hp);
// 建议一个N个小堆
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
}
// Pop N 次
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
a[i] = HeapTop(&hp);
HeapPop(&hp);
}
HeapDestroy(&hp);
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 70, 56, 30, 25, 15, 10, 75, 33, 50, 69 };
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); ++i)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
HeapSort1(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); ++i)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
void HeapSort2(int* a, int n)
{
//把a构建成小堆
//方法1:
//O(N*logN)
/*for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
AdjustUp(a, i);
}*/
//方法2:
//O(N)
for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; --i)
{
AdjustDown(a, n, i);
}
//依次选数,调堆
//O(N*logN)
for (int end = n - 1; end > 0; --end)
{
Swap(&a[end], &a[0]);
//再调堆,选出次小的数
AdjustDown(a, end, 0);
}
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 70, 56, 30, 25, 15, 10, 75, 33, 50, 69 };
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); ++i)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
HeapSort2(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); ++i)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
四、运行结果
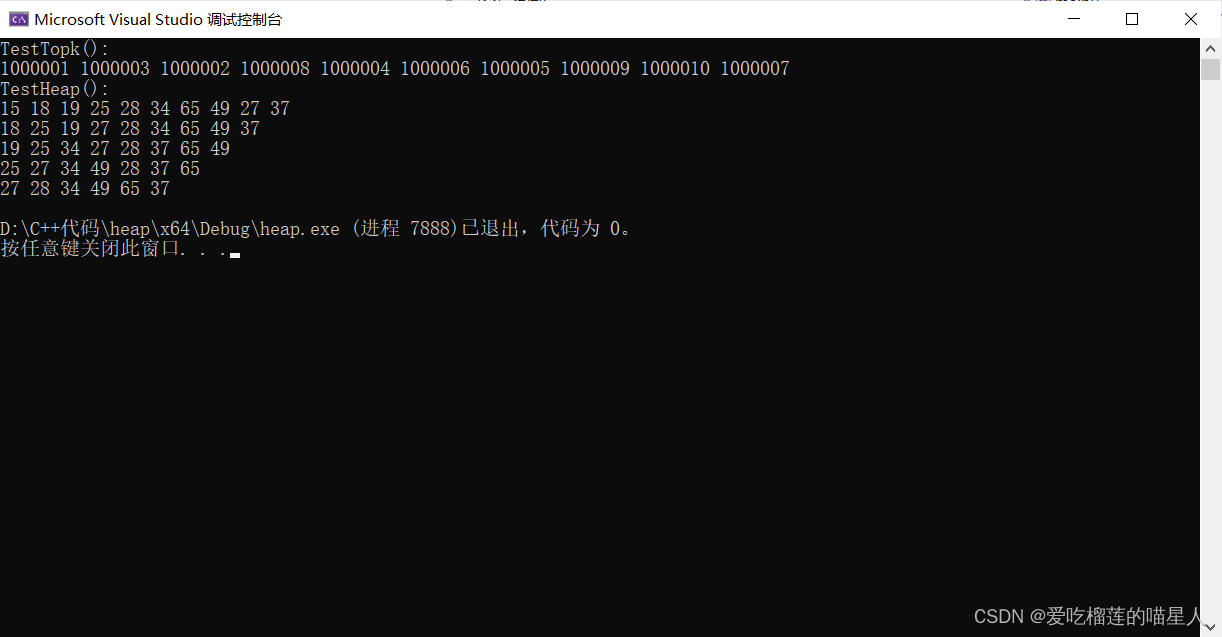
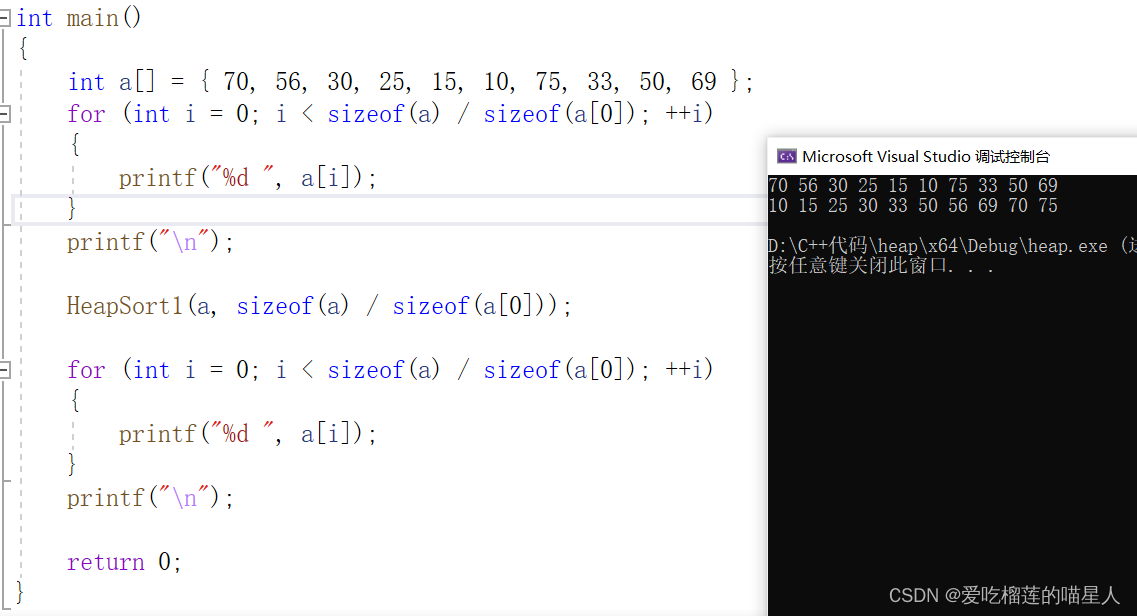
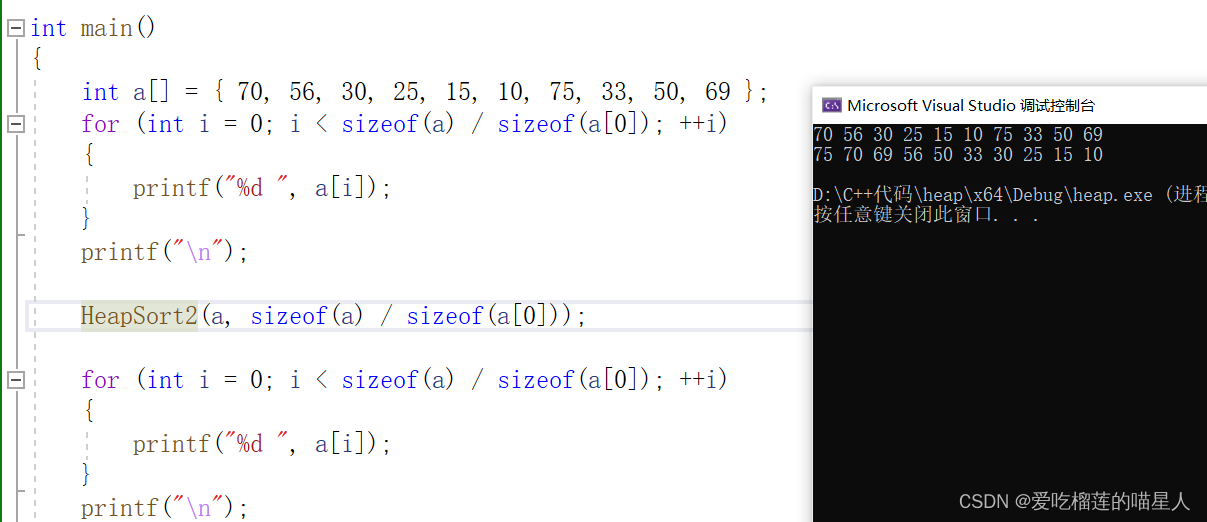
小常识:10亿个整数,大概占用4G内存空间 1G = 1024MB=1024*1024KB=1024*1024*1024Byte=10亿字节
以上是本篇文章的全部内容,如果文章有错误或者有看不懂的地方,多和喵博主交流。互相学习互相进步。如果这篇文章对你有帮助,可以给喵博主一个关注,你们的支持是我最大的动力。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_58944156/article/details/135346564
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!