【霹雳吧啦】手把手带你入门语义分割の番外12:U2-Net 源码讲解(PyTorch)—— 网络的搭建
目录
前言
文章性质:学习笔记 📖
视频教程:U2-Net 源码解析(Pytorch)- 2 网络的搭建
主要内容:根据 视频教程 中提供的 U2-Net?源代码(PyTorch),对 model.py?文件进行具体讲解。
Preparation
├── src: 搭建网络相关代码
├── train_utils: 训练以及验证相关代码
├── my_dataset.py: 自定义数据集读取相关代码
├── predict.py: 简易的预测代码
├── train.py: 单GPU或CPU训练代码
├── train_multi_GPU.py: 多GPU并行训练代码
├── validation.py: 单独验证模型相关代码
├── transforms.py: 数据预处理相关代码
└── requirements.txt: 项目依赖

?
一、U2-Net 网络结构图
原论文提供的 U2-Net 网络结构图如下所示:?
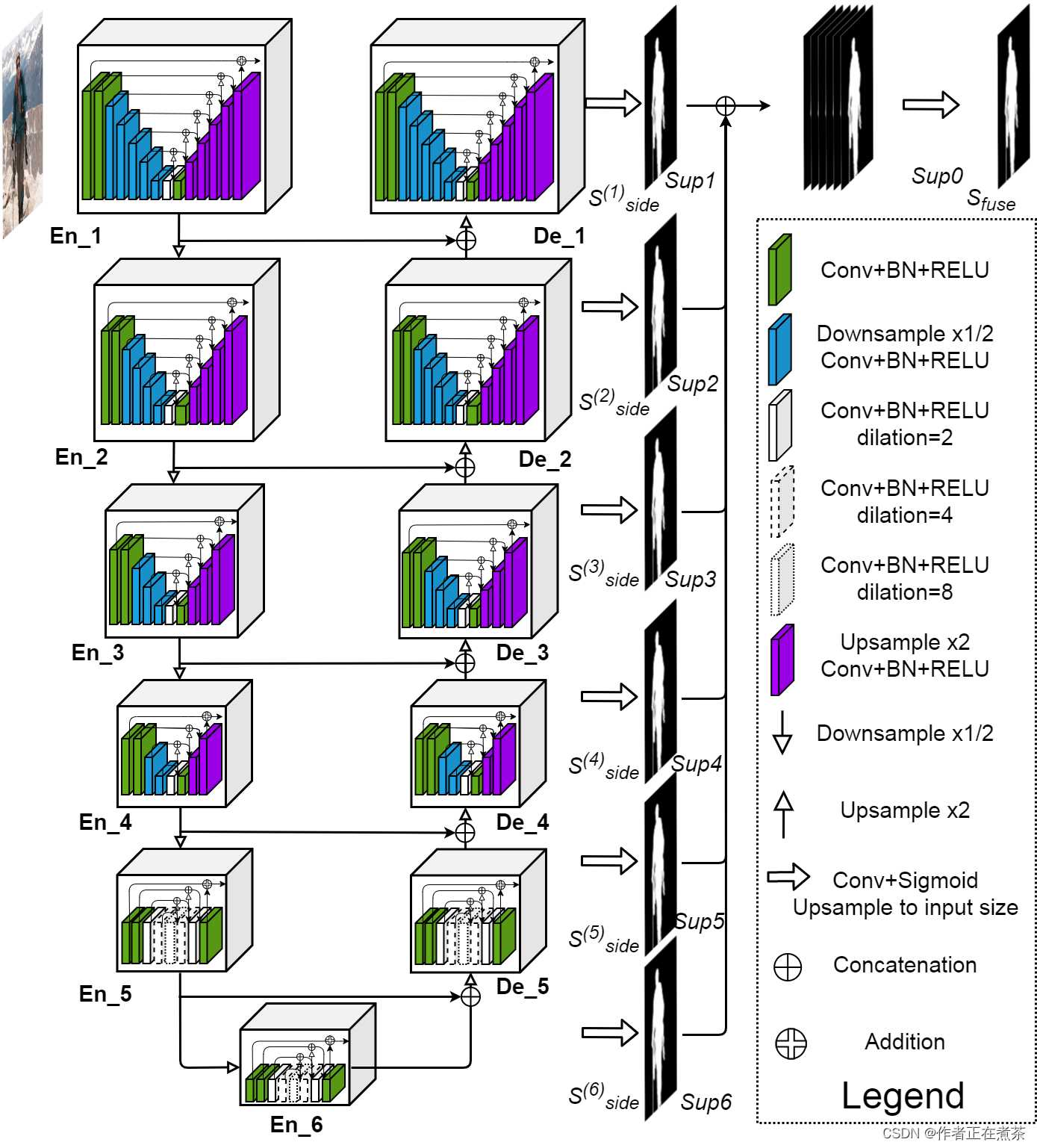 ?
?
【说明】在 Encoder 阶段,每通过一个 block 后都下采样 2 倍(maxpool),在 Decoder 阶段,每通过一个 block 后都上采样 2 倍(bilinear)。U2-Net 网络的核心 block 是 ReSidual U-block,分为具备上下采样的 block 和不具备上下采样的 block(Encoder5、Encoder6、Decoder5)。
二、U2-Net 网络源代码
1、model.py
(1)ConvBNReLU 类
这个 ConvBNReLU 类继承自 nn.Module 父类,传入了输入通道数 in_ch、输出通道数 out_ch、卷积核大小 kernel_size 和膨胀因子 dilation 等参数,当 dilation 设置为 1 时,代表当前这个卷积层是普通卷积,当 dilation 大于 1 时,代表当前这个卷积层是膨胀卷积。
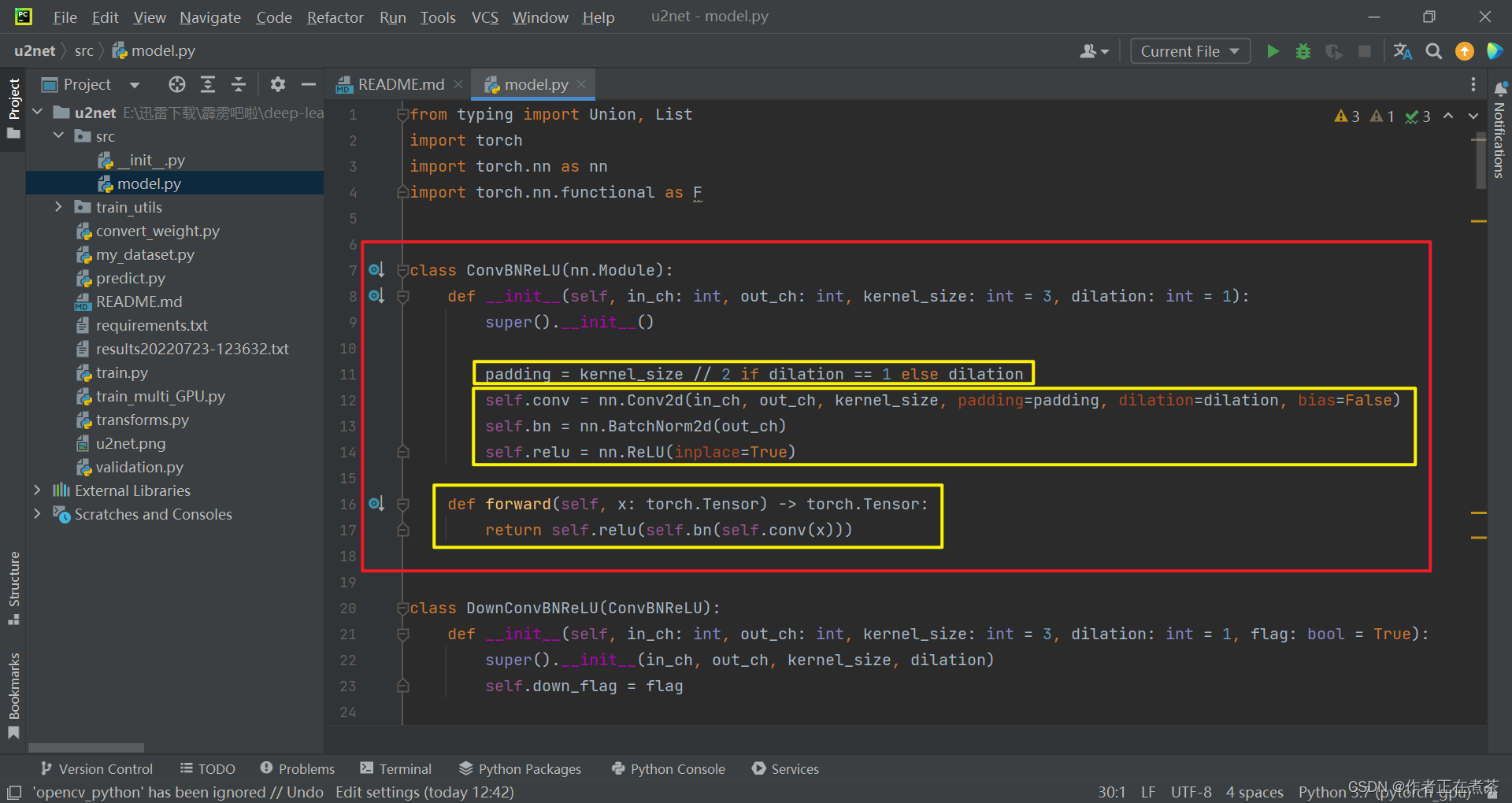
【代码解析】对 ConvBNReLU 类代码进行具体讲解(结合上图):
- ?根据传入的 kernel_size 和 dilation 计算对应的 padding
- ?分别使用 Conv2d、BatchNorm2d、ReLU 实例化卷积层、BN 层、ReLU 层
- ?定义前向传播函数,使得输入张量 x 依次通过卷积层、BN 层、ReLU 层
(2)DownConvBNReLU 类
这个 DownConvBNReLU 类继承自?ConvBNReLU 类。
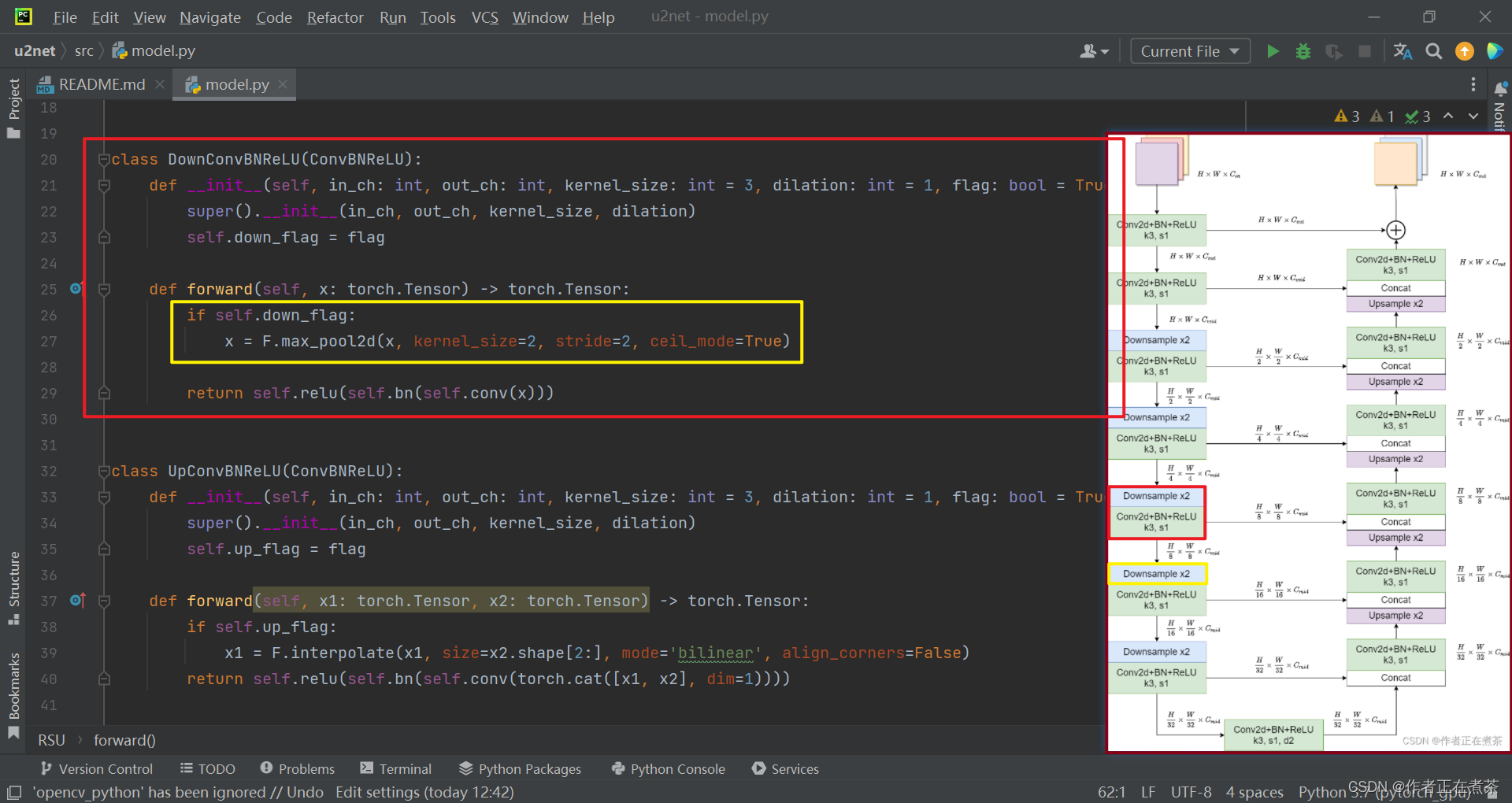
【说明】Encoder 部分:使用 F.max_pool2d 方法进行下采样,再依次通过 Conv2d 层、BN 层、ReLU 层。?
(3)UpConvBNReLU 类
这个 UpConvBNReLU 类继承自?ConvBNReLU 类。
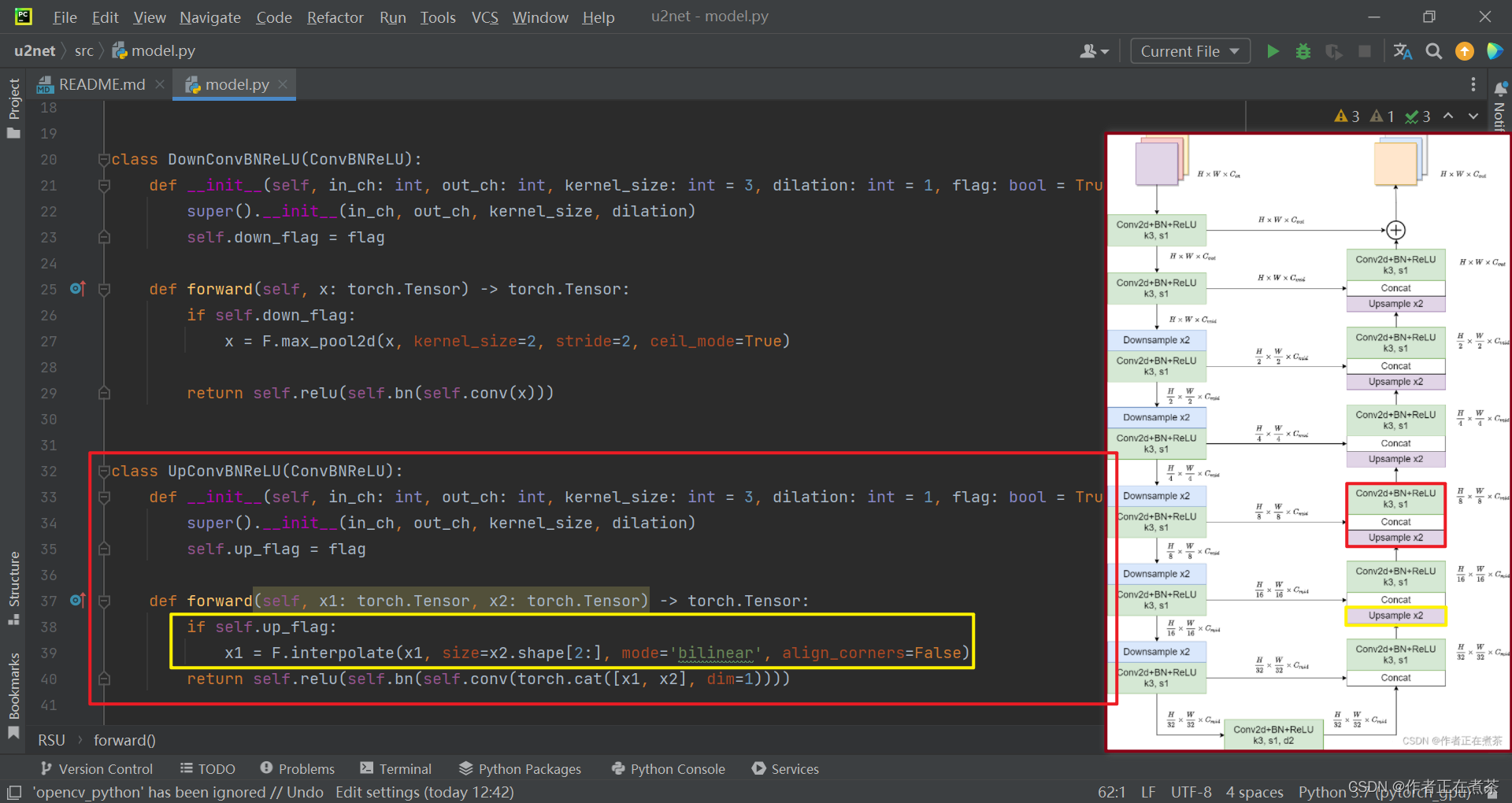
【说明】Decoder 部分:使用 F.interpolate 中的双线性插值方法进行上采样,这里注意,经过双线性插值法后,x2 的宽高将与 x1 的宽高相同,再用 torch.cat 将 Encoder 中的 x2 与 Decoder 中的 x1 连接,最后依次通过 Conv2d 层、BN 层、ReLU 层。
(4)RSU 类 & RSU4F 类
在之前的文章中已经具体介绍过 U2-Net 的两种 block 结构:Encoder1~Encoder4 与 Decoder1~Decoder4 采用的是同一种结构的 block ,只不过深度不同。Encoder5、Encoder6、Decoder5 采用的是另一种结构的 block 。 我们先来简单回忆下第一种 block 结构:
- U2-Net 网络结构中的 Encoder1 和 Decoder1 采用的是 RSU-7 结构
- U2-Net 网络结构中的 Encoder2 和 Decoder2 采用的是 RSU-6 结构
- U2-Net 网络结构中的 Encoder3 和 Decoder3 采用的是 RSU-5 结构
- U2-Net 网络结构中的 Encoder4 和 Decoder4 采用的是 RSU-4 结构
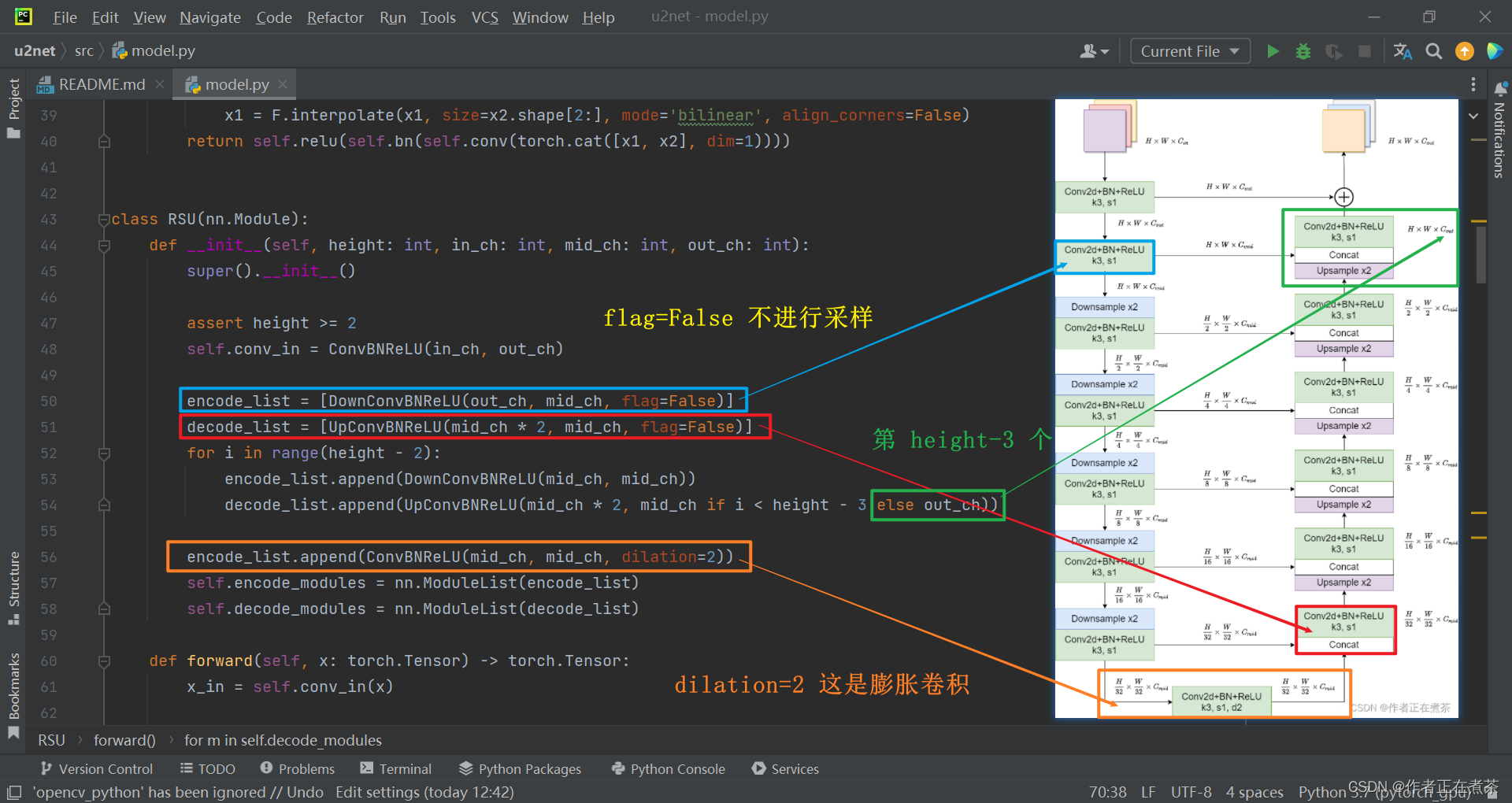
【说明】相邻 block 相差一次下采样和一次上采样,例如 RSU-6 相比于 RSU-7 少了一个下采样卷积和上采样卷积部分,RSU-7 是下采样 32 倍和上采样 32 倍,RSU-6 是下采样 16 倍和上采样 16 倍。
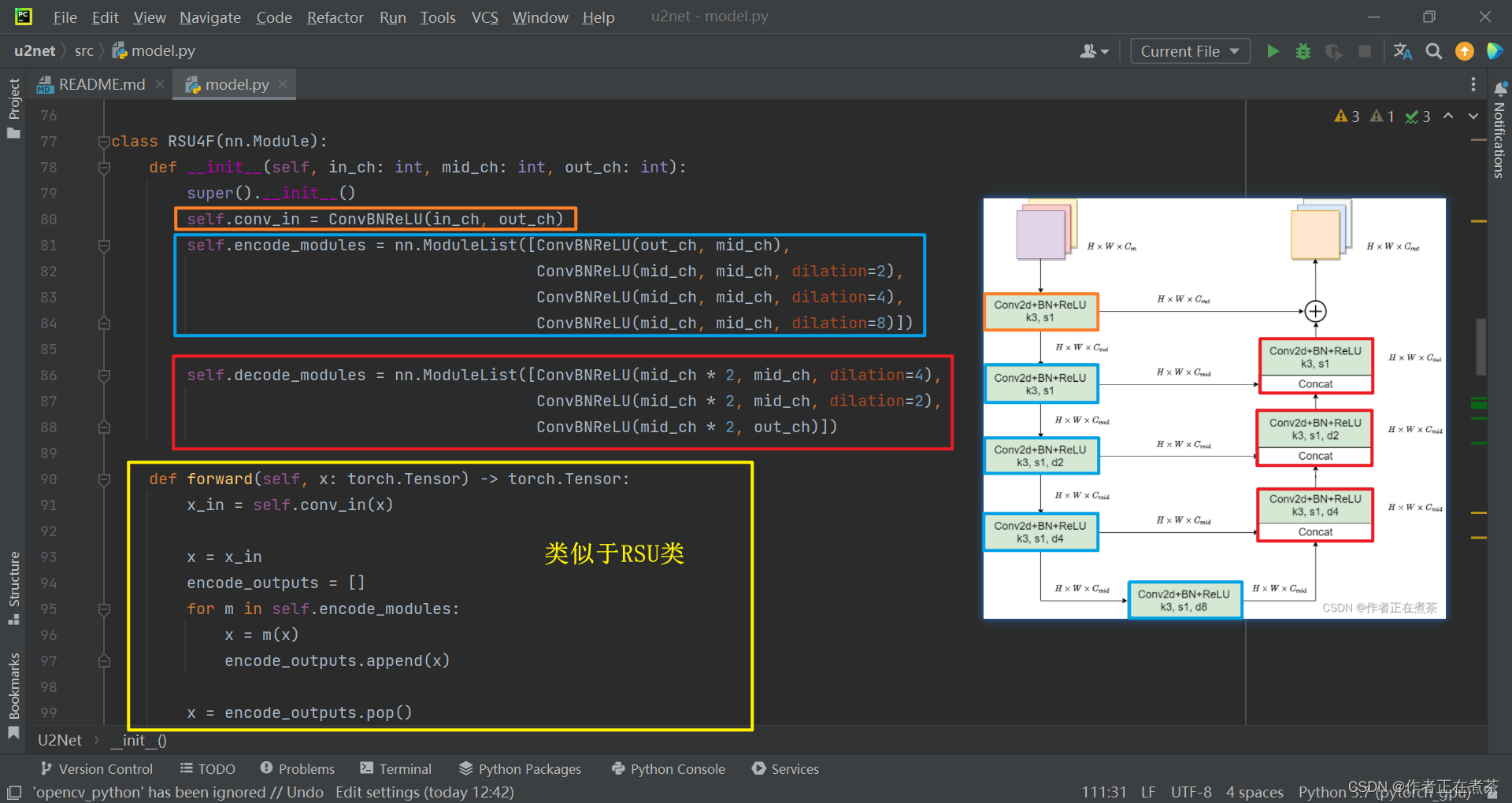
再来回忆第二种 block 结构,U2-Net 中的 Encoder5、Encoder6、Decoder5 采用的都是 RSU-4F 结构,注意 RSU-4F 与 RSU-4 的结构并不相同,在 RSU-4F 中未进行下采样和上采样,而是将?上下采样 全部替换成了?膨胀卷积?,整个过程中特征图的宽高不变。
下面是 RSU 类和 RSU4F 类的代码截图,在 RSU 类的初始化 __init__ 方法中,传入的 height 参数是指 RSU 结构的深度。
(5)U2Net 类
这个 U2Net 类继承自 nn.Module 父类,在其初始化 __init__ 方法中,传入参数包括?cfg ,而在我们搭建 U2-Net 标准版以及轻量级的版本时,都会传入 cfg ,分别可以在 u2net_full 和 u2net_lite 函数中查看:
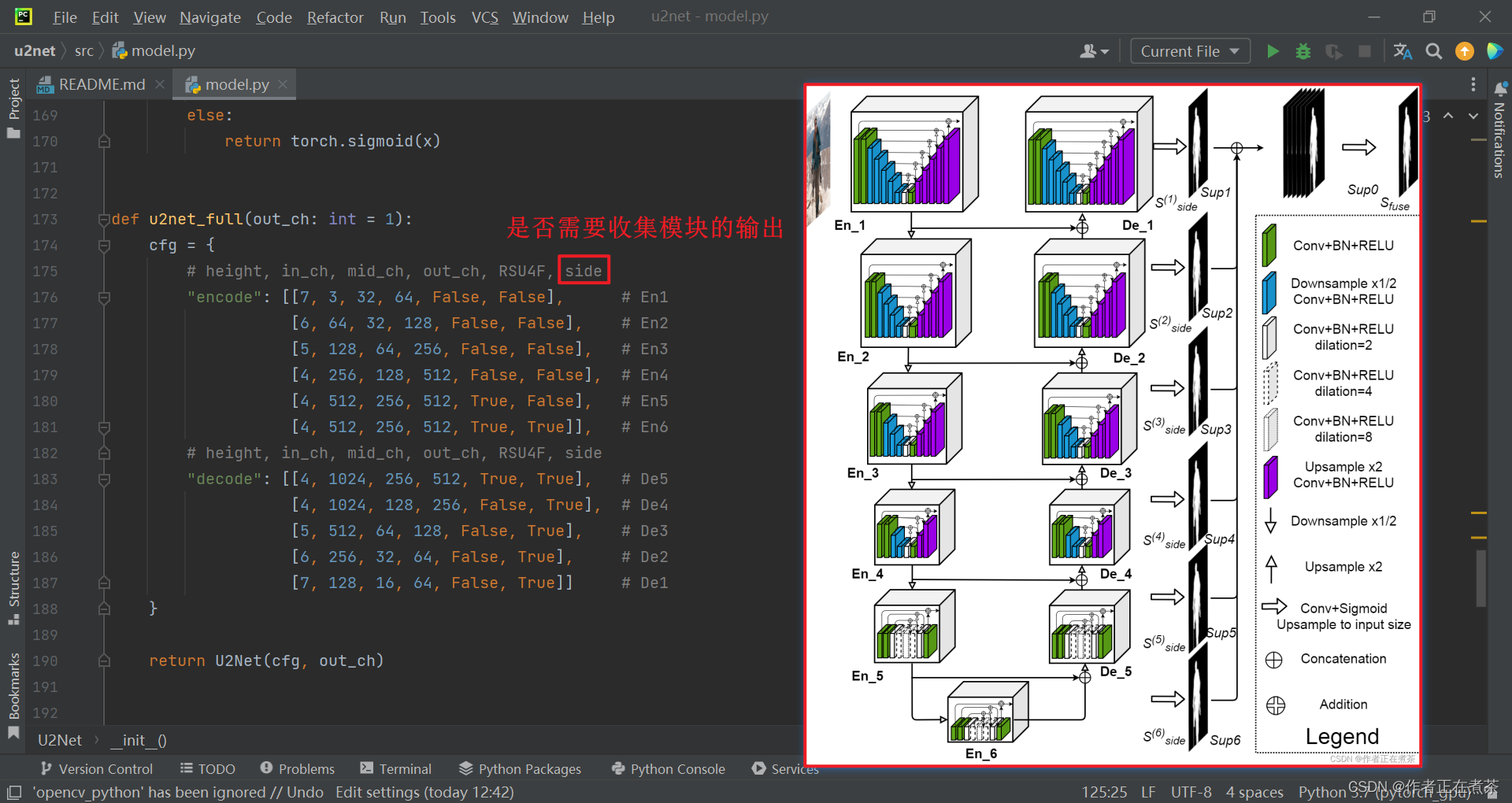
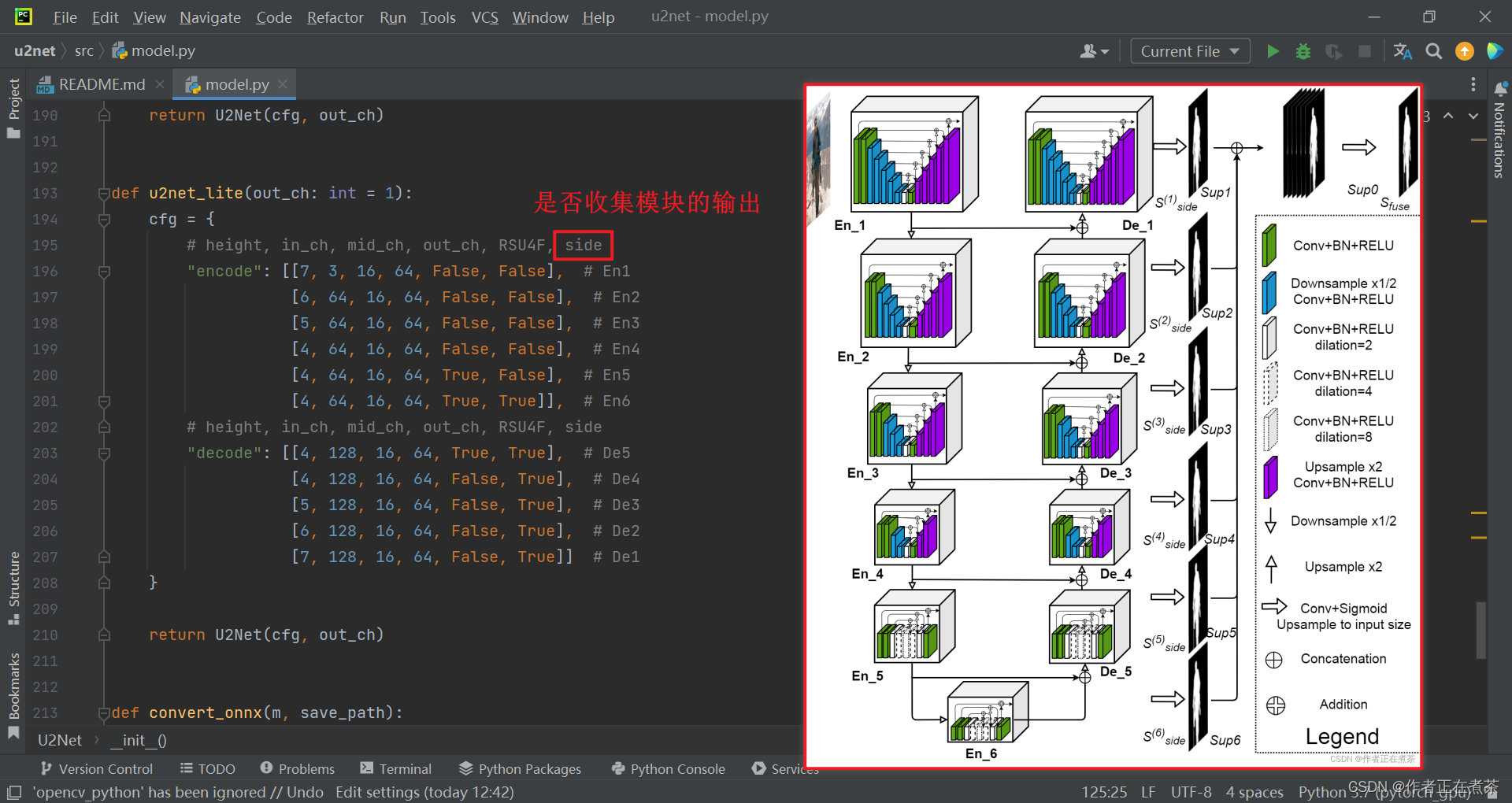
除此之外,在 U2-Net 中,默认是针对显著性目标检测任务去做的,只区分前景和背景,因此整个网络最终输出的预测概率图的通道数 out_ch 将设置为 1 ,也就是说预测的每一个像素的概率分数都是从 0 到 1 的,趋于 1 则说明代表二维前景的概率大,趋于 0 则说明代表背景的概率大。?
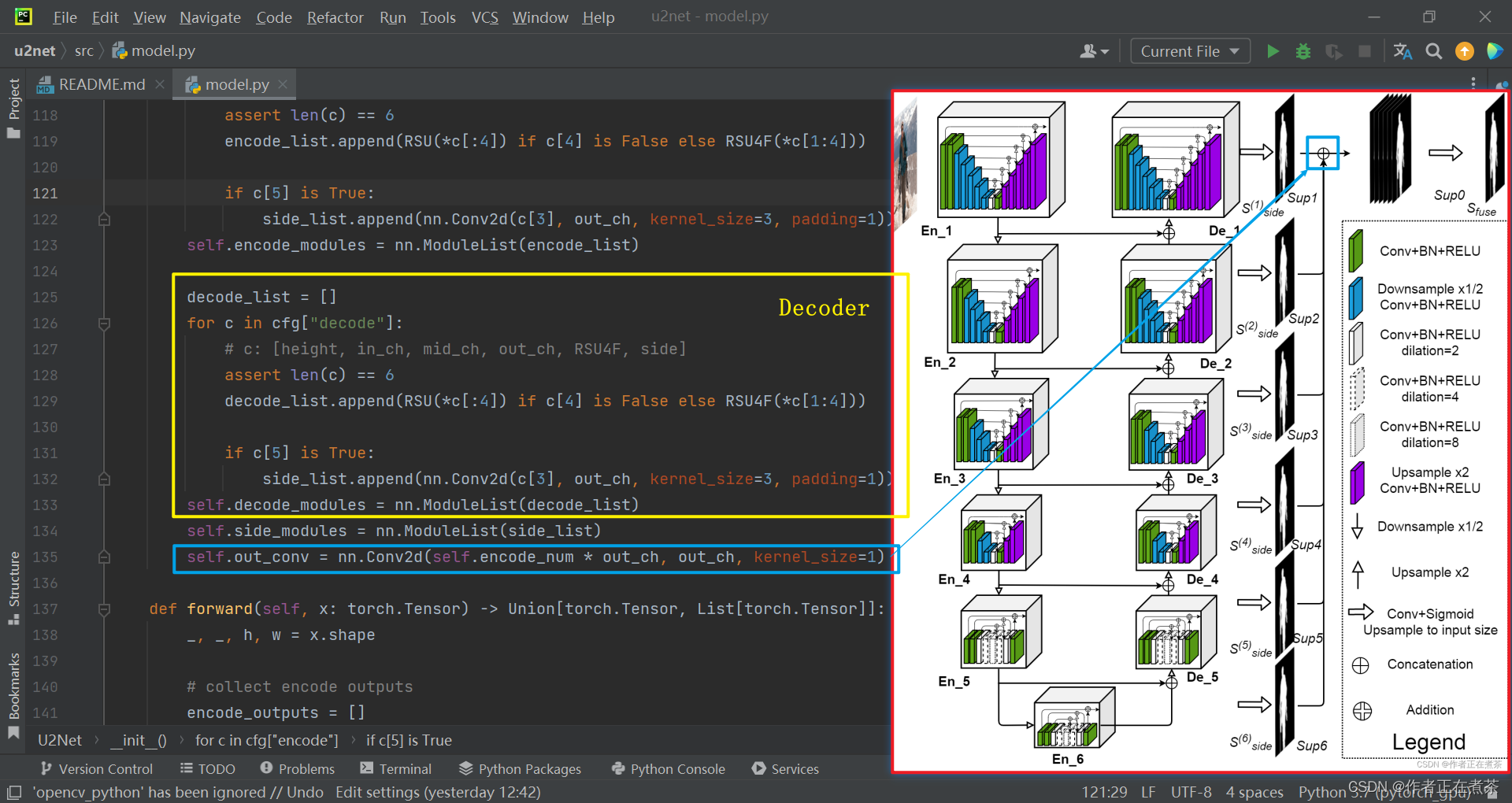
【说明】经过 concat 拼接后,将得到的特征图通过一个 1x1 的卷积层,融合来自不同尺度的信息,最终得到只有一个通道的特征图。

【说明】使用 decode_outputs.insert(0, x) 将处理后的结果 x 插入到 decode_outputs 列表的第一个位置,以 保持解码器输出的顺序 。
(6)model.py 源代码
from typing import Union, List
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class ConvBNReLU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_ch: int, out_ch: int, kernel_size: int = 3, dilation: int = 1):
super().__init__()
padding = kernel_size // 2 if dilation == 1 else dilation
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_ch, out_ch, kernel_size, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_ch)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
return self.relu(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
class DownConvBNReLU(ConvBNReLU):
def __init__(self, in_ch: int, out_ch: int, kernel_size: int = 3, dilation: int = 1, flag: bool = True):
super().__init__(in_ch, out_ch, kernel_size, dilation)
self.down_flag = flag
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
if self.down_flag:
x = F.max_pool2d(x, kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
return self.relu(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
class UpConvBNReLU(ConvBNReLU):
def __init__(self, in_ch: int, out_ch: int, kernel_size: int = 3, dilation: int = 1, flag: bool = True):
super().__init__(in_ch, out_ch, kernel_size, dilation)
self.up_flag = flag
def forward(self, x1: torch.Tensor, x2: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
if self.up_flag:
x1 = F.interpolate(x1, size=x2.shape[2:], mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
return self.relu(self.bn(self.conv(torch.cat([x1, x2], dim=1))))
class RSU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, height: int, in_ch: int, mid_ch: int, out_ch: int):
super().__init__()
assert height >= 2
self.conv_in = ConvBNReLU(in_ch, out_ch)
encode_list = [DownConvBNReLU(out_ch, mid_ch, flag=False)]
decode_list = [UpConvBNReLU(mid_ch * 2, mid_ch, flag=False)]
for i in range(height - 2):
encode_list.append(DownConvBNReLU(mid_ch, mid_ch))
decode_list.append(UpConvBNReLU(mid_ch * 2, mid_ch if i < height - 3 else out_ch))
encode_list.append(ConvBNReLU(mid_ch, mid_ch, dilation=2))
self.encode_modules = nn.ModuleList(encode_list)
self.decode_modules = nn.ModuleList(decode_list)
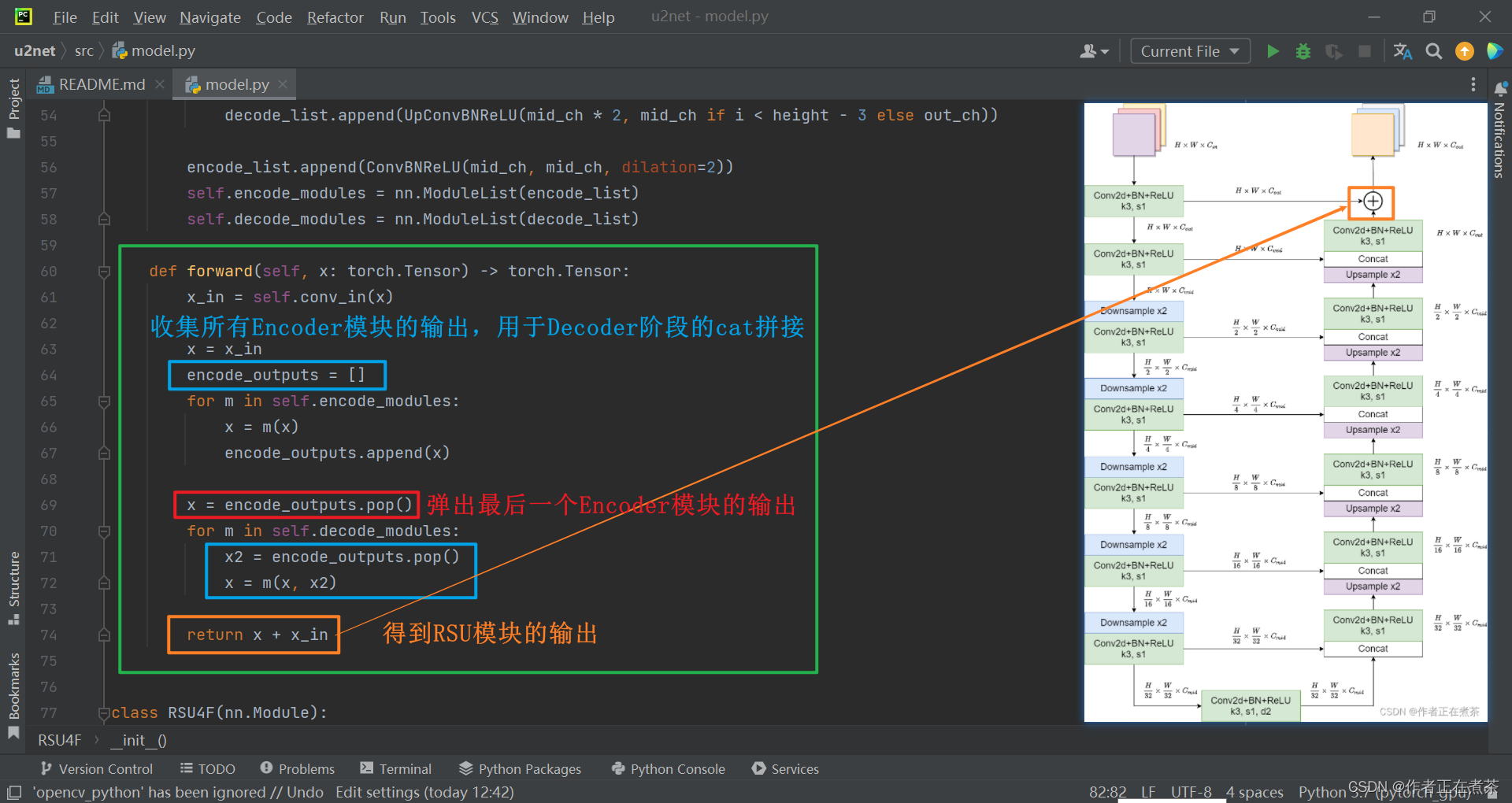
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x_in = self.conv_in(x)
x = x_in
encode_outputs = []
for m in self.encode_modules:
x = m(x)
encode_outputs.append(x)
x = encode_outputs.pop()
for m in self.decode_modules:
x2 = encode_outputs.pop()
x = m(x, x2)
return x + x_in
class RSU4F(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_ch: int, mid_ch: int, out_ch: int):
super().__init__()
self.conv_in = ConvBNReLU(in_ch, out_ch)
self.encode_modules = nn.ModuleList([ConvBNReLU(out_ch, mid_ch),
ConvBNReLU(mid_ch, mid_ch, dilation=2),
ConvBNReLU(mid_ch, mid_ch, dilation=4),
ConvBNReLU(mid_ch, mid_ch, dilation=8)])
self.decode_modules = nn.ModuleList([ConvBNReLU(mid_ch * 2, mid_ch, dilation=4),
ConvBNReLU(mid_ch * 2, mid_ch, dilation=2),
ConvBNReLU(mid_ch * 2, out_ch)])
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x_in = self.conv_in(x)
x = x_in
encode_outputs = []
for m in self.encode_modules:
x = m(x)
encode_outputs.append(x)
x = encode_outputs.pop()
for m in self.decode_modules:
x2 = encode_outputs.pop()
x = m(torch.cat([x, x2], dim=1))
return x + x_in
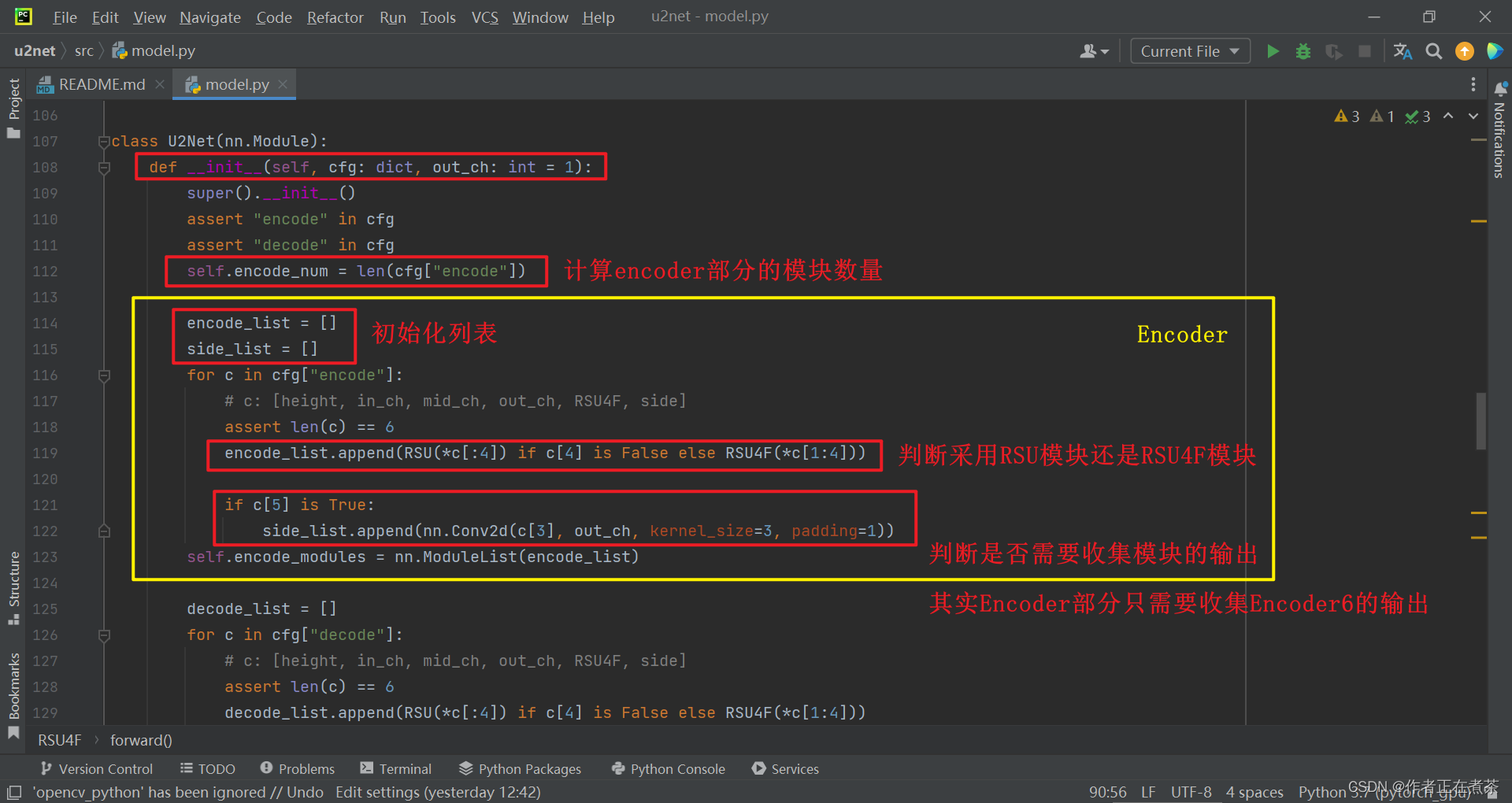
class U2Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfg: dict, out_ch: int = 1):
super().__init__()
assert "encode" in cfg
assert "decode" in cfg
self.encode_num = len(cfg["encode"])
encode_list = []
side_list = []
for c in cfg["encode"]:
# c: [height, in_ch, mid_ch, out_ch, RSU4F, side]
assert len(c) == 6
encode_list.append(RSU(*c[:4]) if c[4] is False else RSU4F(*c[1:4]))
if c[5] is True:
side_list.append(nn.Conv2d(c[3], out_ch, kernel_size=3, padding=1))
self.encode_modules = nn.ModuleList(encode_list)
decode_list = []
for c in cfg["decode"]:
# c: [height, in_ch, mid_ch, out_ch, RSU4F, side]
assert len(c) == 6
decode_list.append(RSU(*c[:4]) if c[4] is False else RSU4F(*c[1:4]))
if c[5] is True:
side_list.append(nn.Conv2d(c[3], out_ch, kernel_size=3, padding=1))
self.decode_modules = nn.ModuleList(decode_list)
self.side_modules = nn.ModuleList(side_list)
self.out_conv = nn.Conv2d(self.encode_num * out_ch, out_ch, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> Union[torch.Tensor, List[torch.Tensor]]:
_, _, h, w = x.shape
# collect encode outputs
encode_outputs = []
for i, m in enumerate(self.encode_modules):
x = m(x)
encode_outputs.append(x)
if i != self.encode_num - 1:
x = F.max_pool2d(x, kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
# collect decode outputs
x = encode_outputs.pop()
decode_outputs = [x]
for m in self.decode_modules:
x2 = encode_outputs.pop()
x = F.interpolate(x, size=x2.shape[2:], mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
x = m(torch.concat([x, x2], dim=1))
decode_outputs.insert(0, x)
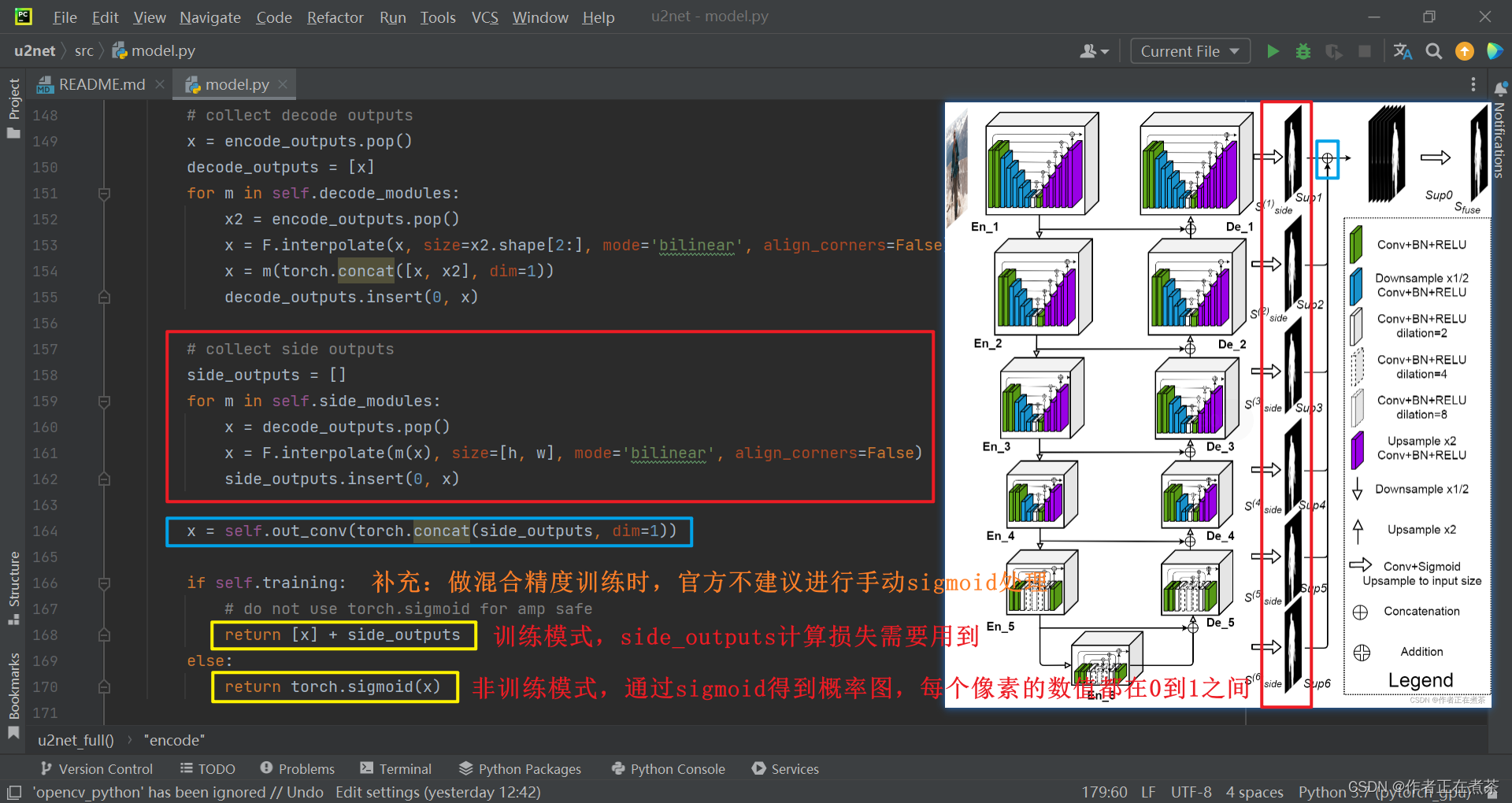
# collect side outputs
side_outputs = []
for m in self.side_modules:
x = decode_outputs.pop()
x = F.interpolate(m(x), size=[h, w], mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
side_outputs.insert(0, x)
x = self.out_conv(torch.concat(side_outputs, dim=1))
if self.training:
# do not use torch.sigmoid for amp safe
return [x] + side_outputs
else:
return torch.sigmoid(x)
def u2net_full(out_ch: int = 1):
cfg = {
# height, in_ch, mid_ch, out_ch, RSU4F, side
"encode": [[7, 3, 32, 64, False, False], # En1
[6, 64, 32, 128, False, False], # En2
[5, 128, 64, 256, False, False], # En3
[4, 256, 128, 512, False, False], # En4
[4, 512, 256, 512, True, False], # En5
[4, 512, 256, 512, True, True]], # En6
# height, in_ch, mid_ch, out_ch, RSU4F, side
"decode": [[4, 1024, 256, 512, True, True], # De5
[4, 1024, 128, 256, False, True], # De4
[5, 512, 64, 128, False, True], # De3
[6, 256, 32, 64, False, True], # De2
[7, 128, 16, 64, False, True]] # De1
}
return U2Net(cfg, out_ch)
def u2net_lite(out_ch: int = 1):
cfg = {
# height, in_ch, mid_ch, out_ch, RSU4F, side
"encode": [[7, 3, 16, 64, False, False], # En1
[6, 64, 16, 64, False, False], # En2
[5, 64, 16, 64, False, False], # En3
[4, 64, 16, 64, False, False], # En4
[4, 64, 16, 64, True, False], # En5
[4, 64, 16, 64, True, True]], # En6
# height, in_ch, mid_ch, out_ch, RSU4F, side
"decode": [[4, 128, 16, 64, True, True], # De5
[4, 128, 16, 64, False, True], # De4
[5, 128, 16, 64, False, True], # De3
[6, 128, 16, 64, False, True], # De2
[7, 128, 16, 64, False, True]] # De1
}
return U2Net(cfg, out_ch)
def convert_onnx(m, save_path):
m.eval()
x = torch.rand(1, 3, 288, 288, requires_grad=True)
# export the model
torch.onnx.export(m, # model being run
x, # model input (or a tuple for multiple inputs)
save_path, # where to save the model (can be a file or file-like object)
export_params=True,
opset_version=11)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# n_m = RSU(height=7, in_ch=3, mid_ch=12, out_ch=3)
# convert_onnx(n_m, "RSU7.onnx")
#
# n_m = RSU4F(in_ch=3, mid_ch=12, out_ch=3)
# convert_onnx(n_m, "RSU4F.onnx")
u2net = u2net_full()
convert_onnx(u2net, "u2net_full.onnx")
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:veading@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!